This page is about n-d array processing algorithms coded in ImgAlgos.PyAlgos. Algorithms are implemented on C++ and also have python callable interface using boost/python wrapper. All examples are shown for python level interface.
import psana from ImgAlgos.PyAlgos import PyAlgos # create object: alg = PyAlgos(windows=winds, mask=mask, pbits=0) # where pbits - is a print info control bit-word: # pbits = 0 - print nothing # + 1 - main results, list of peaks # + 2 - input parameters, index matrix of pixels for S/N algorithm # + 128 - tracking and all details in class PyAlgos.py # + 256 - tracking and all details in class AlgArrProc # + 512 - tracking and all details in class AlgImgProc # set peak-selector parameters: alg.set_peak_selection_pars(npix_min=5, npix_max=5000, amax_thr=0, atot_thr=0, son_min=10) |
Region Of Interest (ROI)is defined by the set of rectangular windows on segments and mask, as shown in example below.
# List of windows
winds = None # entire size of all segments will be used for peak finding
winds = (( 0, 0, 185, 0, 388),
( 1, 20,160, 30,300),
( 7, 0, 185, 0, 388))
# Mask
mask = None # (default) all pixels in windows will be used for peak finding
mask = det.mask() # see class Detector.PyDetector
mask = np.loadtxt(fname_mask) #
mask.shape = <should be the same as shape of data n-d array> |
When peak is found, its parameters can be precised for background level, noise rms, and signal over background ratio (S/N) can be estimated. All these values can be evaluated using pixels surrounding the peak on some distance. For all peak-finders we use the same algorithm. Surrounding pixels are defined by the ring with internal radial parameter r0 and ring width dr (both in pixels). The number of surrounding pixels depends on r0 and dr parameters as shown in matrices below. We use notation
r0=3 dr=0.1 (4 pixels) r0=3 dr=0.5 (12 pixels) r0=3 dr=1 (24 pixels) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 + 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 + 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 + 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 r0=4 dr=0.2 (12 pixels) r0=4 dr=0.3 (16 pixels) r0=4 dr=0.5 (24 pixels) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
r0=5 dr=0.05 (12 pixels) r0=5 dr=0.5 (28 pixels) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 r0=6 dr=0.2 (12 pixels) r0=6 dr=0.5 (28 pixels) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 + 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
Hit finders return simple values for decision on event selection. Two algorithms are implemented in ImgAlgos.PyAlgos. They count number of pixels and intensity above threshold in the Region Of Interest (ROI) defined by windows and mask parameters in object constructor.
npix = alg.number_of_pix_above_thr(data, thr=10) |
intensity = alg.intensity_of_pix_above_thr(data, thr=12) |
two-threshold peak-finding algorithm in restricted region around pixel with maximal intensity.
peaks = alg.peak_finder_v1(nda, thr_low=10, thr_high=150, radius=5, dr=0.05) |
define peaks for regoins of connected pixels above threshold
peaks = alg.peak_finder_v2(nda, thr=10, r0=5, dr=0.05) |
define peaks in local maximums of specified rank (radius), for example rank=2 means 5x5 pixel region around central pixel.
peaks = alg.peak_finder_v3(nda, rank=2, r0=5, dr=0.05) |
r0(ex.=5.0), dr(ex.=0.05) evaluates background level, rms of noise, and S/N for the pixel with maximal intensity.set_peak_selection_pars, for examplealg.set_peak_selection_pars(npix_min=5, npix_max=500, amax_thr=0, atot_thr=1000, son_min=6) |
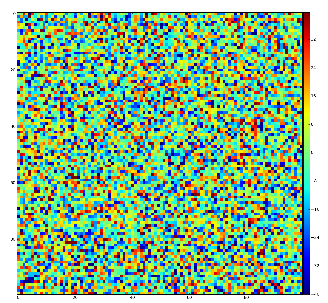
Test for 100x100 image with random normal distribution of intensities
Example of the map of local maximums found for rank from 1 to 5:
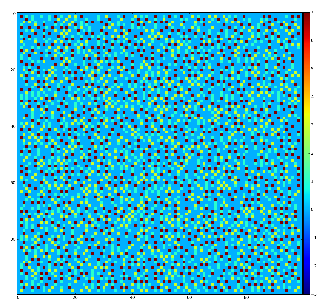
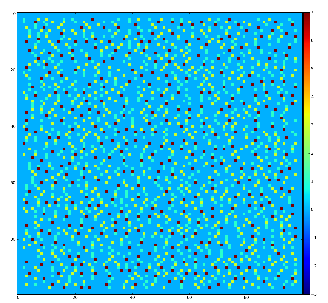
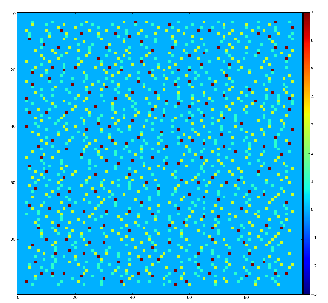
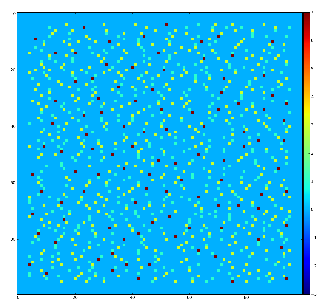
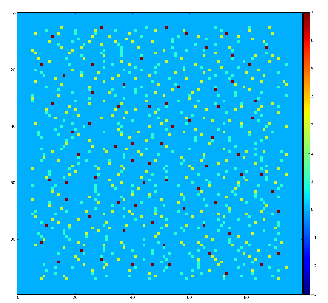
color coding of pixels:
Table for rank, associated 2-d region size, fraction of pixels recognized as local maximums for rank, and time consumption for this algorithm.
| rank | 2-d region | fraction | time, ms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3x3 | 0.1062 | 5.4 |
| 2 | 5x5 | 0.0372 | 5.2 |
| 3 | 7x7 | 0.0179 | 5.1 |
| 4 | 9x9 | 0.0104 | 5.2 |
| 5 | 11x11 | 0.0066 | 5.2 |