G.Chiaro, D.Salvetti, G.La Mura, D.J. Thompson
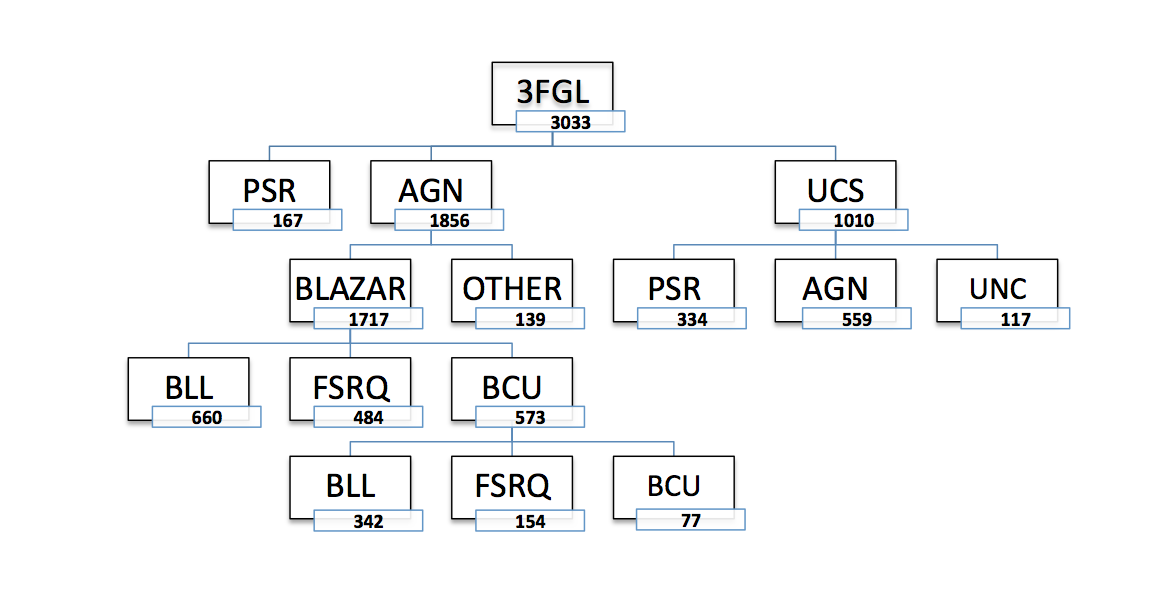
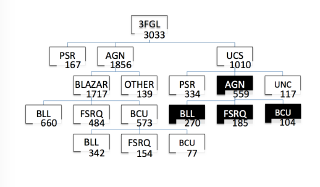
In 3FGL catalog more than 52 % of the FERMI the Fermi LAT 4-Year Point Source Catalog (3FGL) about 52% of the Fermi LAT sources are still unclassifiednot completely classified, including the unassociated sources and the blazars of uncertain type. Learning machine technique is one of the most techniques are an interesting approach for screening and ranking sources, according with their predicted source class. This study is a part of a wider analysis of unclassified sources listed the Fermi LAT 4-Year Point Source Catalog (3FGL) in the 3FGL catalog, as described in Saz Parkinson et al (2016), http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016ApJ...820....8S , ( Paper1 ) and Chiaro et al. (2016) http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016MNRAS.462.3180C (Paper2). The basic concept is to apply the Artificial Neural Network approach of Paper2 to the unassociated sources flagged as likely AGN by Paper1. The final result of this study suggests a new zoo for 3FGL sources where the percentage of uncertain sources drops from 52% to 10 % . 10% and opens new planning opportunities for mutiwavelenght mutiwavelength observational campaingscampaigns.
Fig. 1 3FGL including classification as in Paper1 and Paper2 before this study.
Fig.2 3FGLzoo where in black with the results of this study study in black.
We looked into the literature and BZCat in order to obtain a validation of our statistic by optical spectra.
We found very high consistency of our statistic prevision with the in optical spectra published in:
...