The S3DF (SLAC Shared Science Data Facility) is a new SLAC-wide computing facility. The S3DF is replacing the current PCDS computer and storage resources used for the LCLS experiment data processing. Since August 2023 the data for new experiments are only available in the the S3DF (and FFB during data collection).
A simplified layout of the DRP and S3DF storage and compute nodes.
S3DF main page: https://s3df.slac.stanford.edu/public/doc/#/
S3DF accounts&access: https://s3df.slac.stanford.edu/public/doc/#/accounts-and-access(your unix account will need to be activated on the S3DF system)
- The S3DF (/sdf/) and PCDS (/cds/) should be considered separate sites as currently storage and home folders are not accessible between each other.
- The S3DF has its own users home directories, and the PCDS home directories (/cds/home/) are not accessible in the S3DF.
- The data directories in the S3DF (/sdf/data/lcls/ds) are not accessible in PCDS and vice versa the PCDS data folders (/cds/data/psdm or /reg/d/psdm) are not accessible in the S3DF.
Accessing the S3DF
To access to the S3DF systems connect to the s3dflogin pool and login with you unix account:
% ssh s3dflogin.slac.stanford.edu
Within the S3DF the nodes are named sdf*. The login nodes don't have the data folders mounted and no Slurm tools. For data transfers, data transfer nodes (s3dfdtn.slac.stanford.edu) are provided.
Interactive Cluster
An interactive cluster of nodes is available using the psana name. The interactive node provide access to the LCLS data and allows submitting Slurm jobs.
sdfloginNNN % ssh psana # interactive nodes, same name as in PCDS but different nodes
NoMachine Cluster
s3df also supports NoMachine access for more efficient X11 graphics (see https://s3df.slac.stanford.edu/#/accounts-and-access?id=how-to-connect). By default, in "console" mode the NoMachine xterm is quite primitive. A more full-featured xterm (e.g. with multiple tabs) can be obtained by entering "gnome-terminal" in the "Run the following command" line in this window when setting up the NoMachine connection:
Data and Software
The data-systems group folder, /sdf/group/lcls/ds, contains software packages and tools with several sub-folders:
| /sdf/group/lcls/ds/ana | psana1/psana2 release, detector calibration,.. |
| /sdf/group/lcls/ds/tools | smalldata-tools, cctbx, crystfel, om, .... |
| /sdf/group/lcls/ds/dm | data-management releases and tools. |
Experimental Data
The experiments analysis storage and fast-feed-back storage is accessible on the interactive and batch nodes.
| analysis-storage | /sdf/data/lcls/ds/<instr>/<expt>/<expt-folders> |
| FFB-storage | /sdf/data/lcls/drpsrcf/ffb/<instr>/<expt>/<expt-folders> |
The psana1/psana2 "psconda.sh" scripts shown below set this location for you using this first environment variable (but can also be done with an extra "dir=" DataSource argument). If you are doing realtime FFB analysis you will have to override that with the second value shown here:
export SIT_PSDM_DATA=/sdf/data/lcls/ds/ # offline analysis export SIT_PSDM_DATA=/sdf/data/lcls/drpsrcf/ffb # FFB analysis
So far data are only copied to the S3DF on request and run restores are to the PCDS Lustre file systems.
Contact pcds-datamgt-l@slac.stanford.edu if you would like to access data in the S3DF.
Scratch
A scratch folder is provided for every experiment and is accessible using the canonical path
/sdf/data/lcls/ds/<instr>/<expt>/<expt-folders>/scratch
The scratch folder lives on a dedicated high performance file system and the above path is a link to this file system.
In addition to the experiment scratch folder each users has its own scratch folder:
/sdf/scratch/users/<first character of name>/<user-name> (e.g. /sdf/scratch/users/w/wilko)
The users scratch space is limited to 100GB and as the experiment scratch folder old files will be automatically removed when the scratch file system is filling up. The df command will show the usage of a users scratch folder.
Large User Software And Conda Environments
If you have a large software package that needs to be installed in s3df contact pcds-datamgt-l@slac.stanford.edu. We can create a directory for you under /sdf/group/lcls/ds/tools.
A directory has been created under /sdf/group/lcls/ds/tools/conda_envs where users can create large conda environments (see Installing Your Own Python Packages for instructions).
S3DF Documentation
S3DF-maintained facility documentation can be found here.
Using psana in S3DF
To access data and submit to Slurm use the interactive cluster (ssh psana).
psana1 (LCLS-I data: XPP, XCS, MFX, CXI, MEC)
% source /sdf/group/lcls/ds/ana/sw/conda1/manage/bin/psconda.sh [-py2]
The command above activates by default the most recent python 3 version of psana. New psana versions do not support python 2 anymore, but it still possible to activate the last available python 2 environment (ana-4.0.45) using the -py2 option.
psana2 (LCLS-II data: TMO, TXI, RIX)
% source /sdf/group/lcls/ds/ana/sw/conda2/manage/bin/psconda.sh
Other LCLS Conda Environments in S3DF
- There is a simpler environment used for analyzing hdf5 files. Use "source /sdf/group/lcls/ds/ana/sw/conda2/manage/bin/h5ana.sh" to access it. It is also available in jupyter.
Batch processing
The S3DF batch compute link describes the Slurm batch processing. Here we will give a short summary relevant for LCLS users.
a partition and slurm account should be specified when submitting jobs. The slurm account would be lcls:<experiment-name> e.g. lcls:xpp123456 . The account is used for keeping track of resource usage per experiment
% sbatch -p milano --account lcls:xpp1234 ........
You must be a member of the experiment's slurm account which you can check with a command like this:
sacctmgr list associations -p account=lcls:xpp1234
You can see which accounts you are a member of with this command:
sacctmgr show associations user=<username>
- Submitting jobs using the lcls account allows only to submit preemptable jobs and requires to specify: --qos preemptable . The lcls account is set by --account lcls or --account lcls:default (the lcls name gets automatically translated to lcls:default by slurm, and s-commands will show the default one).
- In the S3DF by default memory is limited to 4GB/core. Usually that is not an issue as processing jobs use many core (e.g. a job with 64 cores would request 256GB memory)
- the memory limit will be enforced and your job will fail with an OUT_OF_MEMORY status
- memory can be increased using the --mem sbatch option (e.g.: --mem 16G, default unit is megabytes)
- Default total run time is 1 day, the --time option allows to increase/decrease it.
Number of cores
Some cores of a milano batch node are exclusively used for file IO (WekaFS). Therefore although a milano node has 128 core only 120 can be used.
submitting a task with --nodes 1 --ntasks-per-node=128 would fail with: Requested node configuration is not availableEnvironment Varibales: sbatch option can also be set via environment variables which is useful if a program is executed that calls sbatch and doesn't allow to set options on the command line e.g.:
% SLURM_ACCOUNT=lcls:experiment executable-to-run [args] or % export SLURM_ACCOUNT=lcls:experiment % executable-to-run [args]
The environment variables are SBATCH_MEM_PER_NODE (--mem), SLURM_ACCOUNT(--account) and SBATCH_TIMELIMIT (--time). The order arguments are selected is: command line, environment and withing sbatch script.
Real-time Analysis Using A Reservation For A Running Experiment
Currently we are reserving nodes for experiments that need real-time processing. This is an example of parameters that should be added to a slurm submission script:
#SBATCH --reservation=lcls:onshift #SBATCH --account=lcls:tmoc00221
You must be a member of the experiment's slurm account which you can check with a command like this:
sacctmgr list associations -p account=lcls:tmoc00221
and your experiment must have been added to the reservation permissions list. This can be checked with this command:
(ps-4.6.1) scontrol show res lcls:onshift ReservationName=lcls:onshift StartTime=2023-08-02T10:39:06 EndTime=2023-12-31T00:00:00 Duration=150-14:20:54 Nodes=sdfmilan[001,014,022,033,047,059,062,101,127,221-222,226] NodeCnt=12 CoreCnt=1536 Features=(null) PartitionName=milano Flags=IGNORE_JOBS TRES=cpu=1536 Users=(null) Groups=(null) Accounts=lcls:tmoc00221,lcls:xppl1001021,lcls:cxil1022721,lcls:mecl1011021,lcls:xcsl1004621,lcls:mfxx1004121,lcls:mfxp1001121 Licenses=(null) State=ACTIVE BurstBuffer=(null) Watts=n/a MaxStartDelay=(null) (ps-4.6.1)
You can use the reservation only if your experiment is on-shift or off-shift. If you think slurm settings are incorrect for your experiment email pcds-datamgt-l@slac.stanford.edu.
MPI and Slurm
For running mpi jobs on the S3DF slurm cluster mpirun (or related tools) should be used. Using srun to run mpi4py will fail as it requires pmix which is not supported by the Slurm version. Example psana MPI submission scripts are here: Submitting SLURM Batch Jobs
Jupyter
Jupyter is provided by the onDemand service (We are not planning to run a standalone jupyterhub as is done at PCDS. For more information check the S3DF interactive compute docs).
ssh <username>@s3dflogin.slac.stanford.edu from a terminal.onDemand requires a valid ssh-key (~/.ssh/s3df/id_ed25519) which are auto generated when an account is enabled in the S3DF. However, older accounts might not have this key but can create it running the following command on a login or interactive node: /sdf/group/lcls/ds/dm/bin/generate-keys.sh
If you still have issues logging, go to https://vouch.slac.stanford.edu/logout and try loging in again.
Please note that the "Files" application cannot read ACLs which means that (most likely) you will not be able to access your experiment directories from there. Jupyterlab (or interactive terminal session) from the psana nodes will not have this problem.
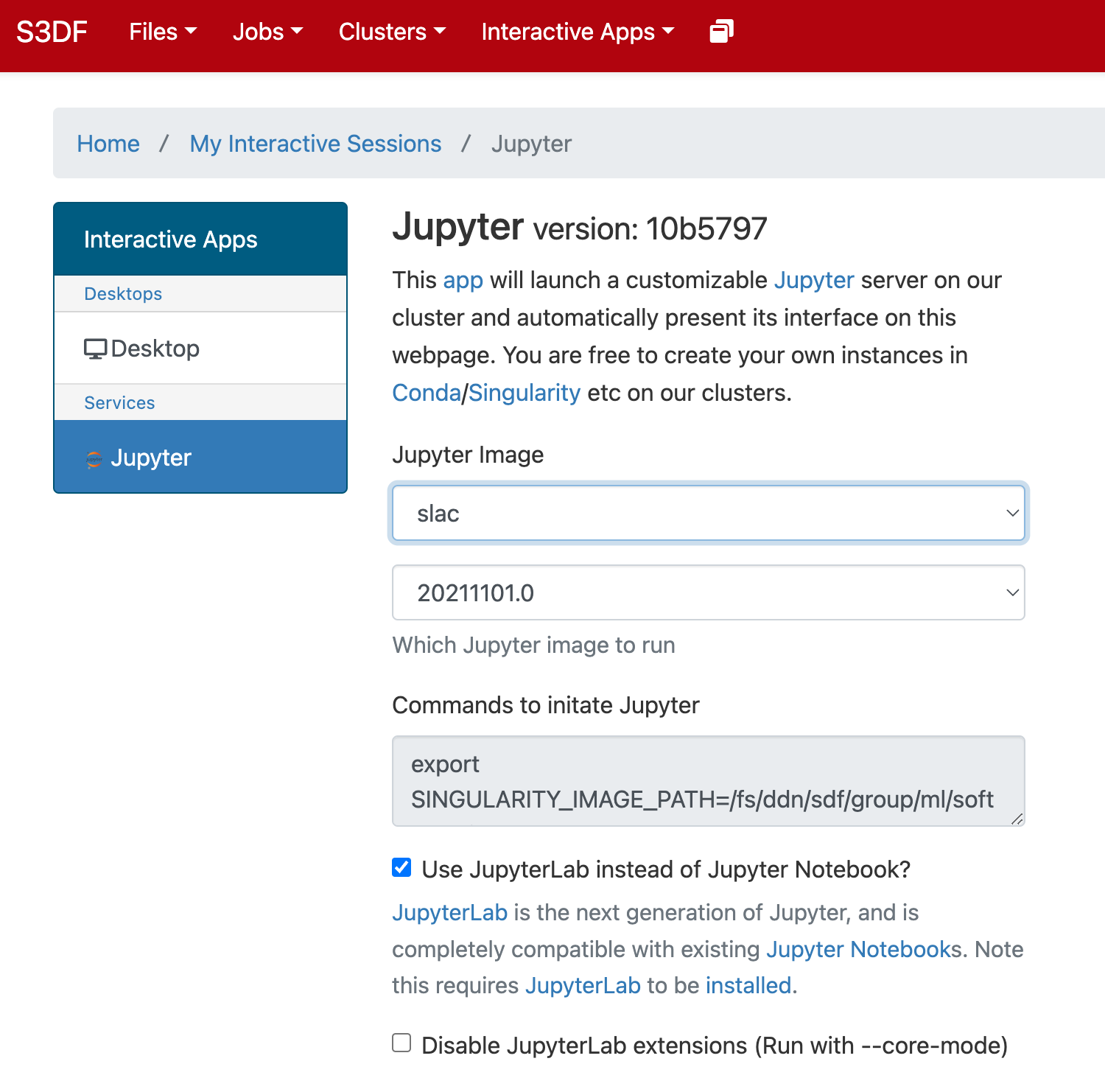
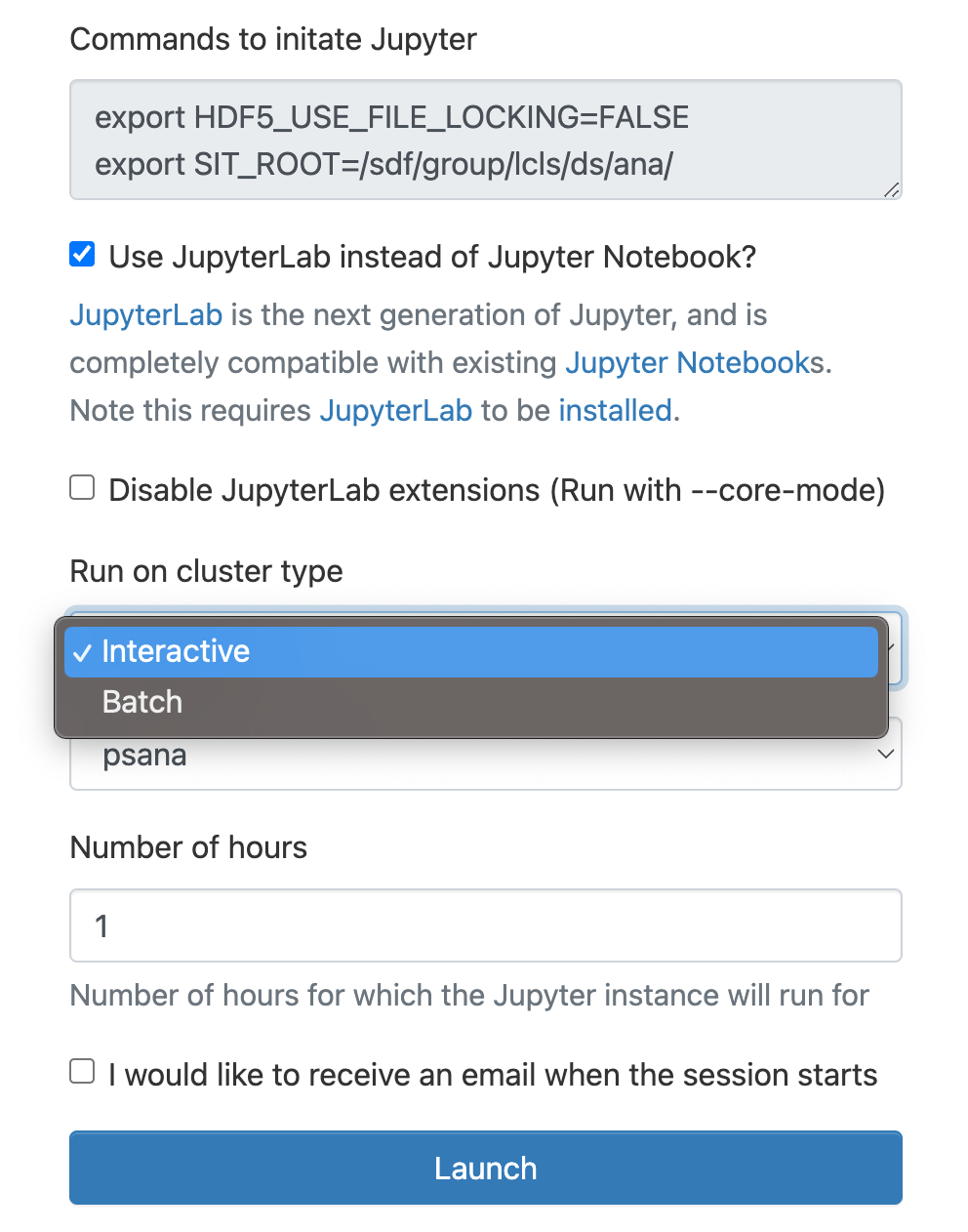
In the "Interactive Apps" select Jupyter, this opens the following form
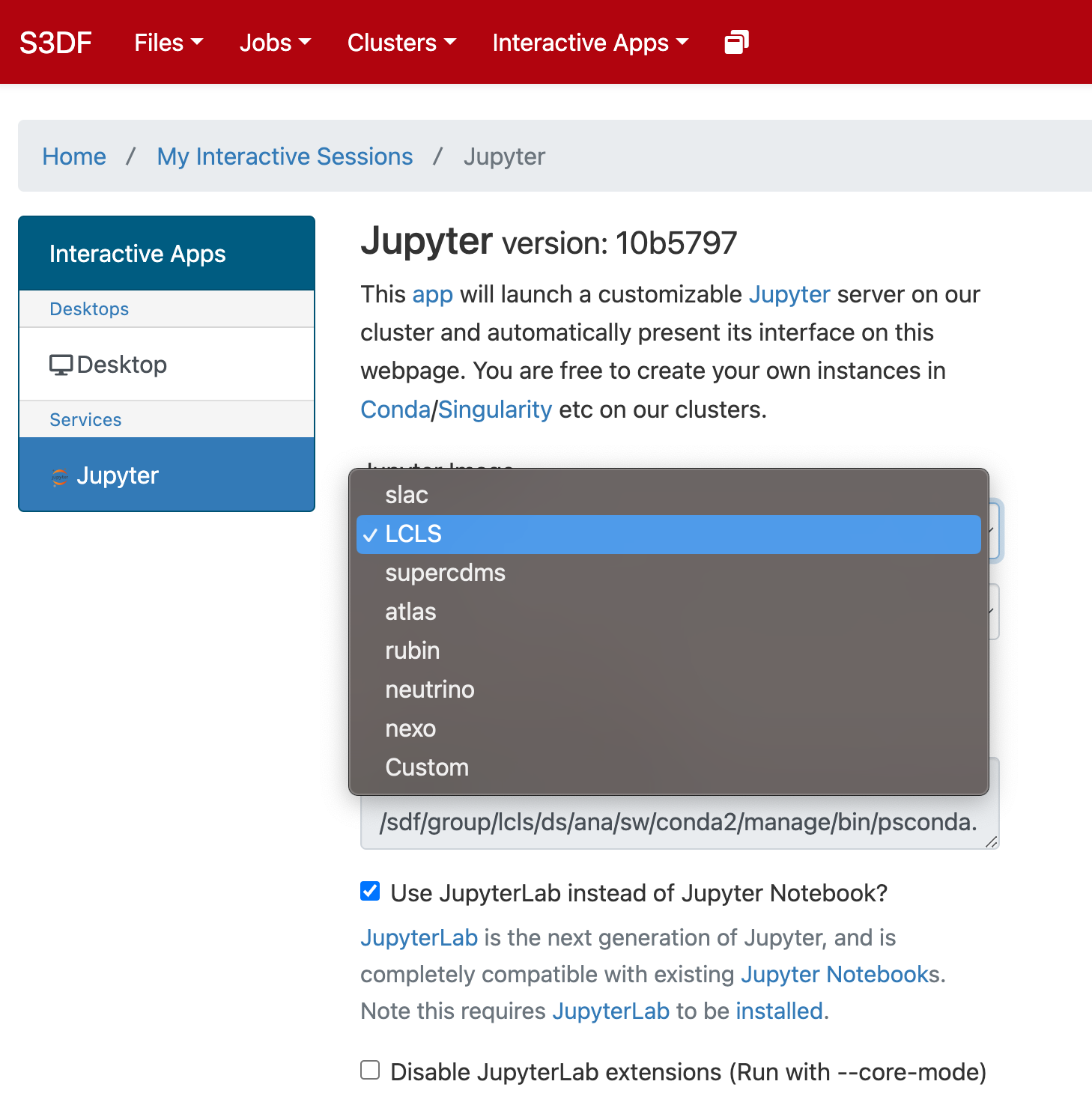
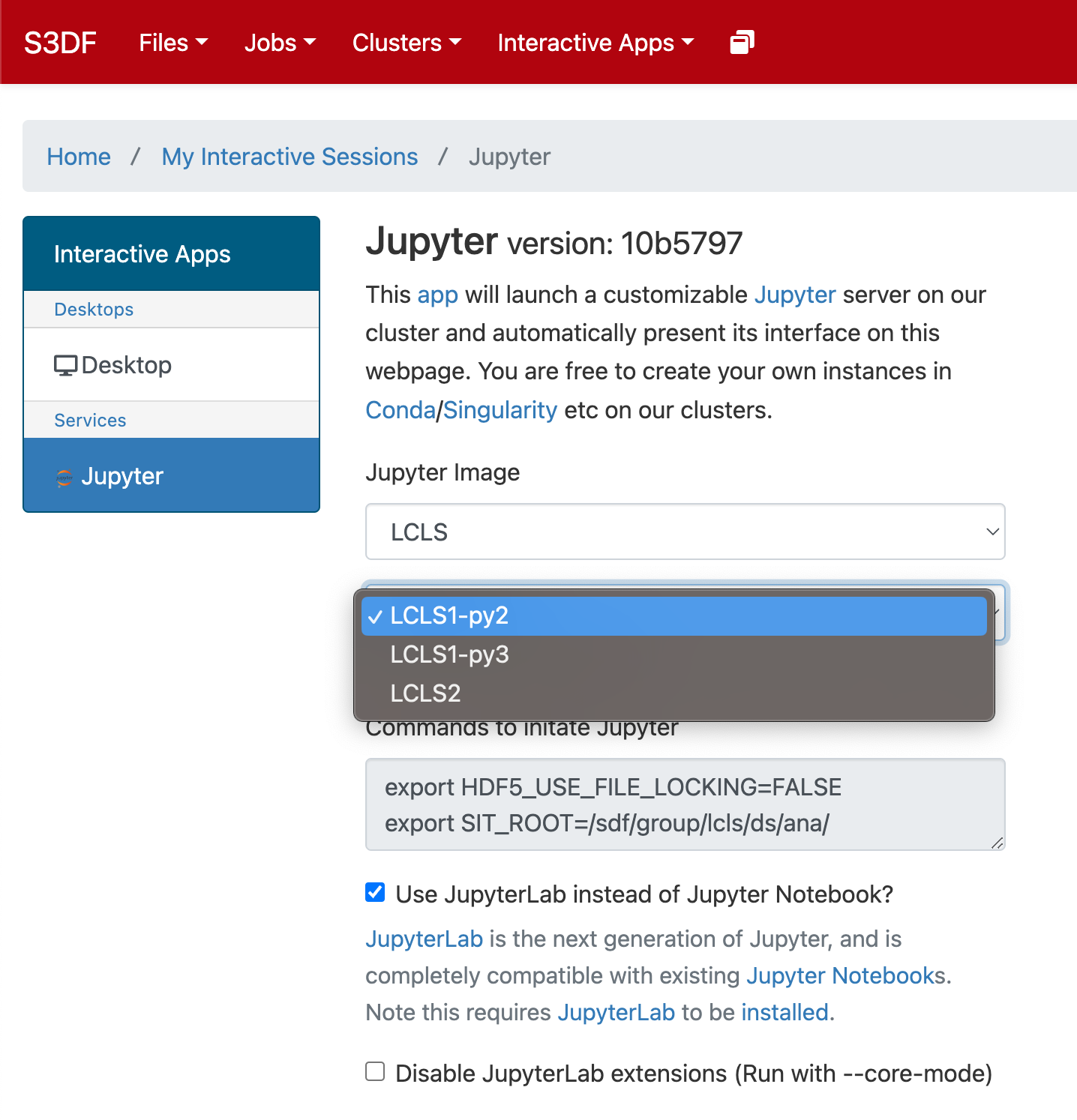
Select the Jupyter image "LCLS" and in the second selection choose "LCLS1-py2", "LCLS1-py3", or "LCLS2".
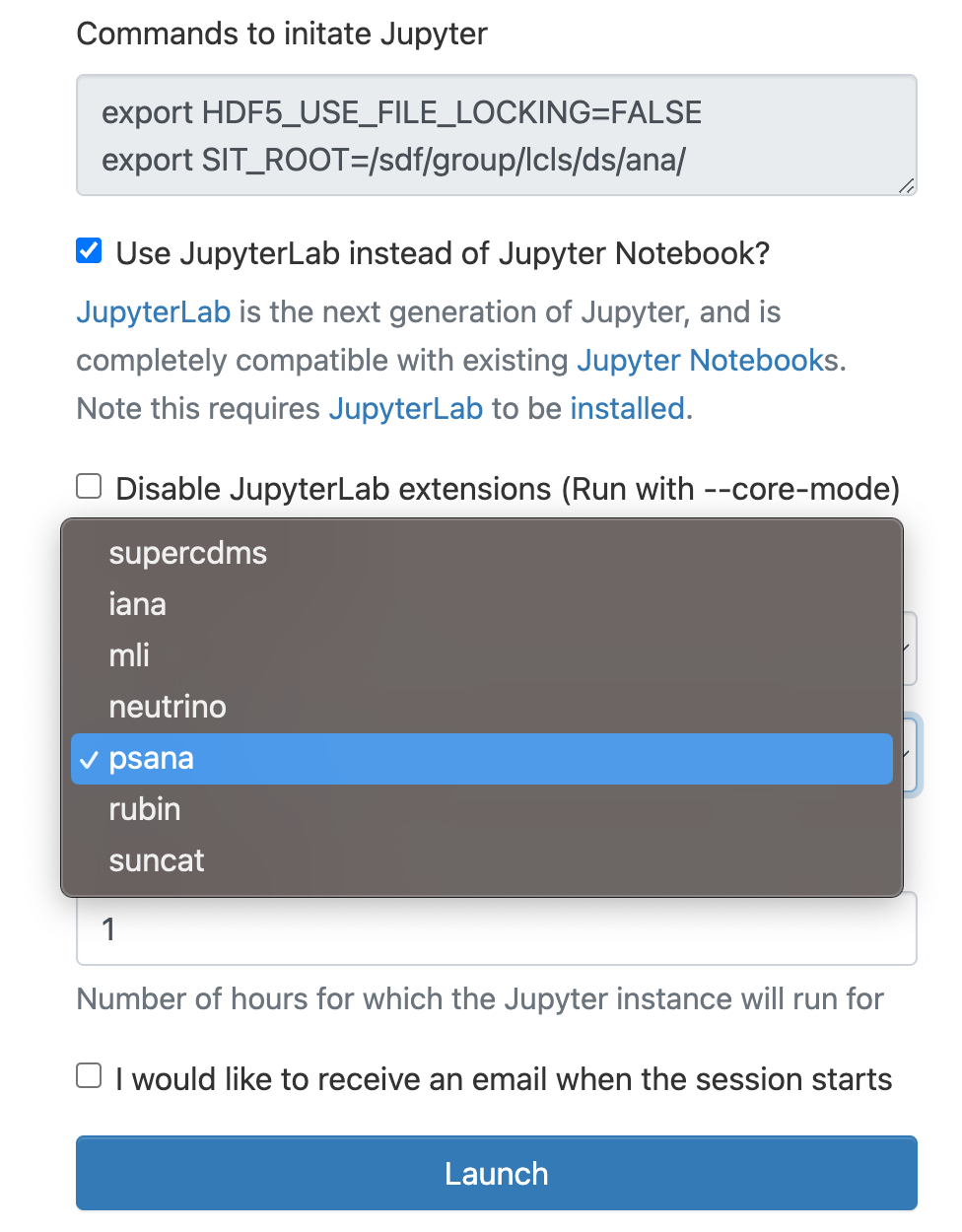
As a cluster type select "Interactive" or "Batch", and then select "psana"(one should always select psana when running LCLS).
Select then how many hours to run and if you prefer Jupyter lab or notebook.
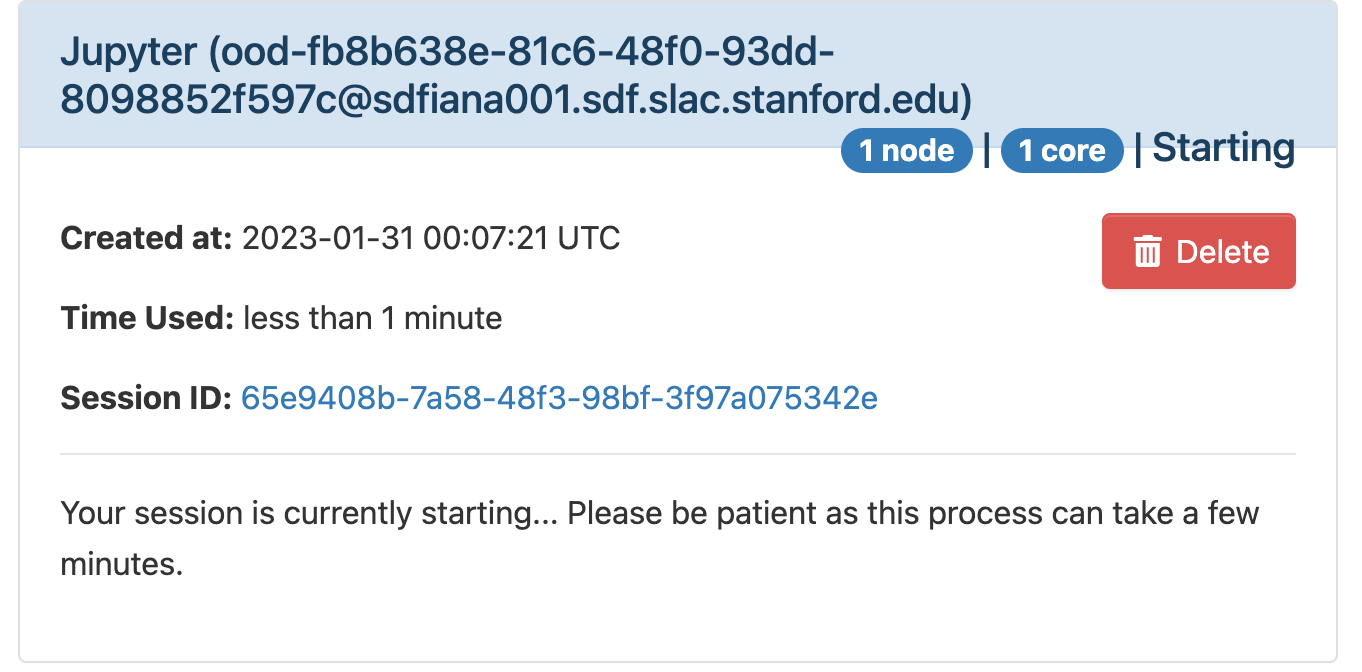
Then click on the "Launch" button:
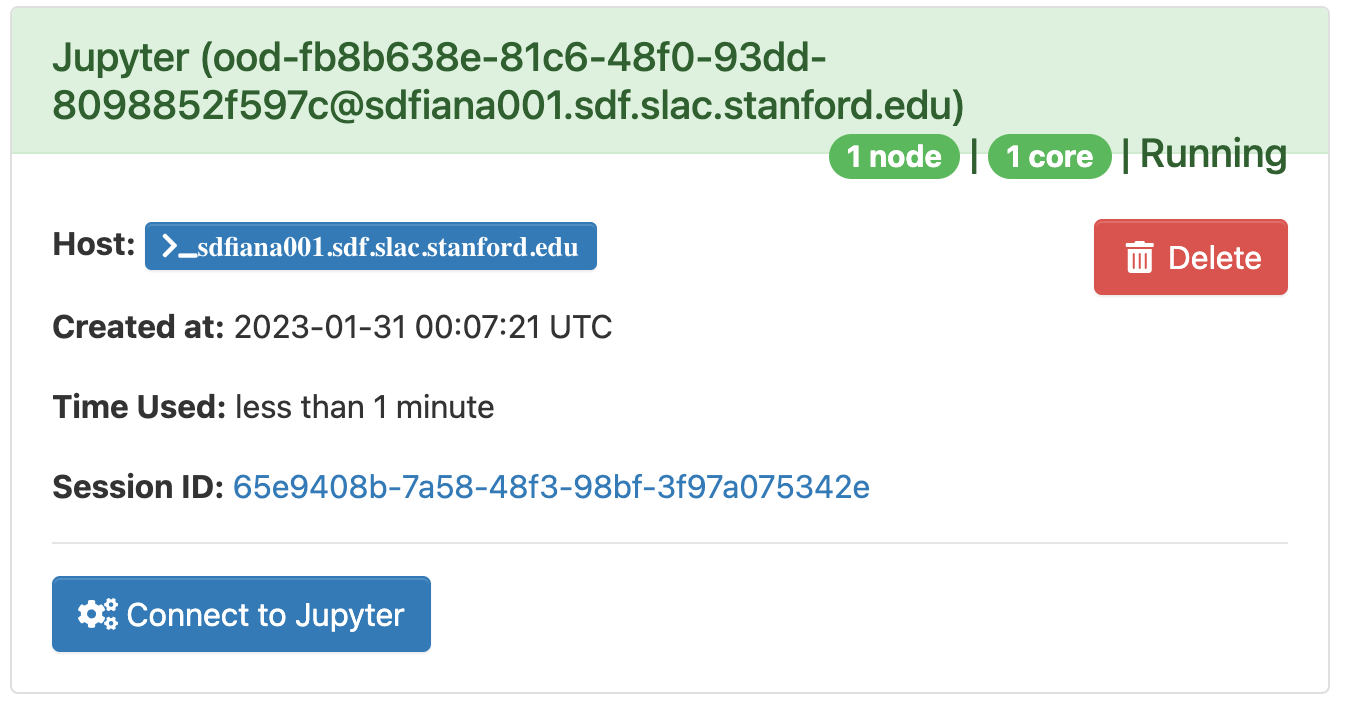
The page will at first show a "Starting" status, after some time it will switch to "Running" and the "Connect to Jupyter" button will be available. Click on the "Connect to Jupyter" button to start working on Jupyter. The Session ID link instead allows to open the directory where the Jupyter is run and access to the files, included the logs.
Offsite data transfers
The S3DF provides a group of transfer nodes for moving data in/out. The nodes are accessed using the load balanced name: s3dfdtn.slac.stanford.edu
A Globus endpoint is available: slac#s3df
Batch Job Memory Usage
Estimating memory usage for a slurm job can be difficult. One approach is to run a representative job once using all the memory of an S3DF milano node by specifying the "--mem 480G" flag to slurm's sbatch command. Do not use this for all batch jobs, as it allocates an entire node which may be wasteful of resources. Slurm can then tell you what the maximum memory usage was for the completed job with:
sacct -j <jobid> -o maxrss
A more complete output of memory usage and parameters can be seen with this command:
sacct -j <jobid> -o partition,maxvmsize,avevmsize,maxrss,averss,maxpages,reqtres%36
The milano cluster in S3DF by default allows users to allocate 4GB/core (so 480GB on the maximum number of cores (120)) but this can be overridden with the above "--mem" option.