Page History
...
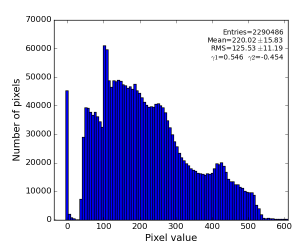
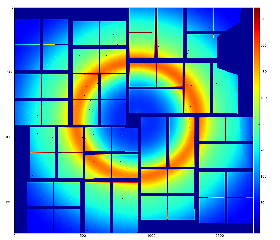
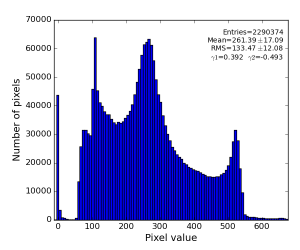
- averaged over all 14636 events calibrated (pedestal, common mode) data
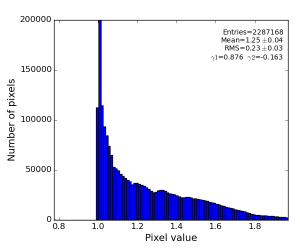
- polarization correction factor
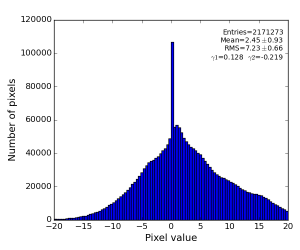
- polarization-corrected data
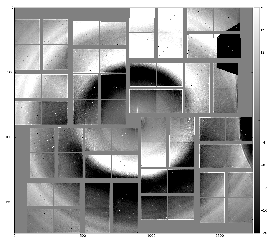
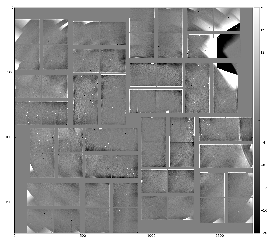
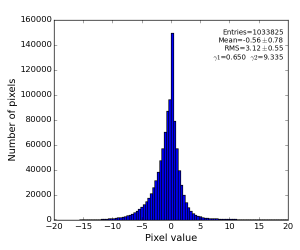
- radial-background subtracted data using single angular bin
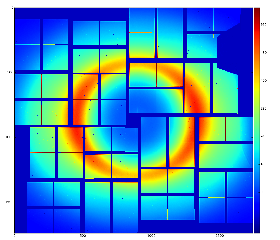
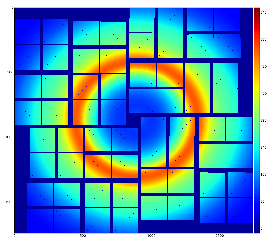
This image indicates on in-correct geometry; background center consistent with beam intersection does not coincide with detector origin (0,0). - radial-background subtracted data using 8 angular bins
dynamically apply some geometry correction
Code Block geo = GeometryAccess(fname_geo) geo.move_geo('CSPAD:V1', 0, 1600, 0, 0) geo.move_geo('QUAD:V1', 2, -100, 0, 0)and plot again radial-background subtracted data using single angular bin
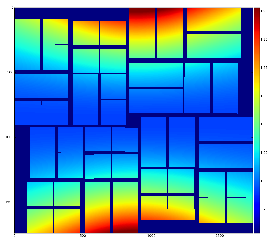
we get that "dish"-like shape disappears.Interpolation (linear) between centers of the background bins could also help:
Code Block bkgd = rb.bkgd_nda_interpol(nda, method='linear') # method='nearest' 'cubic' cdata = rb.subtract_interpol(nda, method='linear')Interpolation for entire detector and for part of the image:
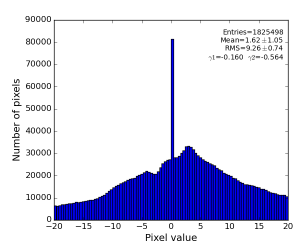
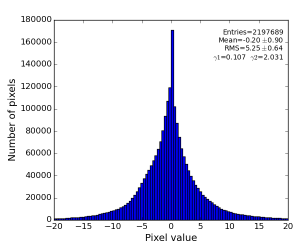
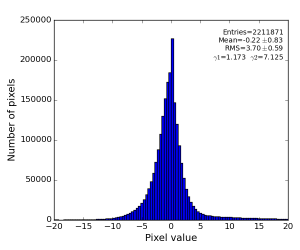
Image is not as impressive as for polarization-corrected sample, but the residual intensity spread shrink down to RMS~3 ADU.
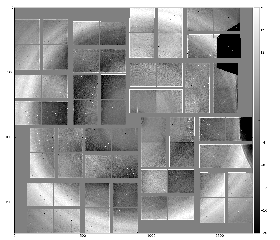
- Subtraction of single Single angular bin interpolated background, data from exp=cxij4915:run=25
and its subtraction from data:
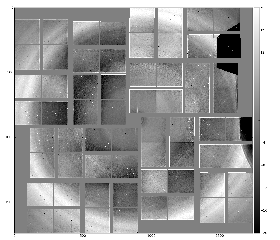
CSPAD "dopping" artifacts
...
Overview
Content Tools