There are some extra steps we need to make in Week 2 to prepare for running analysis tutorials and projects. Please follow the instructions below and reach out for help if needed.
Download data and configuration files
To run the example you will need a few additional files.
- 3C 279 photon and spacecraft files, PH00.fits PH01.fits and SC00.fits.
- Configuration file for fermipy, config.yaml
- Jupyter notebook, LikelihoodWithFermipy2021.ipynb
- Precomputed data files (so you can go through the example quickly the first time without waiting for calculations).
Prepare FermiBottle for analysis
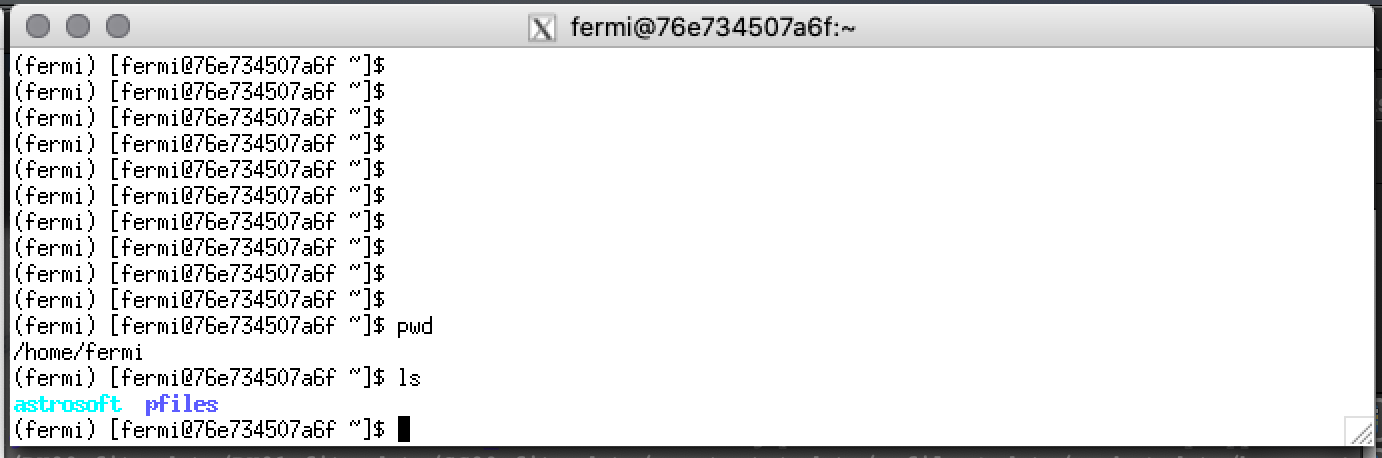
Is FermiBottle running? You should have a window with a fermi prompt similar to this.
If you don't have a window open to FermiBottle, follow the instructions to start docker on your host system and attach to the FermiBottle container. Remember to activate the Fermi analysis using "conda activate fermi" when you restart the FermiBottle container. You'll know this has been done when you see the fermi prompt. The steps to start docker and set up the Fermi environment are described in Using FermiBottle instructions.
Update fermipy
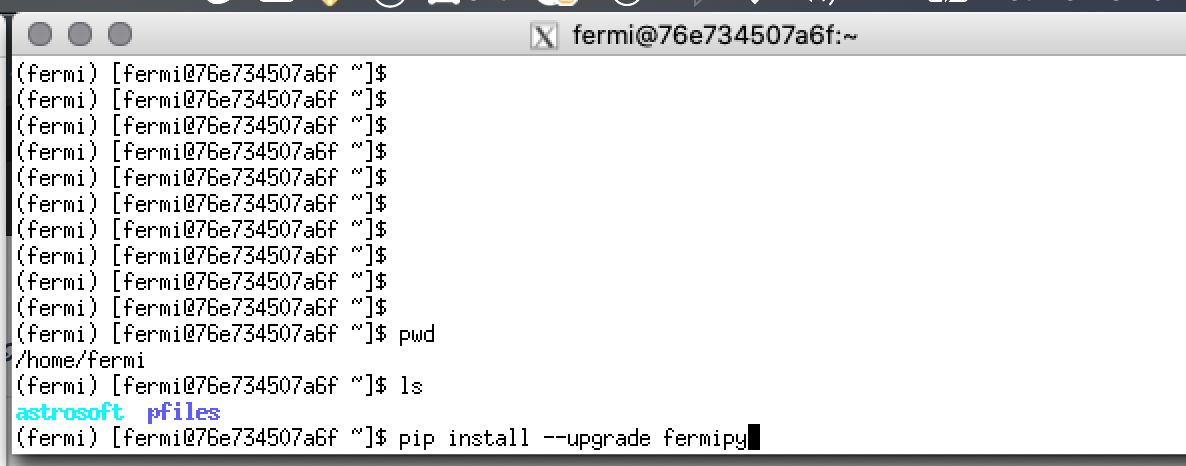
To run the example, you will need to update to the latest version of fermipy, 1.0.1.
In your FermiBottle window run the command
pip install --upgrade fermipy
This will take a little time to download and install the packages.
Make a new directory for the fermipy tutorial in FermiBottle
Follow these steps to prepare to run the Likelihood With Fermipy notebook
In the FermiBottle window
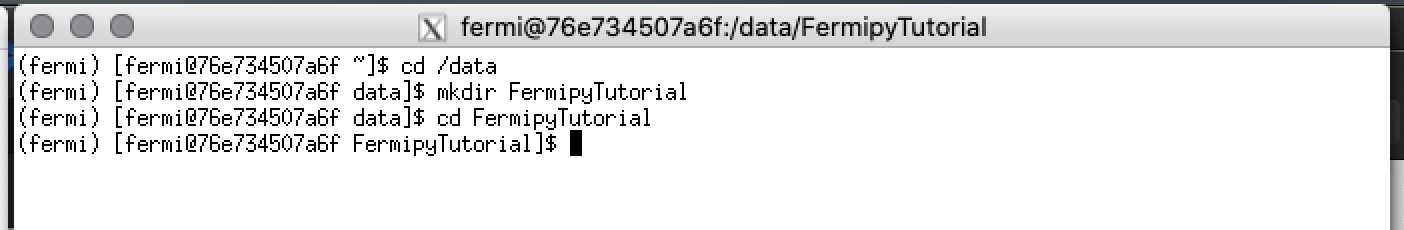
- Change directory to make /data your working directory
- Create a directory for this tutorial in /data. Let's call it FermipyTutorial.
- Change directory to make /data/FermipyTutorial your working directory
Download and unzip the tutorial file in FermiBottle
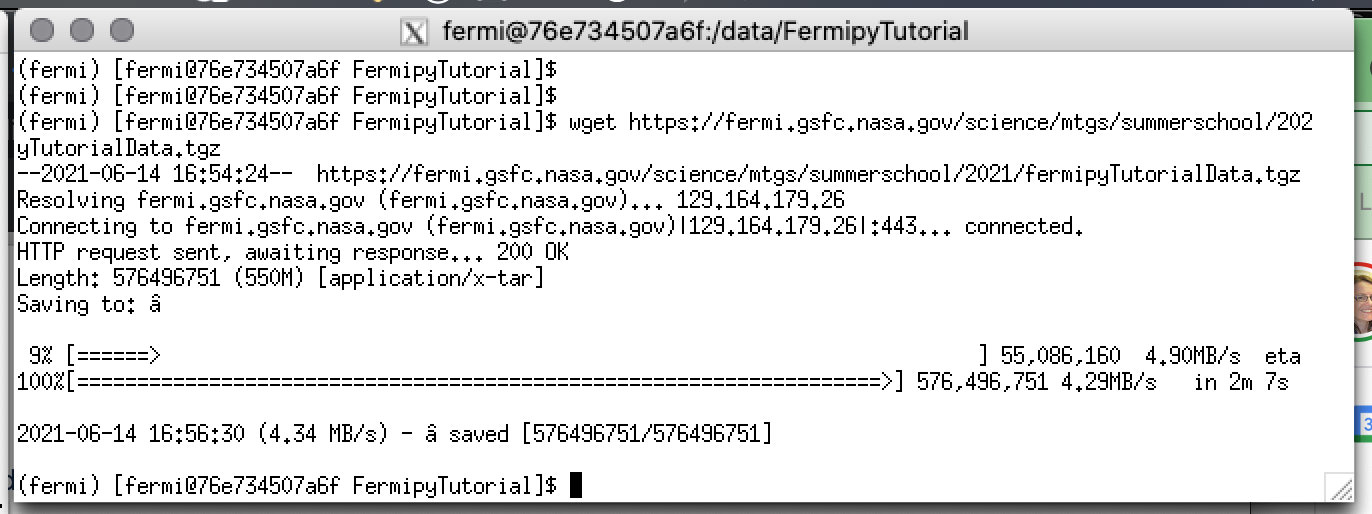
Next, in the FermiBottle window, use wget to download the data file into the tutorial directory using the command shown below.
wget https://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/science/mtgs/summerschool/2021/fermipyTutorialData.tgz
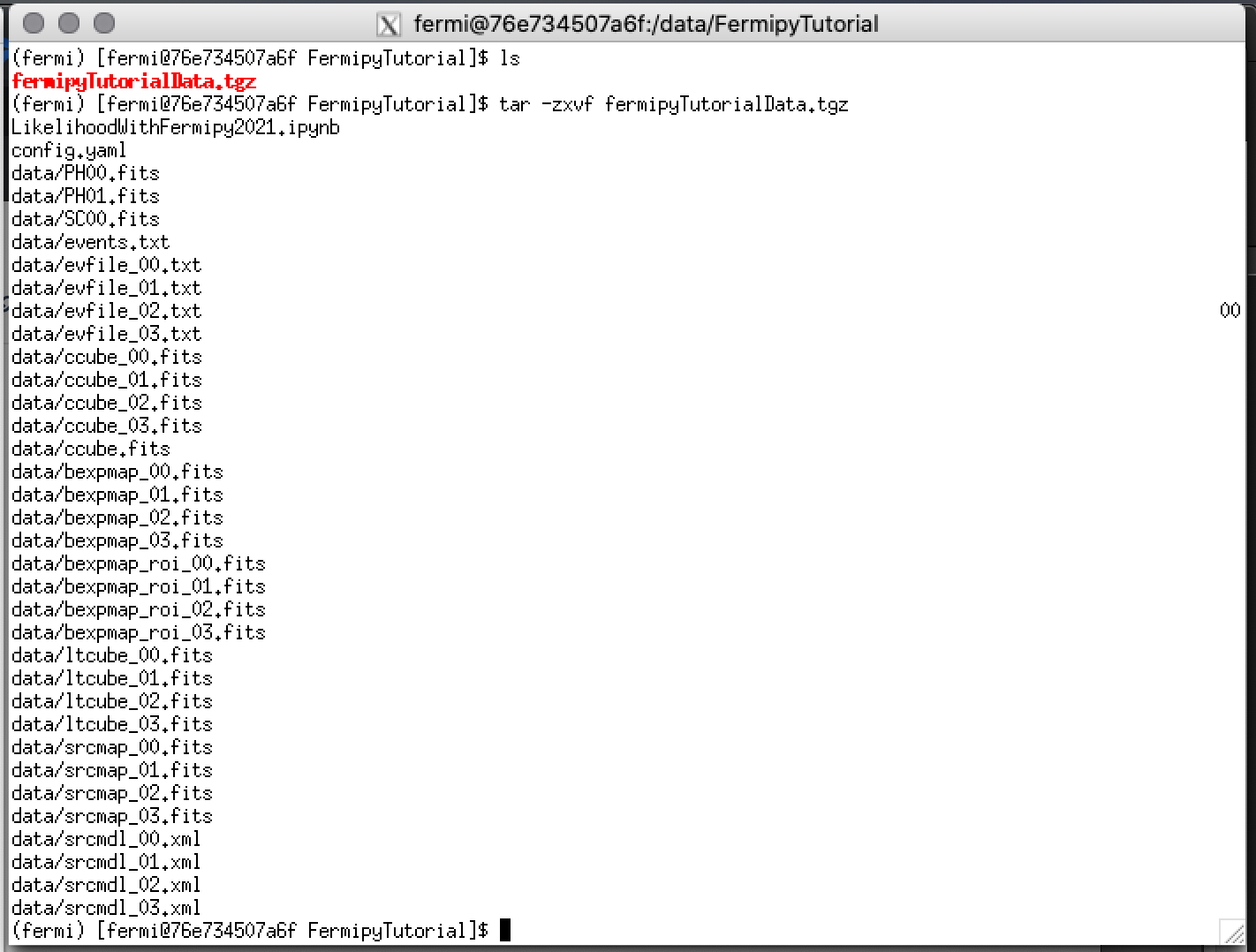
Then unzip and extract the archived files.
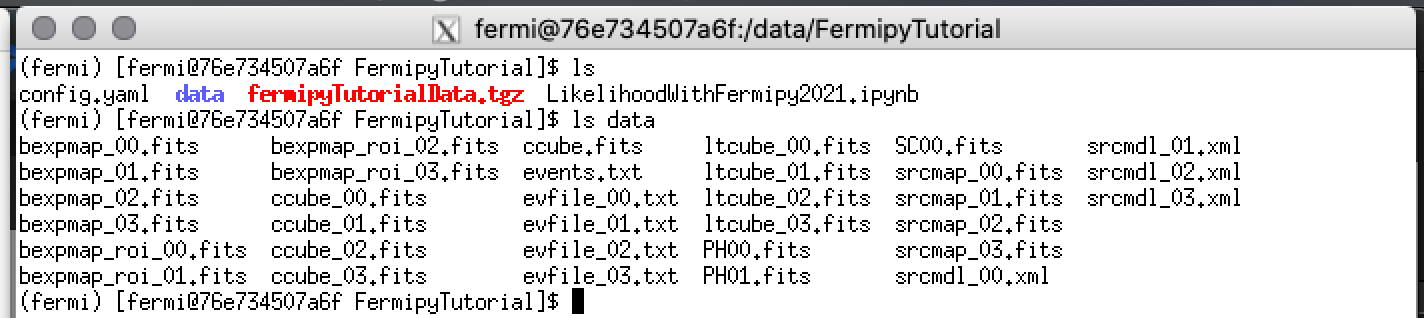
You should see something like this when you list the directory contents.
Start the Jupyter notebook
In that same directory, you can now run the notebook command to start the tutorial.