Page History
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
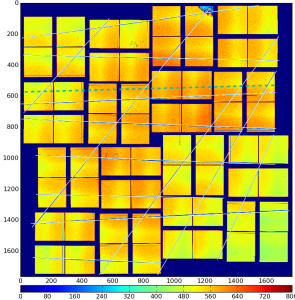
Cornell SLAC Pixel Array Detector (CSPAD) is an imaging X-ray detector made of silicon sensors (2x1) covering about 20x20cm² surface, as shown in the plot:
Pixel coordinates in 2x1 sensor chip are known with sub-micrometer precision. Construction of the detector allows significant freedom in relative positions of 2x1 sensors. To get precise pixel positions in the detector the 2x1 sensor coordinates needs to be calibrated. In this note we describe geometry of the CSPAD detector, optical and quad alignment procedure, parameters, and software providing access to precise geometry information.
2x1 Sensor Geometry
The 2x1 sensor geometry was tested with microscopic measurement. Two slides from Chris Kenney's presentation shows the pixel sizes:
The same slides in PDF format.
...
- Number of rows x columns = 185 x 388. (In DAQ notation of rows and columns is interchanged...)
- Most of pixels have size 109.92 x 109.92 um².
- Gap between two ASICS is covered by the two rows of elongated pixels with size 109.92 x 274.8 um².
- Two versions of sensors have different dimensions between corners, so it is reasonable to define pixel coordinates w.r.t. the sensor center.
Optical measurement
Optical measurement is maintained by Chris Kenney. Detector or its quad is installed on microscope table and 3-d coordinates of all 2x1 sensor corners are measured with precision about 8um (RMS) in x-y plane. All corners in the measurement are numerated in arbitrary order. It is expected that numeration order should be the same for different measurements. This procedure depends on CSPAD construction;
...
Then, text table with "standard" numeration of points in quads is feed to the python script which provides quality check of optical measurement and evaluates the alignment parameters for quads. In the beginning, this script changes the numeration of points adopted in optical measurement to numeration of 2x1 used in DAQ. Further, all calibration parameters are associated with numeration of 2x1 sensors and quads in DAQ.
Quality Check Procedure
For quality check of optical measurement we calculate
S1 - 1st short side length of 2x1
S2 - 2nd short side length of 2x1
L1 - 1st long side length of 2x1
L2 - 2nd long side length of 2x1
D1 - 1st diagonal of 2x1 between corners 1 and 3
D2 - 2nd diagonal of 2x1 between corners 2 and 4
dS and dL are the deviations of the 1st and 2nd corner along the short and long sides, respectively. The sign of all dS are chosen in order to provide correct sign for the tilt angle (the same direction for all 2x1 sensors).
<dS/L> - the tilt angle of 2x1 averaged over two sides in radians.
angle(deg) - the same angle in degrees.
dD = D1 - D2
d(dS) = dS1 - dS2
d(dL) = dL1 - dL2
dz3(um) - signed distance from 2x1 sensor plane and corner 3, where the 2x1 sensor plane contains the corner points p1, p2, and p4. This plane is defined by the vectors v21=p2-p1, v41=p4-p1, and their orthogonal vector
...
| Code Block |
|---|
Mean and standard deviation [um]: 0.376 +- 15.818 |
Alignment parameters from optical measurement
From optical measurement we extract coordinates of the center of each 2x1 sensor and its tilt angle, that populates the calibration types center and tilt, respectively.
The center coordinates are evaluated as an averaged over 4 corners measurements for each axis. Additional correction to the center coordinate center_corr can be applied if the optical measurement has (non-)obvious problems.
The tilt parameters are the same as "angle(deg)" from quality check results table. The tilt parameters are used along with rotation to completely define orientation of 2x1 in quad (for CXI) or in detector (for XPP).
Alignment of quads in the detector
For CSPad with fixed quad geometry (like in XPP) optical measurement of entire detector (should) produces complete information for geometry alignment.
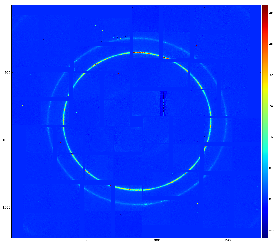
For CSPad with moveable quads (like in CXI) quads relative position needs to be adjusted through the alignment parameters for quads. It is usually done using typical images with diffraction rings, wires or other shading objects:
Although few algorithms of automatic quad alignment were tried, we did not find good generic way for automated quad tuning. Currently, the quad tuning parameters in marg_gap_shift and offset_corr are adjusted manually for runs with specific images.
Detector geometry model
In calibration parameters all coordinates are defined in terms of pixel size 109.92um. In this units the reserved square space for each quadrant is 850x850. The margins, shifts and gaps in marg_gap_shift are defined for these quads. The offset and offset_corr are defined for low-left angle of the rotated by n*90 degree quad. Size of entire CSPad image does not matter for this alignment.
Alignment parameters
Location of alignment parameters and file naming conventions
The official space for CSPad alignment parameters is
/reg/d/psdm/<INSTRUMENT>/<experiment>/calib/CsPad::Calib<VERSION>/<CSPad-name>/<type>/<run-range>.data
For example:
...
The file name consists of the run range followed by the .data extension, for example, 0-end.data, 11-end.data, 47-52.data, etc.
Description of types
All CSPAD geometry alignment parameters are split for 9 types:
...
beam_vector- (description given by TJ Lane) a R^3 vector pointing from the interaction site to the location ofbeam_intersect(below), along the direction the beam travels. The magnitude of this vector is the distance between the interaction site and the rough plane of the detector.beam_intersect- (description given by TJ Lane) a R^3 vector pointing from the origin (of CSPAD?) to thebeam_vector, and intersecting the beam in an orthogonal manner. This can intuitively be though of as the "center" of the detector – and will be that center in the case that the detector is completely contained in a plane normal to the beam, and the origin is in that plane.
File format for calibration types
center
Tail of the path: center/<run-range>.data
Parameters: x,y,z coordinates of 8 2x1 centers in 4 quads in pixels:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
199.14 198.05 310.67 98.22 629.71 629.68 711.87 499.32 198.52 198.08 311.50 98.69 627.27 627.27 712.35 499.77 198.32 198.04 310.53 97.43 626.68 628.45 710.86 498.01 198.26 198.04 308.70 96.42 627.66 628.04 711.12 498.25 308.25 95.11 625.60 625.70 515.02 727.37 198.53 199.30 307.18 95.08 622.98 623.51 514.99 727.35 199.27 198.94 307.68 95.09 623.95 625.29 512.32 724.63 198.04 200.35 307.39 95.12 627.57 626.65 518.03 730.95 200.02 199.70 0.31 0.12 0.05 0.12 0.28 0.24 0.40 0.27 0.45 0.36 0.62 0.33 1.02 0.92 1.30 1.07 0.23 0.22 0.11 0.15 0.24 0.20 0.60 0.42 0.25 0.21 0.12 0.10 0.35 0.28 0.66 0.40 |
center_corr
Tail of the path: center_corr/<run-range>.data
Parameters: x,y,z coordinate corrections of 8 2x1 centers in 4 quads in pixels:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 -1 0 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -1 -2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
offset
Tail of the path: offset/<run-range>.data
Parameters: x,y,z coordinates of 4 quad "origins" in CSPad pixel matrix:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 820 820 0 820 820 0 0 0 0 0 |
offset_corr
Tail of the path: offset_corr/<run-range>.data
Parameters: x,y,z coordinate corrections of 4 quad "origins" in CSPad pixel matrix:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 5 2 0 5 4 4 0 0 0 0 |
marg_gap_shift
Tail of the path: marg_gap_shift/<run-range>.data
Parameters:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
15 40 0 32
15 40 0 32
0 0 0 0
|
quad_rotation
Tail of the path: quad_rotation/<run-range>.data
Parameters: rotation angle of 4 quads in CSPad in n*90 degree:
...
Typical values:
| Code Block |
|---|
180 90 0 270 |
quad_tilt
Tail of the path: quad_tilt/<run-range>.data
Parameters: rotation angle correction (tilt) of 4 quads in CSPad in degree:
...
Typical values:
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 0 0 |
rotation
Tail of the path: rotation/<run-range>.data
Parameters: rotation angle of 8 2x1 in 4 quads in n*90 degree:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 270 270 180 180 270 270 0 0 270 270 180 180 270 270 0 0 270 270 180 180 270 270 0 0 270 270 180 180 270 270 |
tilt
Tail of the path: tilt/<run-range>.data
Parameters: rotation angle correction (tilt) of 8 2x1 in 4 quads in degree:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
-0.33819 0.00132 0.31452 -0.03487 0.14738 0.07896 -0.21778 -0.10396 -0.27238 -0.00526 0.02545 0.03066 -0.03619 0.02434 0.08027 0.15067 -0.04803 -0.00592 0.11318 -0.07896 -0.36125 -0.31846 -0.16527 0.09200 0.12436 0.00263 0.44809 0.25794 -0.18029 -0.00117 0.32701 0.32439 |
center_global
Tail of the path: center_global/<run-range>.data
Parameters: x,y,z coordinates of all 2x1 centers in the detector in units of pixel size (109.92 um).
As usually, the matrix-style of the coordinate system is used:
...
| Code Block |
|---|
477.78 690.20 159.77 160.06 277.17 64.77 591.30 591.01
990.78 989.30 1105.38 891.19 1421.65 1423.66 1502.28 1289.93
1143.85 932.00 1461.86 1463.74 1349.75 1562.62 1032.39 1033.60
633.06 632.80 518.88 731.75 200.62 198.75 118.50 331.23
1018.54 1019.42 1134.27 921.94 1451.06 1451.01 1532.55 1319.23
1173.24 960.71 1490.18 1491.45 1374.97 1587.78 1058.56 1061.14
658.23 658.54 542.73 755.26 225.91 224.22 146.39 358.27
507.44 720.59 189.73 190.28 306.25 93.65 620.68 619.85
1.00 1.04 0.64 1.14 0.05 -0.03 -0.18 0.45
0.92 1.37 0.26 -0.02 0.62 0.13 1.35 1.25
-2.10 -1.76 -3.00 -2.29 -3.85 -4.20 -3.63 -2.94
1.83 1.57 2.23 2.31 1.91 2.07 1.41 0.54
|
beam_vector
Tail of the path: beam_vector/<run-range>.data
Parameters: 3 components of the vector:
...
Typical values:
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 0 |
beam_intersect
Tail of the path: beam_intersect/<run-range>.data
Parameters: 3 components of the vector:
...
Typical values:
| Code Block |
|---|
0 0 0 |
Pixel coordinate reconstruction
The list of CSPad geometry alignment parameters is over-defined; different parameters can be used to get the same final effect on pixel coordinate. It is done intentionally in order to keep flexibility in the alignment stage.
...
| Code Block |
|---|
Xoffset_qi = XOffQ + xqi + dxqi + [-gapX+shiftX, -gapX-shiftX, +gapX-shiftX, +gapX+shiftX] Yoffset_qi = YOffQ + yqi + dyqi + [-gapY-shiftY, +gapY-shiftY, +gapY+shiftY, -gapY+shiftY] ... |
Software supporting CSPad geometry
There is a couple of packages which reconstruct CSPad pixel coordinates and images developed in C++ and python code;
- C++-based package: Psana Module Catalog - Old.
- Description of C++ package supporting calibration types: CSPAD Geometry Software - Old.
- Python-based package:
...
- Note about organization of the calibration database: CsPad calibration in translator.
References
Description of CSPAD layout from DAQ
CSPAD quad metrology
CSPad pixel layout in quads