Please note, this page is a work in progress, viewing has been restricted to staff with editing privileges and should be removed when it is ready for public viewing.
Introduction
LCLS is providing a number of tools that allow users and staff to participate remotely in experiments while access to the site is restricted due to COVID-19 safety protocols. These were demonstrated in the LCLS User Town Hall held on July 23, 2020, and available at this link.
Teleconferencing software:
Description, Stanford site license, passwords, distribution (via eLog or email), live plots of AMI (camera images, histograms, etc.)
Link to download and install
Software Applications Provided by LCLS at https://pswww.slac.stanford.edu/index.html, including:
Other technologies:
Interactive chat software
Stanford University maintains an enterprise license to the slack chat application. Guests from other facilities can be added to specific channels.
Remote Access Software
To support remote operations a dedicated NoMachine Terminal Server has been deployed: psnxopr.slac.stanford.edu.
Then, NoMachine Enterprise Desktop will be installed on all DAQ workstations.
The following link provides guidelines to configure NoMachine Client: Remote Visualization.
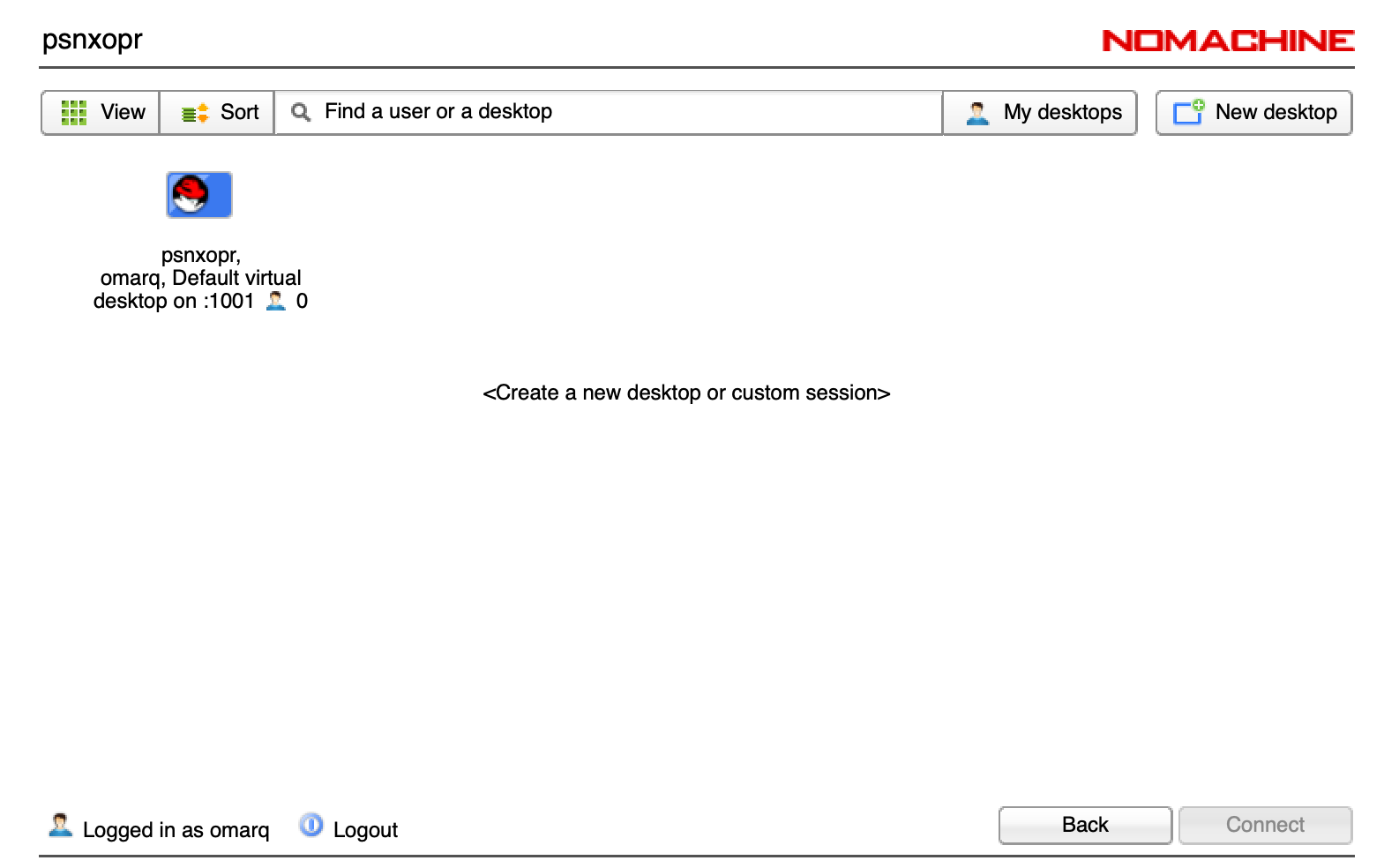
To access the DAQ workstation, use the following steps:
- Access or create a new desktop session.
- Select the NoMachine icon on the upper right to get a drop down menu, then select the control room workstation:
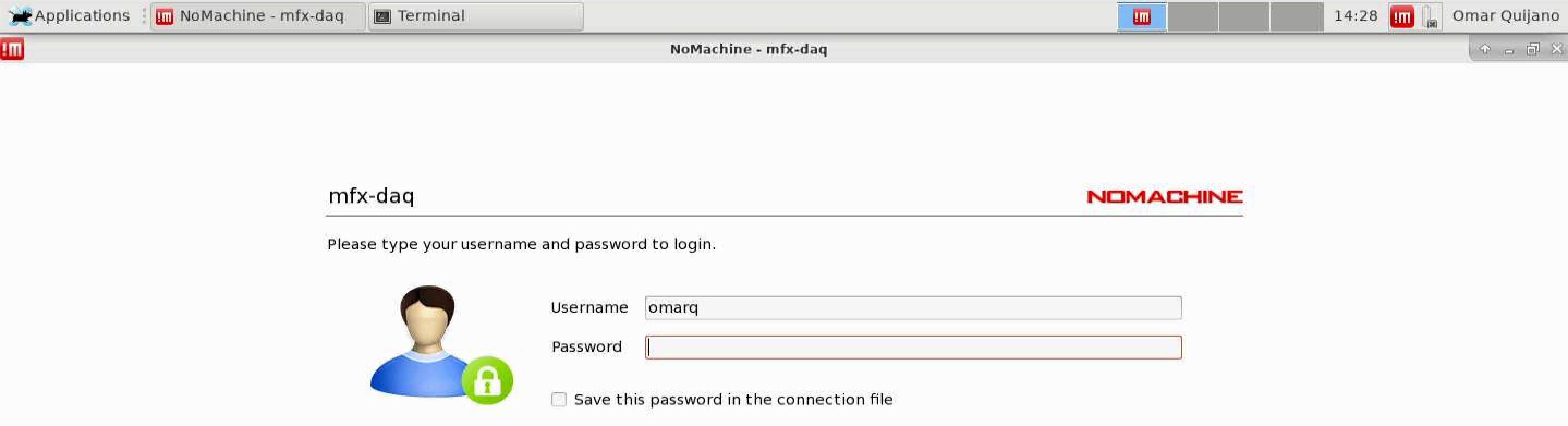
- A new window requesting login access will appear
- After login, the operator will have to grant authorization for view-only mode.
- As the remote user, any display can be accessed...
AR Headsets
LCLS has acquired a number of augmented reality headsets to allow staff technicians and engineers to co-view a workspace while respecting social-distancing protocols.
Hardware: https://www.realwear.com/products/hmt-1/
Software: https://www.amaxperteye.com/
We are using Space1 as the software platform for communicating with the AR headset.
Login here to call the headset and use the communication tools:
Login for operator:
Help1@slac.stanford.edu Help1!
Login for headset (Virtual collaboration – Space1)
User3@slac.stanford.edu User3!
Within the call you can,
- share screen with the headset
- control the headset (camera zoom, flashlight, volume, etc)
- send files, pictures, 3D models
- draw on their camera feed and draw on a whiteboard
- chat via text
We were able to establish calls from psconsole to the headset over EDUROAM wifi in the FEH.
Demo video recorded from psconsole screen (no sound):
Robotic assistants
We have purchased two remote presence robots to assist remote viewing and debugging of instrumentation at beam height where fixed overhead web cameras may have difficulty looking while an area is locked during beam delivery. https://www.doublerobotics.com/double3.html. At present these
Current features:
- Driving and viewing
- User joins call with a web browser on PC, Mac, Linux, iPhone, Android, or mobile app on iOS with their unique login credentials
- Authorize audio and video (required)
- Receive video and audio feed from the Double 3, the robot has pan, and zoom options
- Take photo of current view
- Drive with point-and-click on ground or by navigating with arrow keys
- Built in collision avoidance works very well
- Built in stabilization, does not knock over
- Able to go over cables on the ground
- Auto-docking
- Screen sharing
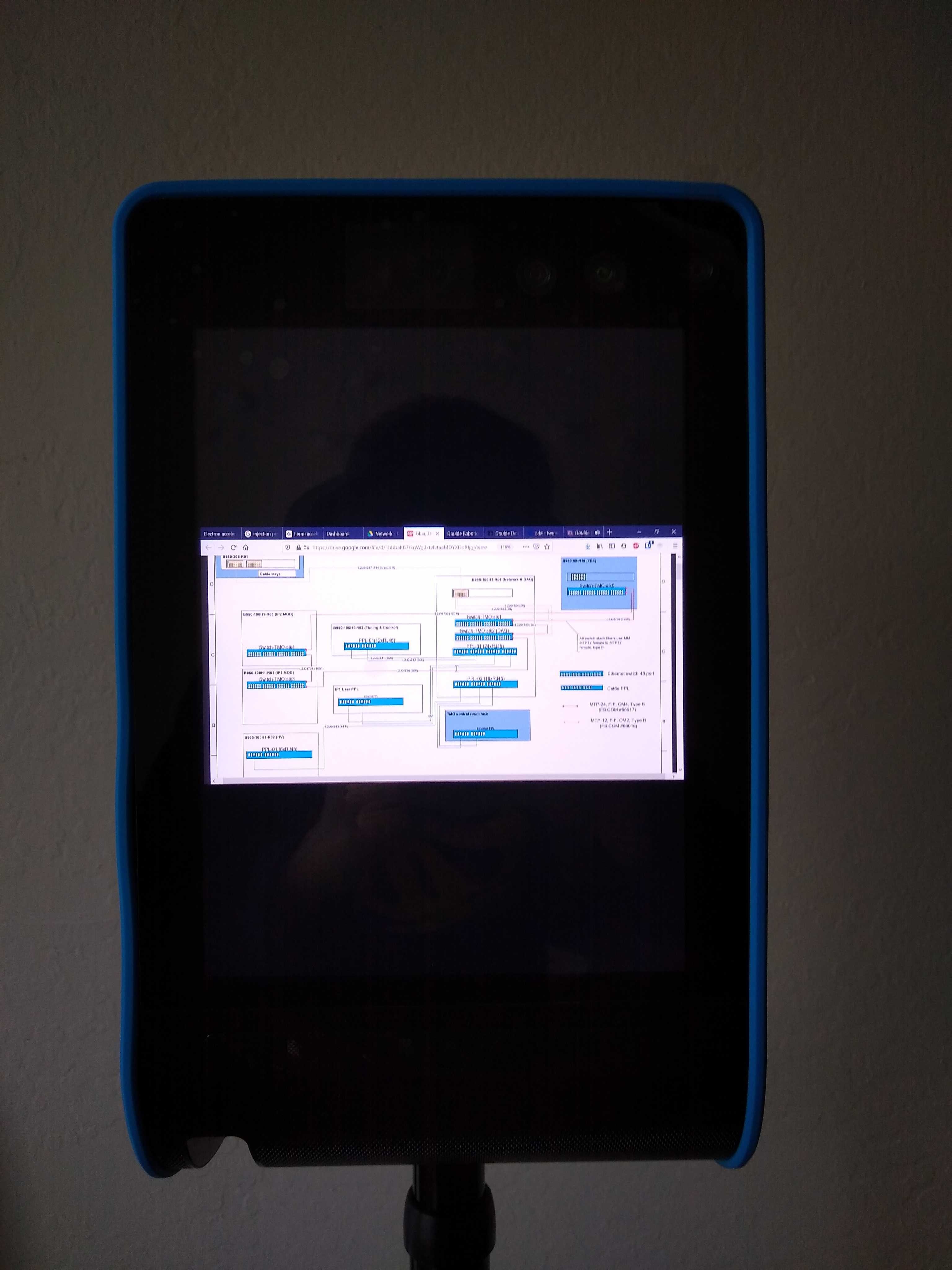
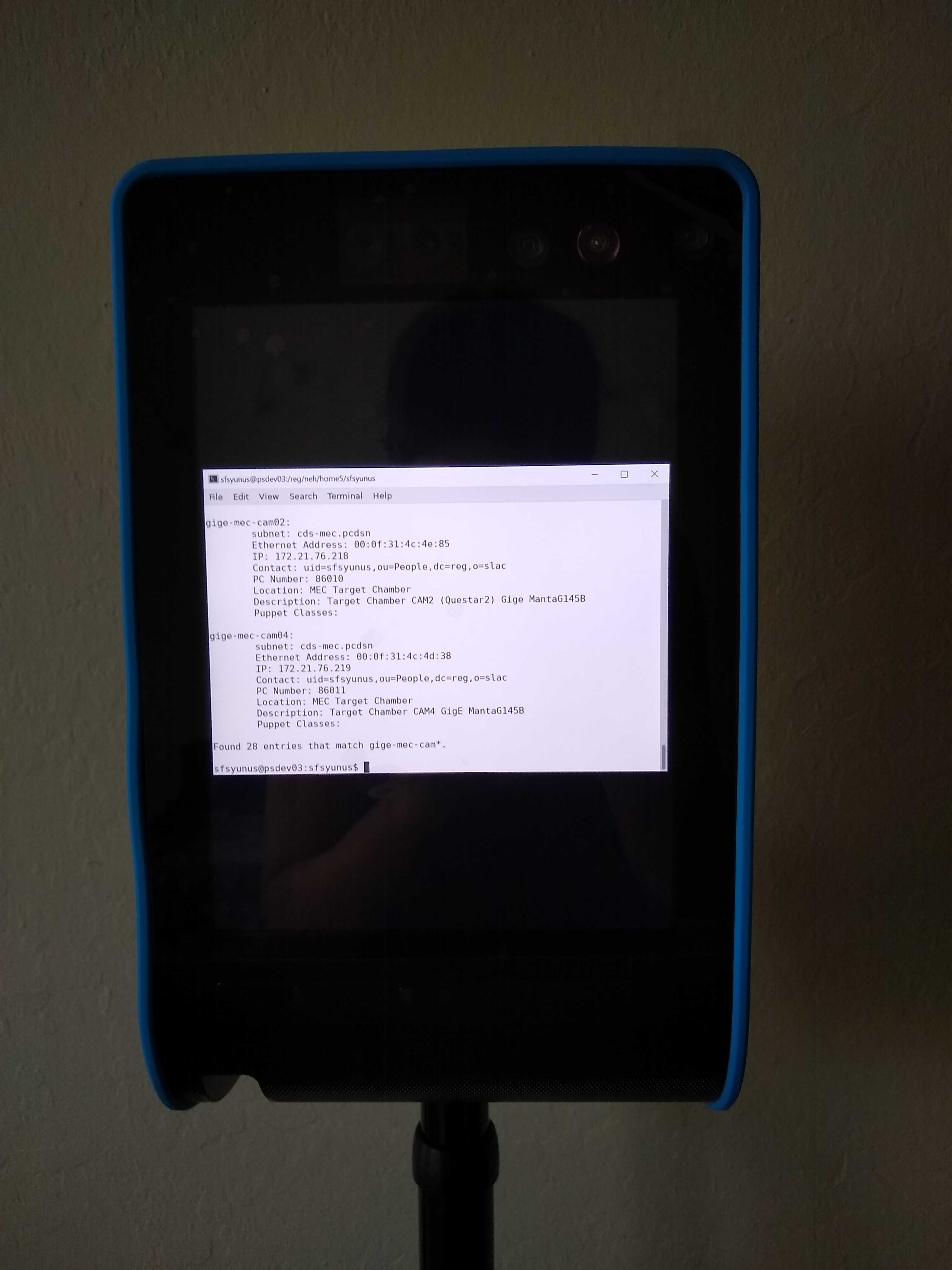
- Share specific windows, e.g. interconnect or cable drawings, grafana pages, terminal output
- Share web window interactively, allow user at robot to navigate the webpage you share
- Share specific windows, e.g. interconnect or cable drawings, grafana pages, terminal output
- Administrative controls: fleet usage
- Manage user access, allow multiple users with different usage privilege levels
- Schedule users to avoid access conflict
- Monitor calls, usage, drive time
- Manage user access, allow multiple users with different usage privilege levels
Developer features:
One of the units in enabled in developer mode, this allows development work with the base Unix environment that the robot is running on, as well as full access to the programming of the robot drive, and detectors.
Potential development features include:
- Enable Zoom conferencing
- Video recording
- Direct controls interface