Content
Problem
In Run 18 planned on Aug 2019 the new single-piece 4M Jungfrau detector is going to be used with a couple of controllers. In daq and psana it will be seen as two independent detectors, i.e. MfxEndstation.0:Jungfrau.0 and 1. It seems natural to process data of these two detectors as a single piece. To make it feasible class AreaDetectorCompound was developed with functionality as explained in this note.
Details of implementation
Class AreaDetectorCompound constructor receives as input parameter a list of detector names which need to be processed together. From this list it generates a list of AreaDetector objects, which is used to wrap most of AreaDetector interface methods. Wrapping methods concatenates numpy arrays for the 3-rd to last index, assuming that two last index describes 2-d AreaDetector. This type of concatenation can be done for identical two last indexes, e.g. for Jungfrau
raw or calib arrays: (2, 512, 1024) (+) (1, 512, 1024) (=) (3, 512, 1024) pedestals, gain and offset: (3, 2, 512, 1024) (+) (3, 1, 512, 1024) (=) (3, 3, 512, 1024)
Generalized methods from Detector interface
methods returning concatenated arrays
raw, calib, pedestals, rms, gain, offset, bkgd, status, mask, photons,
coords_x, coords_y, coords_z,
indexes_x, indexes_y, indexes_z,
common_mode_correction, common_mode_apply,
mask_geo, mask_comb, mask_edges, mask_neighbors, mask_calib,
datast, status_as_mask, gain_mask, gain_mask_non_zero, areas
methods returning a couple of concatenated arrays
coords_xy, indexes_xy, indexes_xy_at_z
methods returning a list of per detector values
list_raw, list_calib, list_shape, list_size, list_ndim, list_common_mode, list_geometry
re-implemented methods
common_mode - returns array of the common mode parameters
Difference between compound and regular detector
Detector interface provides for user uniform access to any detector data and hides specific detector complexity. The same is valid for compound detector. There is a couple of differences too keep in mind.
- the 1-st parameter of Detector class object should be
- detector name in regular case
- string or list of detector names in case of compound detector
- calibration constants for compound detector components needs to be calibrated and provided separately. All data access and processing methods work for separate detectors and their output arrays are concatenated at return.
Code example
Compound Detector object creation
There are a few options of the detector object initialization usyng class AreaDetectorCompound directly or through the standard Detector factory.
Detector is a standard wrapper for all LCLS detectors including AreaDetectorCompound. Compound detector object can be created usind generic Detector, e.g.
import psana # DataSource object MUST be defined before Detector. ds = psana.DataSource(dsname) # i.e. dsname='exp=xpptut15:run=460' det = psana.Detector(<str-or-list-of-derector-names>)
Example of direct AreaDetectorCompound object initialization:
from Detector.AreaDetectorCompound import AreaDetectorCompound det = AreaDetectorCompound(<str-or-list-of-derector-names>, env)
Input parameters
Parammeter <str-or-list-of-derector-names> can be the space separated string of detector names prepended by keyword 'compound', e.g.
'compound MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.1 MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.2 MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.3'
or just a list of detector names, e.g.
['MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.1', 'MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.2', 'MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.3']
Second parameter, env = ds.env(), is mandatory for AreaDetectorCompound and is optional for Detector (passed from DataSource initialization).
Complete example
### Direct usage:
# from Detector.AreaDetectorCompound import AreaDetectorCompound
# det = AreaDetectorCompound(..., env)
import psana
from Detector.GlobalUtils import print_ndarr
ds = psana.DataSource('exp=xpptut15:run=460')
# Make Detector object using:
# space separated string of detector names prepended by 'compound':
det = psana.Detector('compound MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.1'\
' MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.2'\
' MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.3')
# or list of string detector names:
det = psana.Detector(['MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.1',\
'MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.2',\
'MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.3'])
env = ds.env()
evt = ds.events().next()
rnum = evt.run()
if True :
print 'rnum :', rnum
print 'calibdir :', str(env.calibDir())
print 'size :', str(det.list_size(evt))
print 'shapes :', str(det.list_shape(evt))
print 'ndims :', str(det.list_ndim(evt))
raws = det.list_raw(evt)
for nda in raws : print_ndarr(nda, name='-- per det list_raw', first=0, last=5)
raw = det.raw(evt)
print_ndarr(raw, name='raw as nda', first=0, last=5)
calib = det.calib(evt)
print_ndarr(calib, name='calib', first=0, last=5)
xy0_offset = (550,550)
img_raw = det.image(evt, nda_in=raw, xy0_off_pix=xy0_offset)
#img_calib = det.image(evt, nda_in=calib, xy0_off_pix=xy0_offset)
#img_at_z = det.image_at_z(evt, zplane=500000, nda_in=raw, xy0_off_pix=xy0_offset)
if True : # True or False for to plot image or not
from pyimgalgos.GlobalGraphics import plotImageLarge, show
img = img_raw
plotImageLarge(img, title='img as %s' % str(img.shape), amp_range=(0,5000))
show()
Methods for imaging
img = det.image(evt, nda_in=raw, xy0_off_pix=xy0_offset) img = det.image_at_z(evt, zplane=500000, nda_in=raw, xy0_off_pix=xy0_offset)
det.image - generates image in the "detector plane" assuming all detector sensors are in the same plane
det.image_at_z - projects intensities from each detector to the plane orthogonal to the beam with specified z coordinate relative to IP.
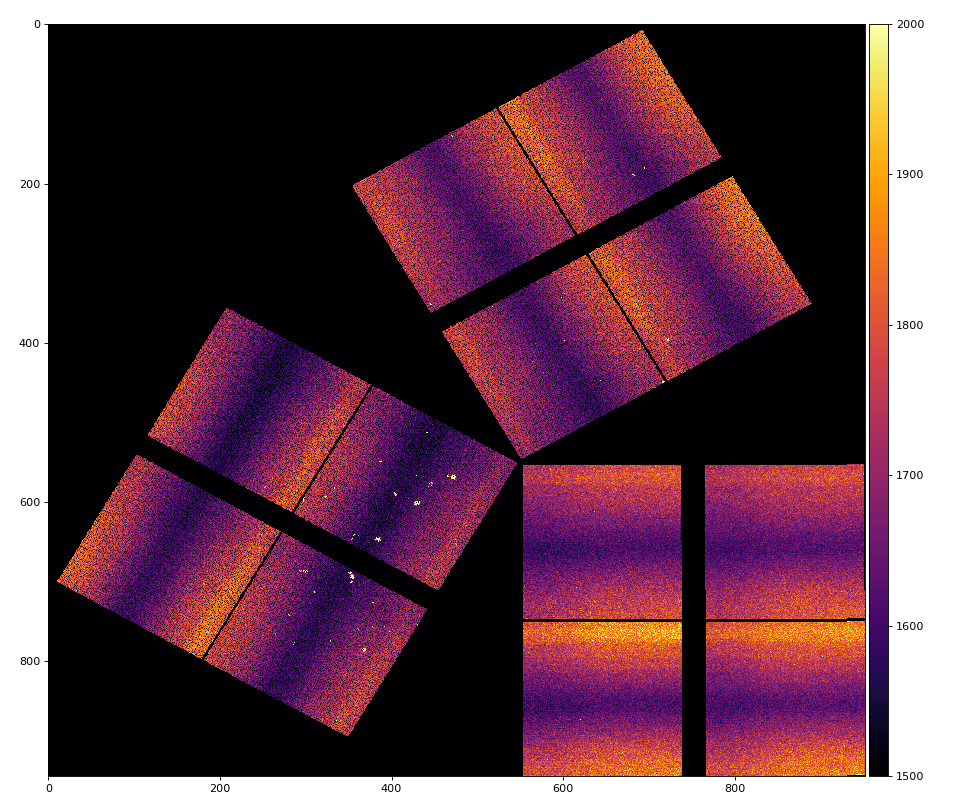
Compound detector image examples for three cspad2x1 from exp=xpptut15:run=460 and 1M and 512k Jungfrau from exp=mfxls4916:run=298
Geometry files from this example
/reg/d/psdm/xpp/xpptut15/calib/CsPad2x2::CalibV1/MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.1/geometry/460-460.data /reg/d/psdm/xpp/xpptut15/calib/CsPad2x2::CalibV1/MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.2/geometry/460-460.data /reg/d/psdm/xpp/xpptut15/calib/CsPad2x2::CalibV1/MecTargetChamber.0:Cspad2x2.3/geometry/460-460.data
The last line of each file is responsible for clpad2x1 position and rotation, i.e
IP 0 CSPAD2X2:V1 0 0 0 1000000 120 0 0 0.00000 0.00000 0.00000
See Detector Geometry for detail.
Run test example
Until release grater than ana-1.4.6 is available
ssh -Y pslogin.slac.stanford.edu ssh -Y psana . /reg/g/psdm/etc/psconda.sh source conda_setup --reldir /reg/neh/home/dubrovin/LCLS/con-ana-1.4.6 python /reg/neh/home/dubrovin/LCLS/con-ana-1.4.6/Detector/examples/ex_AreaDetectorCompound.py 3 # or other test # from 1 to 5.
References
- AreaDetectorCompound - source
- AreaDetector - source
- Detector interface
- Detector Geometry