Page History
Content
| Table of Contents |
|---|
This algorithm is intended to subtract background from "non-assembled" images with approximately angular-symmetric radial distribution of intensities.
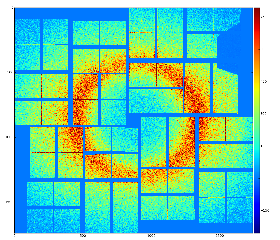
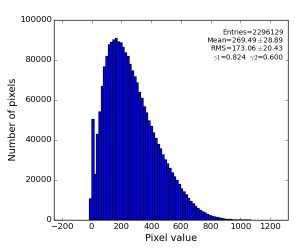
For example, pure water ring background from exp=cxij4716:run=22 for single event has an angular symmetry as shown in the plot:
Code location
Class RadialBkgd resides in the package pyimgalgos.
Auto-generated documentation for class RadialBkgd
Initialization
| Code Block |
|---|
from pyimgalgos.RadialBkgd import RadialBkgd, polarization_factor rb = RadialBkgd(xarr, yarr, mask=None, radedges=None, nradbins=100, phiedges=(0,360), nphibins=32) |
See parameters' description in Auto-generated documentation for class RadialBkgd.
Input n-d arrays can be obtained through the Detector (AreaDetector) interface or directly through the class working with geometry. For example,
| Code Block |
|---|
from PSCalib.GeometryAccess import GeometryAccess geo = GeometryAccess(fname_geo) xarr, yarr, zarr = geo.get_pixel_coords() iX, iY = geo.get_pixel_coord_indexes() mask = geo.get_pixel_mask(mbits=0377) # mask for 2x1 edges, two central columns, and unbound pixels with their neighbours ... |
Algorithm
...
This algorithm is intended to subtract background from images with approximately angular-symmetric radial distribution of intensities.
For example, pure water ring background from exp=cxij4716:run=22 for single event has an angular symmetry as shown in the plot:
To evaluate background n-d array of data is split for 2-d bins in polar coordinate frame. Total intensity and number of involved pixels are counted for each bin and converted to the average bin intensity. Then this averaged intensity is per-pixel subtracted from data n-d array.
Input per-pixel coordinates passed as numpy n-d arrays xarr and yarr are used to evaluate per-pixel radial and polar angle coordinate arrays:
...
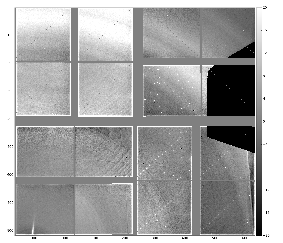
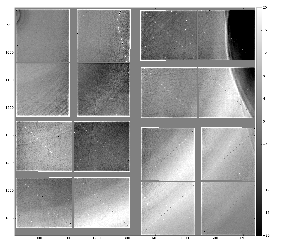
- zoomed-in regions of four quads
- Shows some "doping" artifacts.
- A few smooth curves earlier interpreted as "scratches" apparently become a nice "chart" probably on the detector shield. This "chart" can be used for alignment.
References