Page History
Content
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Mask
To create mask use Mask Editor command med or launch it through the calibman.
Geometry center
ix_cent, iy_cent = det.point_indexes(runnum)
879, 871 (then x and y are swapped to Cartesian system).
Equatorial mask
Mask parameters
| Code Block |
|---|
Wedge 871 879 454 387 148 196 1 k False False Wedge 871 879 454 387 -27 21 1 k False False |
...
| Code Block |
|---|
t = pars[0] # figure type, ex. 'Wedge' x = float(pars[1]) # x coordinate of the wedge center y = float(pars[2]) # y coordinate of the wedge center r = float(pars[3]) # 1-st radius of the wedge w = float(pars[4]) # radial width of the wedge t1 = float(pars[5]) # 1-st angle t2 = float(pars[6]) # 2-nd angle lw = int(pars[7]) # line width col = str(pars[8]) # color s = self.dicBool[pars[9].lower()] # isSelected boolean parameter rem = self.dicBool[pars[10].lower()] # isRemoved - helper parameter |
Involved sensors in adopted cxif5315 geometry: 0, 1, 9,15, 16,17, 25,31
...
| Code Block |
|---|
--------- | 1 | 0 | ----+---- | 2 | 3 | --------- |
Arc mask
| Code Block |
|---|
Wedge 871 879 454 26 -174 186 1 k False False |
...
Involved sensors in the top part of the image in adopted cxif5315 geometry: 0, (1), 7, 8, (9), 15
Equatorial and arc combined mask
Radial background subtraction
For some reason polarization correction does not work well in this experiment for entire image.
Comparison of the 2-d interpolated radial background subtraction
- nbins (rad:500, phi:1)
- nbins (rad:500, phi:32)
SIngle angular bin still works fine in our ROI defined by both masks.
Comparison of the pfv2 with Cheetah list of peaks
Code for comparison: cxif5315/peak-list-comp-cheetah.py
Peak lists for comparison:
- peakfinder:
pfv2-cxif5315-r0169-2016-03-28T15:02:47.txt - cheetah: r0169-cheetah-peaks.txt - with unknown origin...
Comparison algorithm and conditions
Use pyimgalgos.TDFileContainer for both peakfinder and cheetah
| Code Block |
|---|
fc_ch = TDFileContainer(fncheet, indhdr='frameNumber', objtype=TDCheetahPeakRecord) # , pbits=256)
fc_pf = TDFileContainer(fnpeaks, indhdr='Evnum', objtype=TDPeakRecord) #, pbits=256) |
...
Masks for segments
Code below shows how to generate mask n-d arrays for particular set of segments (2x1s)
| Code Block |
|---|
shape_cspad = (32,185,388)
seg1 = np.ones((185,388))
mask_winds_all = np.zeros(shape_cspad, dtype=np.int16)
mask_winds_equ = np.zeros(shape_cspad, dtype=np.int16)
mask_winds_arc = np.zeros(shape_cspad, dtype=np.int16)
mask_winds_all[(0,1,7,8,9,15,16,17,23,24,25,31),:,:] = seg1
mask_winds_equ[(0,1,9,15,16,17,25,31),:,:] = seg1
mask_winds_arc[(0,7,8,15),:,:] = seg1 |
Only listed segments are highlighted on plots:
Background
Averaged background shape
Background shape evaluated in exp=cxif5315:run=162 with common mode correction - central segments got offset to higher intensity
Background shape evaluated evaluated in exp=cxif5315:run=162 without common mode correction - common mode offsets averaged out to zero and image represents true background shape.
Command to average data with options for processing algorithms:
| Code Block |
|---|
det_ndarr_average -d exp=cxif5315:run=162 -s CxiDs2.0:Cspad.0 -n 10000 -m 5000 -a 3 -f nda-bkgd -p -v |
skips 5000 and averages next 10000 events.
Deployed as: /reg/d/psdm/cxi/cxif5315/calib/CsPad::CalibV1/CxiDs2.0:Cspad.0/pixel_bkgd/95-end.data
Radial background subtraction
polarization correction factor map orientation should be consistent with geometry file - in cxif5315 it should be rotated by 90°.
| Code Block |
|---|
from pyimgalgos.RadialBkgd import RadialBkgd, polarization_factor
X, Y, Z = geo.get_pixel_coords()
rb = RadialBkgd(X, Y, mask, nradbins=500, nphibins=1)
pf = polarization_factor(rb.pixel_rad(), rb.pixel_phi()+90, 91.33e3)
# in event loop:
nda, title = rb.subtract_bkgd_interpol(arr * pf) * mask |
For example we apply this algorithm to the water background averaged sample from exp=cxif5315:run=162:
Radial background fails to work in the region of shadow, where image miss symmetry. This region can be removed by constraining the range of angles phiedges=(40, 325).
In the next plot the radial range is also constrained as radedges=(5000,100000) for the purpose of example:
| Code Block |
|---|
# the same as in previous case, but
rb = RadialBkgd(X, Y, mask, nradbins=500, nphibins=1, phiedges=(40, 325), radedges=(5000,100000)) |
SIngle angular bin still works fine in our ROI defined by both masks.
Background subtraction examples
Subtract background shape evaluated in run 192
| Code Block |
|---|
from pyimgalgos.GlobalUtils import subtract_bkgd
# once per run:
nda_peds = det.pedestals(runnum)
nda_bkgd = det.bkgd(runnum) # get n-d array with averaged background from calib/.../pixel_bkgd
nda_smask = det.mask(evt, calib=False, status=True, edges=True, central=True, unbond=True, unbondnbrs=True)
# windows for background normalization
winds_bkgd = [(s, 10, 100, 270, 370) for s in (4,12,20,28)] # use part of segments 4,12,20,28 to subtr bkg
# in the event loop
nda_raw = det.raw(evt |
...
Statistics for number of peaks:
- total in Cheetah: 14002
- matched: 10593
- not-matched: 3409
- fraction of matched: 0.757
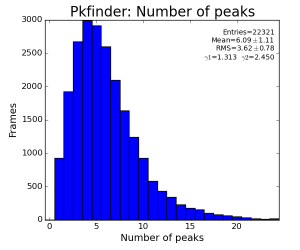
Plots for number of peaks in peak-finder, Cheetah, and number of non-matched:matched Cheetah peaks.
Peak-finder number of peaks accounts for arc region.
Peak finding
Try to work with versions > v1 of peak-finders:
Parameters:
| Code Block |
|---|
alg_arc = PyAlgos(windows=winds_arc, mask=mask_arc, pbits=2) alg_arc.set_peak_selection_pars(npix_min=4, npix_max=500, amax_thr=0, atot_thr=600, son_min=5) alg_equ = # all parameters are the same as for alg_arc #peaks_arc = alg_arc.peak_finder_v2(nda, thr=10, r0=6, dr=0.5) #peaks_equif nda_raw is not None : nda = alg_equ.peak_finder_v3 np.array(nda_raw, rankdtype=5np.float32, r0=6, dr=0.5) ??????????? finds too many peakscopy=True) nda -= nda_peds # Subtract background shape averaged for pure water peaks_arc nda = alg_arc.peak_finder_v4subtract_bkgd(nda, thrnda_low=10bkgd, thr_high=150mask=nda_smask, rank=5, r0=6, dr=0.5) |
...
winds=winds_bkgd) |
Radial background subtraction
Image corrected up to 80mm, rings span for entire phi
Image corrected up to 80mm, 40<phi< 320:
OLD IMAGE PROCESSING
Subtract background shape evaluated in run 192.
| Note |
|---|
Background shape was evaluated WITH common mode correction; central 2x1s got offset due to non-uniform water background shape. |
Averaged Fraser- transformed image using angles from fit to 2 arc peaks
Spectrum of intensities
Spectrum of intensities of all quad 2x1-segment 0 (close to beam) and 4 (water ring region)
before background subtraction
after background subtraction
- masked pixels contributes to peak at 0
- 1-, 2- and 3- photon peaks are seen
- common mode correction before background subtraction does not work well in this data sample due to significant fraction of 1-photon peak next to noise peak, which makes an offset due to illumination.
- common mode correction after background subtraction does not work - it moves noise peak to 0 and destroys background subtraction results.
| Note |
|---|
Potentially any non-dark data spectra can be used to calibrate pixel gain. |