When users are off-site or have slow internet connections, displaying graphics can be cumbersome. PCDS has explored two solutions for this problem:
- The first ("NX technology") gives the user a special remote desktop that is specifically designed to improve the performance of X11 graphics with slow connection speeds.
- The second ("Virtual Box") allows the user to directly install the psana analysis environment on their Windows, Linux or MAC machine, so that LCLS data analysis (including graphics) can be done with no network connection (click here for information on the virtual box approach).
This page is about the usage of NoMachine for providing NX technology to users involved in LCLS experiments or operations.
NX Technology
NoMachine NX is supported on Windows, MAC and Linux computers. You can download the latest version of the client from www.NoMachine.com. Ubuntu/Mint users should download the Debian version of the NoMachine client.
LCLS is currently making three different servers available for remote connections:
- psnxopr.slac.sstanford.edu (aka psnxserv01): for machine and beamline operators
- psnxana.slac.stanford.edu (aka psnxserv02): for interactive data analysis
- psnxserv.slac.stanford.edu (aka psnxserv03): for general purpose connections
The allocation of theses servers to the various activities is just to provide a low-tech load balancing and is not enforced.
After opening a connection to one of these servers using your SLAC UNIX account, make sure to run in console mode: from the 'Custom session' dialog window, accept the default options (Application - Run the console, Options - Run the command in a floating window) by clicking Continue.
For performance and reliability reasons we have disabled the ability to open a remote desktop (GNOME) on the NX servers. We plan to keep allowing only the console mode for the foreseeable future since the multiple GNOME sessions were taking too many resources on the NX servers. Let us know if you see any fundamental reason why the ability to open a remote desktop is required to do your job.
This will open a remote terminal on your local desktop from which you can type the name of the application you want to launch. For example, you can type "xterm&" to open additional terminals or "emacs&" to open the emacs editor. Type "ssh psana" to connect to the interactive pool to do data analysis. When you disconnect and reconnect to NoMachine, these terminals and applications will remain in the state you left them in.
Please contact pcds-help@slac.stanford.edu if you need more information or additional assistance with NoMachine.
Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
If you are not able to connect to NoMachine, check the followings:
- The server is setup to limit to 4 connection attempts per minute, this is to discourage brute force attempts for security purpose. If it seems to take a long time to connect after you made multiple connection attempts quickly, you can just cancel out and try to log back in after a couple of minutes.
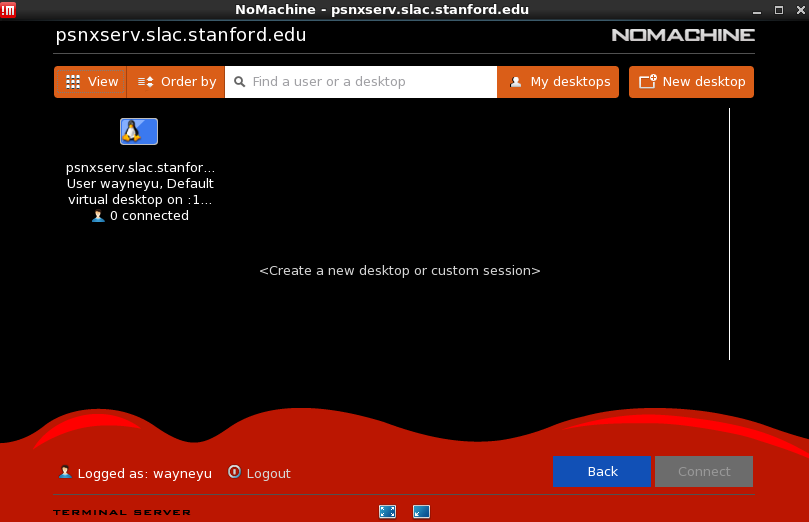
- If you have disconnected your session without logging out and try to reconnect, once you hit the connect button, you will see the following dialog box. You can create a new session by selecting 'Create a new desktop or custom session' or you can reconnect to your existing session. If the existing session failed to reconnect, you can right-lick on the icon representing your previous session and select Terminate session. And then click on 'Create a new desktop or custom session' and select 'Create a new virtual desktop' to click on continue.
Reconnect "Black Screen" Issues
Sometimes users will find that they are unable to reconnect to an existing session, and are shown only a blank screen. We do not yet understand this issue, so our solution is to terminate the user's existing sessions, and kill all the user's running processes on the NoMachine server. The easiest way for the users to deal with this is to send a note to pcds-it-l@slac.stanford.edu and we will remove all old sessions and process.
It's also possible for users to fix with this themselves by ssh'ing to psnxserv.slac.stanford.edu and killing their own process. Potentially useful commands follow:
Show all running user processes:
ps -f -u $USERNAME
Kill a specific process using its process ID (found in the PID column of the "ps" command output):
kill <PID>
Kill a specific process that doesn't want to die (i.e. was not killed by "kill <PID>"):
kill -9 <PID>
Kill all user owned processes running on the server, including current ssh session, shell and the pkill command itself. This is a quick way to remove the majority of user owned processes:
pkill -u $USERNAME
Note that the user will have to reconnect after running pkill and may have to try a number of times (possibly using the -9 option, as shown with the kill command).
Resuming a NoMachine Connection
If you are not able to resume a NX Connection and you typically connect from multiple computers, be sure to use similar version of NoMachine client where you initiate the connection from. To check for NoMachine version, after you have launch NoMachine client, go to Preferences on top, then click on Updates, it will show you the version that you are running NoMachine on.
Other issues
If Ctrl-C (Ctrl-break) does not work on the Linux client, hit the Alt-Ctrl-C (Use it in proper sequence so hold down the key one at a time). WindowsKey-Ctrl-C, or turn on Caps Lock and hit Ctrl-C will also work.