Introduction
PingER (Ping End-to-End Reporting) is a project that monitors network performance of Internet links world wide. It has almost 1000 nodes that spread through out the world and covers 99% of internet population of world. Every day monitoring nodes collect data available by pinging remote nodes and provides this data to archive node that is responsible for analysis of this data. PingER has a decade old data of network performance of different internet links which is very useful in many internet applications related fields.
Motivation and Purpose
PingER archive site(or node) architecture is based on flat-files i.e it collects ping data, processes this data, stores the results, and display results to end user using flat-files. As the internet usage increases in world, number of PingER nodes for network monitoring also increases due to which a huge amount of data is to be processed and store by archive site daily using flat-files. Now this flat-files approach is no longer scaleable and manageable with current amount of data so the PingER archive site architecture should be changed from flat-files to relational database for achieving performance, speed, manageability and scaleability in PingER archive sit operations.
Methodology and Mechanism
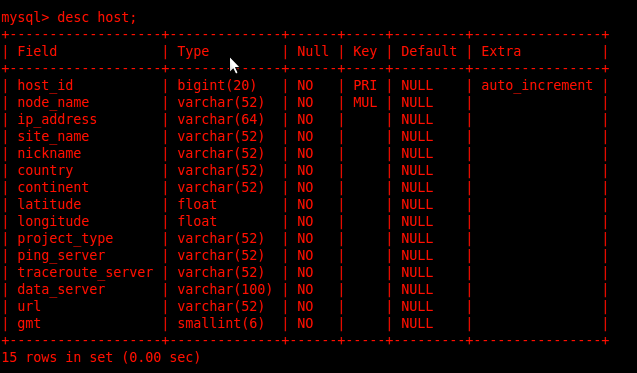
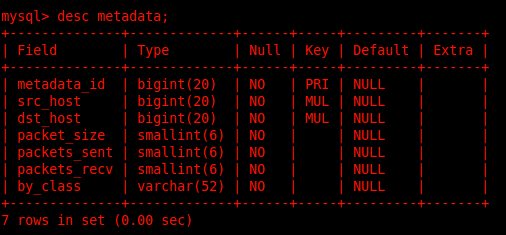
For change archive site architecture from flat-files to relational databases we first make a database schema which is suitable for archive site data requirements i.e tables instead of flat-files are used for collection,processing and storage of data. Our final purposed has three tables one has nodes information, one has metadata and last table is data which contains results. Schema is shown below:
Host table containing all PingER nodes information:-
Metadata table contains all metadata of results:-
Data table contains final results of different network metrics:-