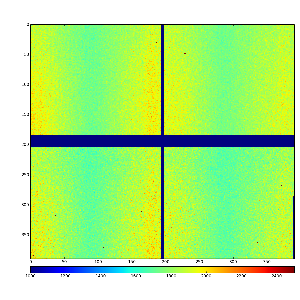
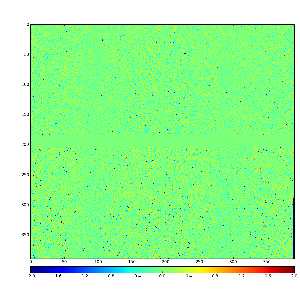
Content
Algorithms
In this note we discuss common mode correction algorithms implemented in psana module ImgAlgos::NDArrCalib.
We use algorithms earlier developed for CSPADs from ImgAlgos::GlobalMethods(#1) and from psalg package (#2 and #3).
Selection of algorithm for particular device can be controlled by the parameters in common_mode type of calibration constants.
#1 - common mode peak finding algorithm
common_mode parameters for CSPAD and CSPAD2x2
1 50 50 100
- par[0] - algorithm #
- par[1] - maximal deviation of the peak mean from 0
- par[2] - maximal allowed value of the peak RMS
- par[3] -threshold on number of pixels in the ADU bin in the peak finding algorithm
for other detectors
- par[4] - number of segments for common mode evaluation
- par[5] - segment size (number of pixels for common mode evaluation)
par[6] - stride (step for jump to the next pixel)
For example:
1 50 50 100 8192 128 1
#2 - MEAN evaluation
- par[0] - algorithm #
- par[1] - maximal threshold on intensity to evaluate mean for low intensities
- par[2] - maximal allowed common mode correction
par[3] - length of consecutive pixel array for common mode evaluation
For example, for pnCCD1 1000 1000 128
#3 - MEDIAN evaluation
Parameters are the same as in #2
Test of the common mode correction for pnCCD
To test implementation of algorithms in ImgAlgos::NDArrCalib we use the same data sets as in 2014-03-25-Ankush-CommonModeNoise.pdf
Use data from experiment amob5114
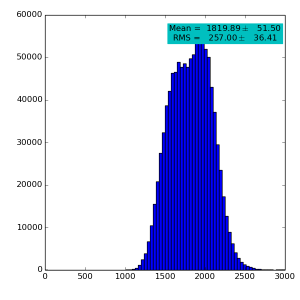
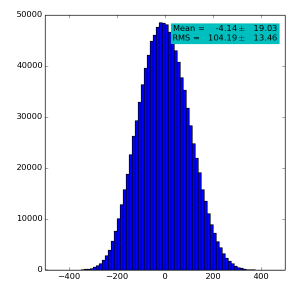
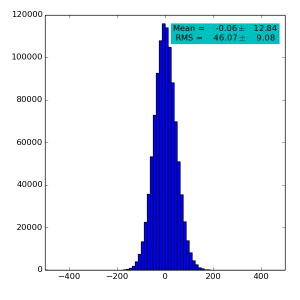
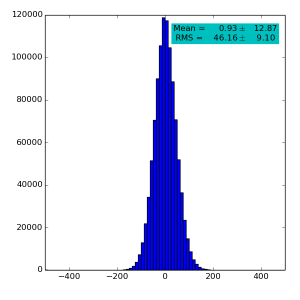
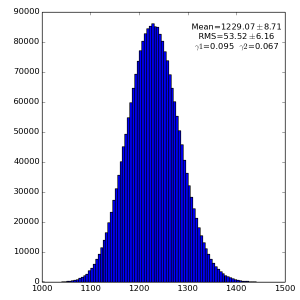
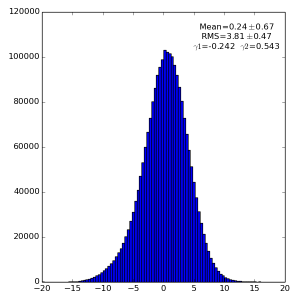
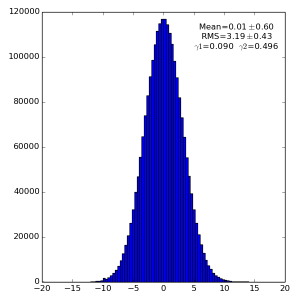
High gain pnCCD run 121
2(or 3) 1000 1000 128
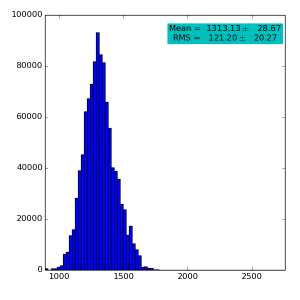
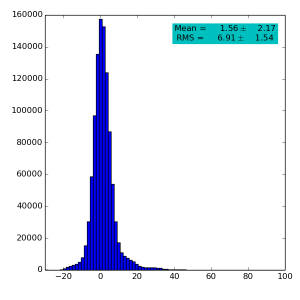
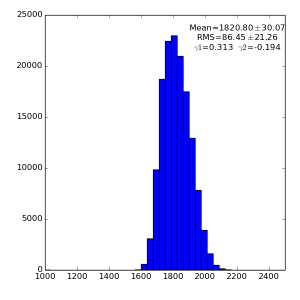
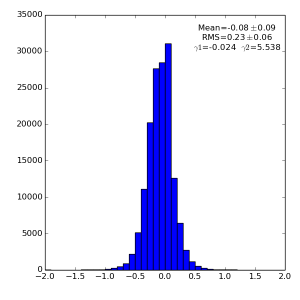
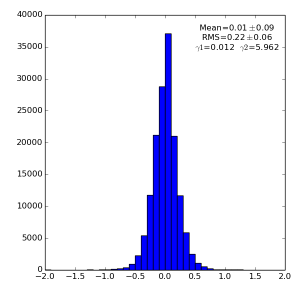
Spectra for 1) raw data, 2) subtracted pedestals, 3) subtracted common mode correction algorithm #2 and 4) algorithm #3:
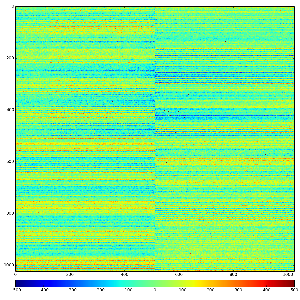
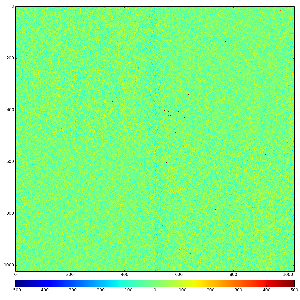
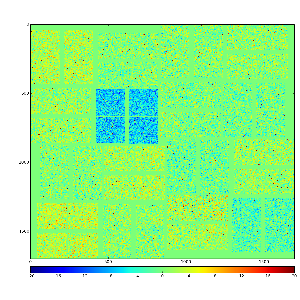
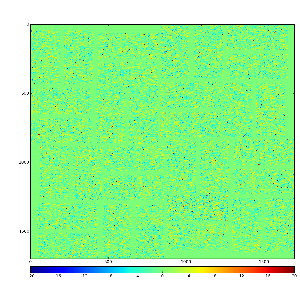
Images 1) for subtracted pedestals and 2) common mode correction algorithm #2:
High gain pnCCD run 329
2(or 3) 1000 1000 128
Spectra for 1) raw data, 2) subtracted pedestals, 3) subtracted common mode correction algorithm #2 and 4) algorithm #3:
Images 1) for subtracted pedestals and 2) common mode correction algorithm #2:
Summary for pnCCD
Common mode correction for pnCCD
- gives significant effect in low gain mode and is negligible in high gain mode
- algorithm #2 gives the best results, #3 a little bit worse, #1 - does not work for pnCCD
Test of common mode correction for CSPAD
Use cxi83714-r0136 with
1 10 10 100
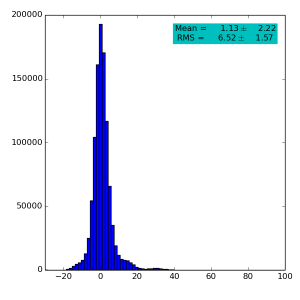
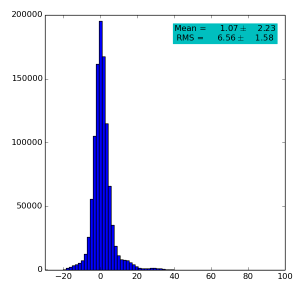
Spectra for 1) raw data, 2) subtracted pedestals, 3) subtracted common mode correction algorithm #1:
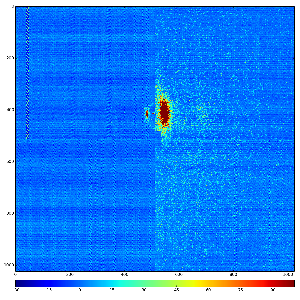
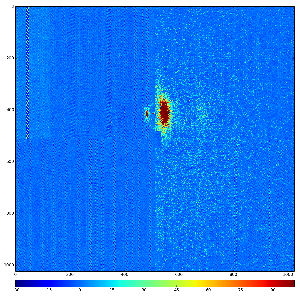
Images 1) for subtracted pedestals and 2) common mode correction algorithm #1:
Summary for CSPAD
Common mode correction for CSPAD works with algorith #1 and shows significant effect.
Test of common mode correction for CSPAD2x2
Use meca1113-r0045 with
1 50 10 (100) - last parameter is set by default
Spectra for 1) raw data, 2) subtracted pedestals, 3) subtracted common mode correction algorithm #1:
Images 1) raw data and 2) subtracted pedestals with common mode correction algorithm #1:
Summary for CSPAD2x2
Common mode correction for CSPAD2x2 in this example shows minor improvement.
References
2014-03-25-Ankush-CommonModeNoise.pdf - stand-alone test of common mode correction for pnCCD
psana - Module Catalog - Module ImgAlgos::NDArrCalib