Page History
...
| Code Block |
|---|
from pyimgalgos.RadialBkgd import RadialBkgd rb = RadialBkgd(xarr, yarr, mask=None, radedges=None, nradbins=100, phiedges=(0,360), nphibins=32) |
See parameters' description in Auto-generated documentation for class RadialBkgd.
Input n-d arrays can be obtained through the Detector (AreaDetector) interface or directly through the class working with geometre:
| Code Block |
|---|
from PSCalib.GeometryAccess import GeometryAccess
geo = GeometryAccess(fname_geo)
xarr, yarr, zarr = geo.get_pixel_coords()
iX, iY = geo.get_pixel_coord_indexes()
mask = geo.get_pixel_mask(mbits=0377) # mask for 2x1 edges, two central columns, and unbound pixels with their neighbours
... |
Algorithm
Intention
This algorithm is intended to subtract background from images with quasi-symmetric radial distribution of intensities.
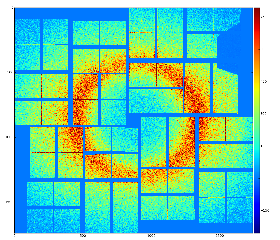
For example, pure water ring background from exp=cxij4716:run=22:
To evaluate background in data, n-d array of data is split for 2-d bins in polar coordinate frame, total intensity and number of involved pixels are counted for each bin and converted to the average bin intensity.
...
- For good statistical precision of the background averaging 2-d bins should contain large number of pixels. However large bins produces significant binning artifacts whech which are seen in resulting image.
- The main reason for angular bins is a variation of intensity with angle due to polarization effect. The beam polarization effect can be eliminated with appropriate correction.
Method for polarization correction factor:
Code Block collapse true def polarization_factor(rad, phi_deg, z) : """Returns per-pixel polarization factors, assuming that detector is perpendicular to Z. """ phi = np.deg2rad(phi_deg) ones = np.ones_like(rad) theta = np.arctan2(rad, z) pol = 1 - np.sqrt(np.fabs(np.sin(theta)*np.cos(phi))) return divide_protected(ones, pol, vsub_zero=0)
Then, radial background can be estimated for a single angular bins (ring-shaped radial bins):
| Code Block |
|---|
pf = polarization_factor(rb.pixel_rad(), rb.pixel_phi(), z) res = rb.subtract_bkgd(nda * pf) |
...
Effect of polarization is somehow accounted, but most likely the sample-to-detector distance 1m is not correct.
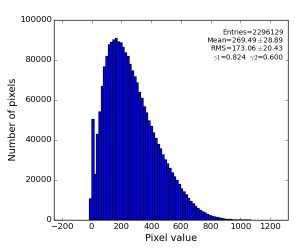
The data set exp=cxij4716:run=22 was collected at sample-to-detector distance z=94mm. In this case polarization correction formula gives distribution for correction factor and "corrected" data averaged over all 14636 events:
So, it looks like polarization correction formula is wrong
CSPAD "dopping" artifacts
...