...
We want to compare the various methods of geolocation using ping RTT measurements to estimate the distance between landmarks and targets. The landmarks are at known lat/longs and the min RTT from the three (Tri-Lateration) or more closest landmarks to the target are used. From each min RTTs the distance to the target is estimated as distance (km) = alpha * minRTT(ms) * 100 (km/ms). In these tests we use each of the other landmarks (at known locations) one at a time as targets (si we know the location of the targets also). Comparing the actual location of the target and the estimated location we were able to calculate the error as the distance between these two values. There is a spreadsheet with more details.
Constraint Based Geolocation (CBG) using Tri-lateration vs Tri-Lateration with no constraints
...
It is seen that Trilateration with no constraints has a median value of ~ 412km, while CBG with Tri-lateration is closer to 250km.
...
Comp. The rearison with the Apollonius Geolocation Algorithm
We also evaluated the performance of the Apollonius geolocation algorithm that uses tangential circles rather than the intersecting circles of tri-lateration. In this case we had successes with 105 targets. The frequency and cumulative distributions are seen in Figure 1. It is seen that Apollonius performs similarly to Tri-lateration with a median error of about 449ms.
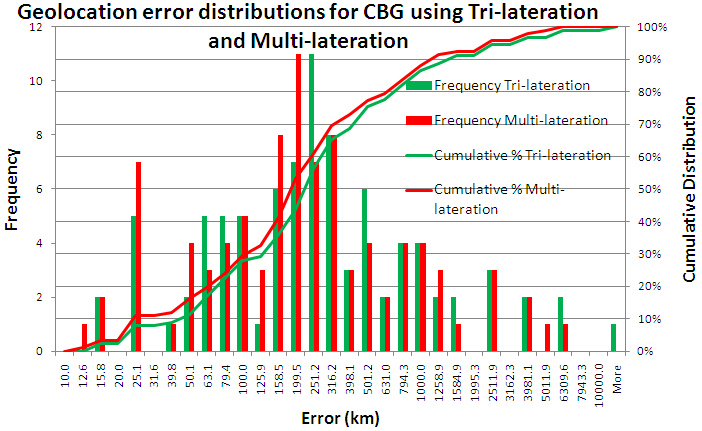
Comparison of CBG with Multi-lateration and Tri-lateration
We then compared our modified CBG using tri-lateration with CBG using Multi-lateration. The distributions are shown below, and more details are in the spreadsheet.
It is seen that the two dsitributions are very similar with multi-lateration having a smaller median error. It also has a higher success rate (see the table below).
Metric | CBG with Multi-lateration | CBG with tri-lateration | Trilateration | Apollonius | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
% success rate | 92% | 91% | 44% | 63% | ||
Median | 190km | 250km | 413km | 449km |
| |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|