How to Find It
Use "(/reg/g/xpp/scripts/)iocmanager" from a terminal. It will guess the hutch you want the IocManager for by looking at the hostname of the machine. If you would like to see another hutches/areas IocManager, do e.g. "iocmanager XXX".
where XXX is a three-letter lowercase hutch name (ie: fee, las, amo, sxr, xpp, xrt, xcs, cxi, mec).
The IocManager GUI
Starting version R1-1-2 or later of the IocManager will open a window similar to the following:
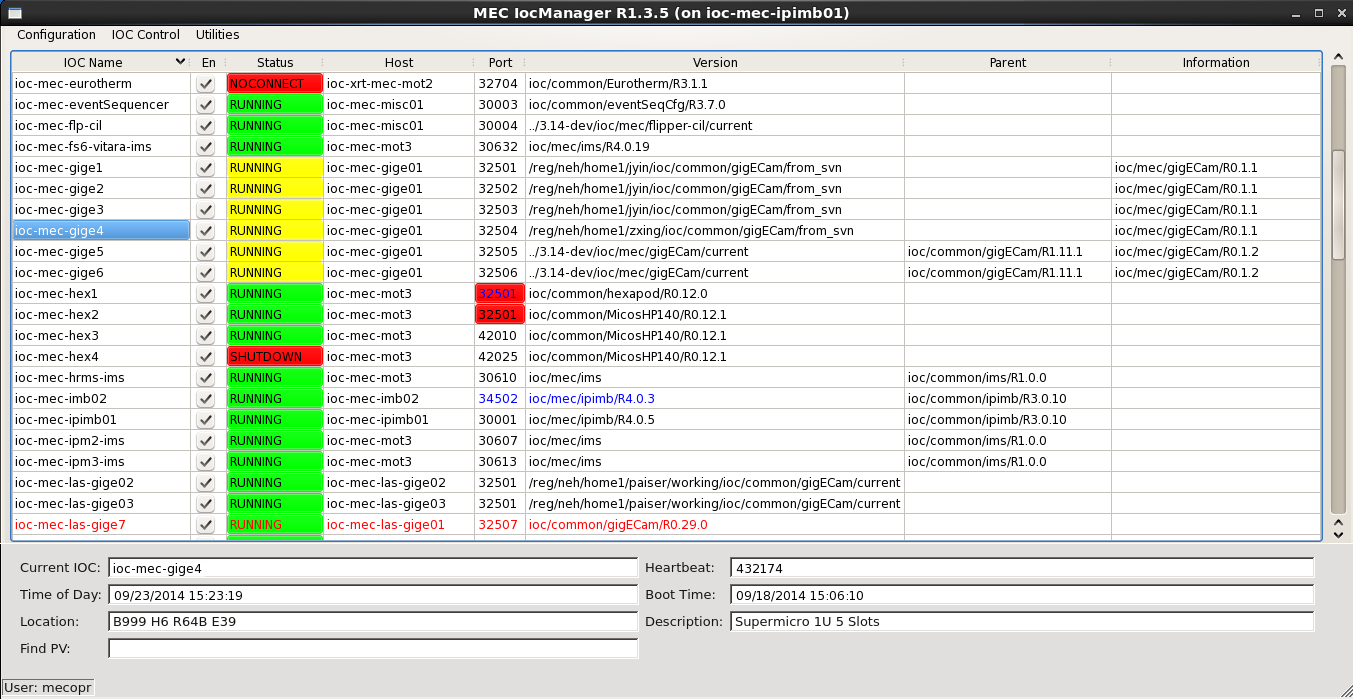
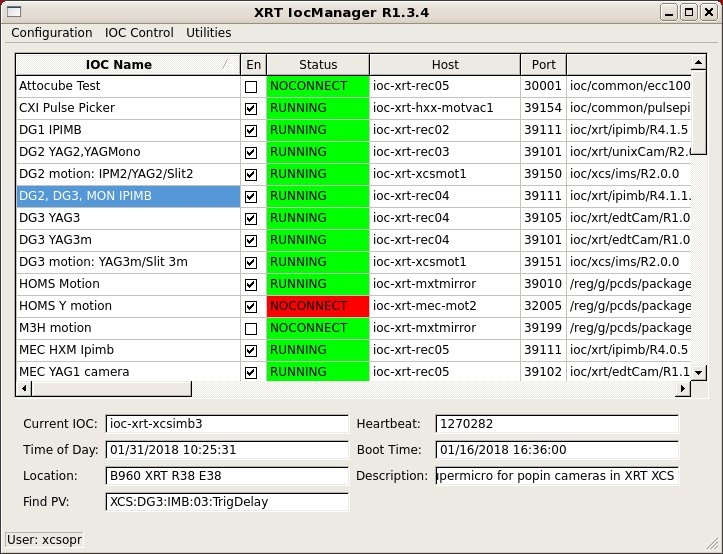
Each IOC in the configuration file is displayed along with its status:
- En is checked if the IOC is enabled and unchecked if disabled. Starting with R2-0-4, this is replaced by State, which can be either "Off" (disabled), "Prod" (enabled with a version in the release area), or "Dev" (enabled with a non-release version). Clicking on this, users can toggle between "Off" and "Dev/Prod".
- Status is either "RUNNING" (the IOC is up), "SHUTDOWN" (the procServ process is up, but the IOC is down), or "NOCONNECT" (the procServ process for the IOC is not reachable). Furthermore, the color indicates the correctness of the IOC state relative to the configuration: green is OK (the IOC is either running the correct version if enabled, or down if disabled), yellow indicates an incorrect version, and red indicates an actual problem (the IOC is up when disabled, or down when enabled).
- Host and Port are the host and telnet port for this IOC.
See Port Ranges, below for advice on selecting a port number.
- Version is the current directory setting for this IOC.
- Parent is the parent version, if this is a templated IOC.
- Information currently holds the running version if the IOC is running some other version than the one that is configured.
Unapplied changes to the host, port, or version fields are shown in blue. In this picture, for example, ioc-mec-imb02 is running version ioc/common/ipimb/R4.0.5, but the user has made an uncommitted change to version ioc/common/ipimb/R4.0.3. The port that this IOC should be run on has also been changed to 34502.
Port conflicts are shown highlighted in red. In the example, both ioc-mec-hex1 and ioc-mec-hex2 are configured to be on port 32501 on host ioc-mec-mot3, due to a recent uncommitted change to ioc-mec-hex1.
Deleted but still running IOCs are shown in red. In the example, ioc-mec-las-gige7 has been deleted.
Clicking on the header of any column will sort the display by that attribute, either up or down.
Clicking on a particular IOC Name selects that IOC and displays status information at the bottom of the screen, along with id of the currently authorized user.
Starting with R1-3-3, the IocManager has limited support for hard IOCs. If an IOC is created with port number -1, it will be considered a hard IOC, and the Port field will be greyed out and the Information field will show "HARD IOC". In general, hard IOCs cannot be reconfigured or disabled using the IocManager, but an alias may be set and changed.
The menu bar at the top of the screen contains commonly performed actions. Under "Configuration", the actions are:
- Apply will save the current configuration and make all requested changes.
- Save will save the current configuration without changing any IOCs.
- Revert will discard all user changes and re-read the saved configuration.
Under "IOC Control", the options are:
- Soft IOC Reboot will write the reset PV to restart the currently selected IOC, whether it is a soft IOC or a hard IOC. (It should be noted that the "soft" in the name refers to the reboot, not the type of IOC!)
- Hard IOC Reboot will send a ^X to the IOC console of a soft IOC, killing it and forcing a restart. For a hard IOC, the "exit" command will quit any iocsh, and "rtemsReboot()" will restart the server.
- Reboot Server will use IPMI to attempt to power cycle the server of a soft IOC. For a hard IOC, the "power" script is run to attempt to power cycle it.
- Show Log will open a window to display the last 1000 lines of the log for the currently selected IOC.
- Show Console will open a telnet connection to the console of the currently selected IOC, hard or soft.
"Utilities" contains a few miscellaneous functions:
- Help provides a link to this confluence page.
- Remember Versions will add each current version to the history list for that IOC, if not already there.
- Authenticate User will login an alternate user with privileges to modify the configuration, etc.
- Quit will exit the program and kill all log viewers an telnet sessions.
Right-clicking on an IOC name will bring up a context menu that will have some or all of the following options:
- Delete IOC will delete the current IOC from the configuration.
- Add New IOC will bring up a window to prompt for parameters for a new IOC to be managed.
Add Running to Config will add an IOC that was found to be running but not in the configuration file to the configuration. (This could also be considered an "undelete" function.)
Set from Running will change the configured parameters to agree with what is currently running.
Revert IOC will discard all unapplied user changes to this IOC and restore the values saved in the configuration file.
Remember Version will add the current version to the history list for this IOC.
Edit Details will allow the changing of the rarely changed fields cmd, flags, and delay.
FindPV
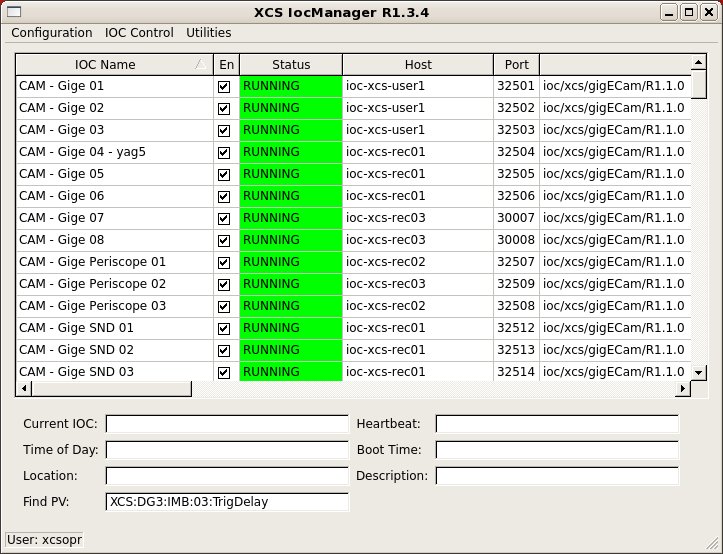
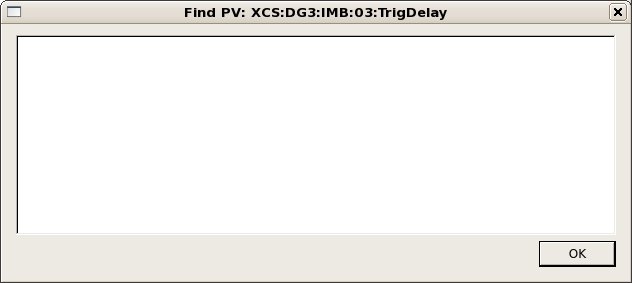
In version R1-3-4, a tool was added to assist finding IOCs by PV name. Enter a regular expression contained in the PV into the "Find PV" field and hit enter. A popup window will show which IOCs have a matching PV. If only one IOC has a match, it will be selected as well.
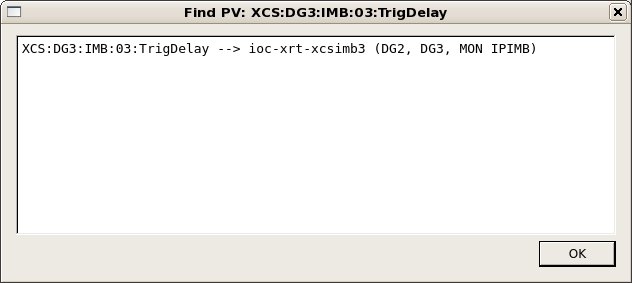
Should this window remain empty, then this PV is not served from any IOC controlled by this IOC manager. Try another area (e.g. the XRT for some of the IOCs serving hutches in the FEH). In case of success, you should see something like:
In the IocManager, this IOC is now also selected (if there is only a single IOC found as findPV allows for regular expressions).
More details
More information about the IocManager (mostly aimed at PCDS personnel) can be found here: IOC Manager Staff Guide
Procserv
The 'console' option will drop you into the procServ session running the IOC. How to use procServ to reboot the underlying process/IOC (and how to connect to a session if you have issues with the console option) is described here.
So you do:
telnet <hostname> <port>
Among the printout you will see:
@@@ Use ^X to kill the child, auto restart mode is ON, use ^T to toggle auto restart
So you type ctrl-t until you have auto restart in ON or OFF, depending on what you want. With ON, ctrl-x will restart. With autorestart OFF, ctrl-x will stop the process and you will see:
@@@ ^R or ^X restarts the child, ^Q quits the server
So with ctrl-q, the session will be closed.