...
| Host | Lat | Long | Great Circle distance from SLAC | Min RTT (as constrained by speed of light in fibre) | Directivity based on measured min RTT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pinger.slac.stanford.edu | 37.4190 N | 122.2085 W | 0 km | 0.0003 ms | 0.001 |
| pinger-raspberry.slac.stanford.edu | 37.4190 N | 122.2085 W | 0 km | 0.0003 ms | 0.001 |
| sitka.triumf.ca | 49.2475 N | 123.2308 W | 1319.6 km | 13.196 ms | 0.6 |
| ping.cern.ch | 46.23 N | 6.07 E | 9390.6 km | 93.90 ms | 0.63 |
...
Requirement
Two major points need to be addressed before we can comfortably deploy Raspberry PI MAs.
...
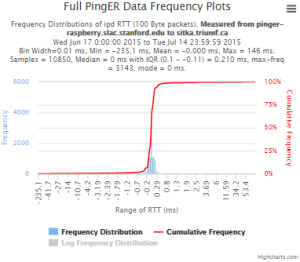
The following plots are the raw metric data from the MA measurements from which we have to craft our text (with some plot examples).
Measurements
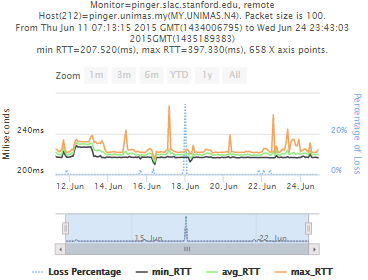
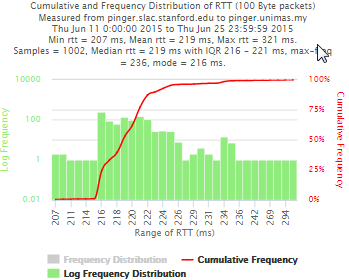
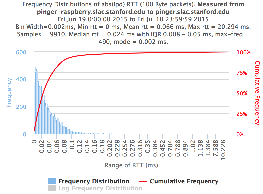
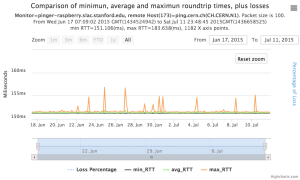
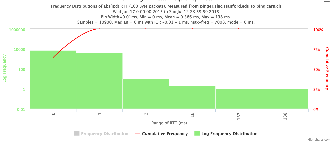
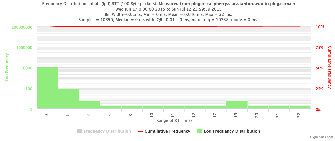
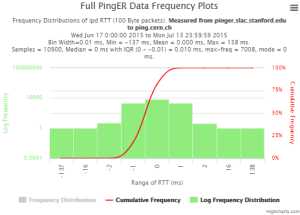
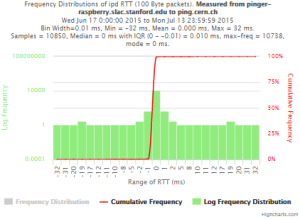
Example target = pinger.unimas.my (~220 msec.)
For both 100Byte and 1000 Byte pings (not shown above) the round trip time series for RTTs have similar behaviour and there are similar losses 7:10 (pinger : pinger-raspberry for 100 Byte pings), note the different Y scales for losses. The losses are about double for 1000Byte pings.
| Time Series | Frequency Distributions |
|---|---|
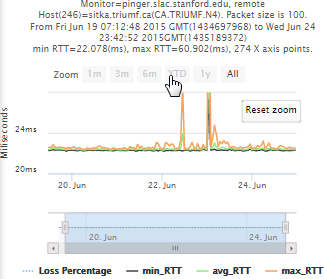
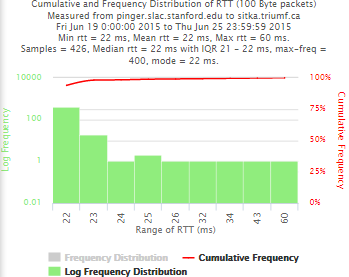
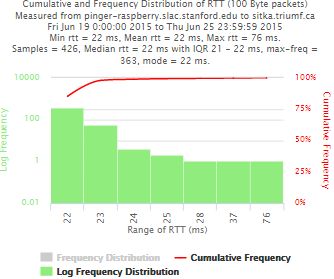
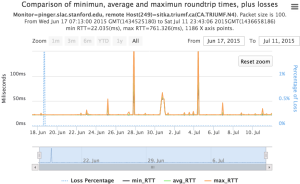
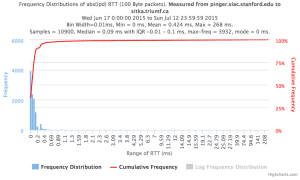
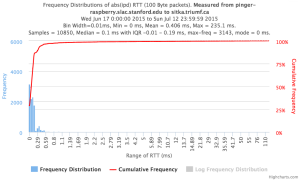
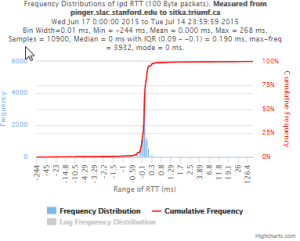
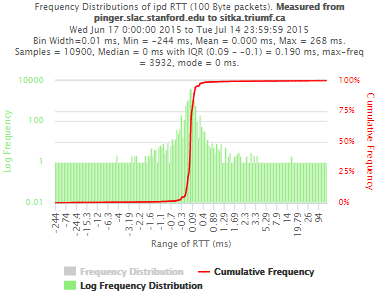
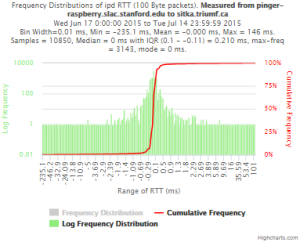
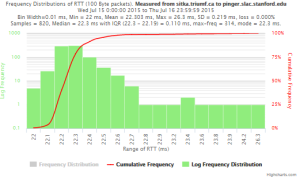
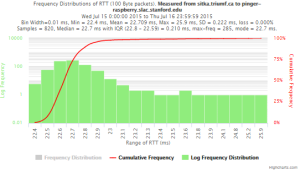
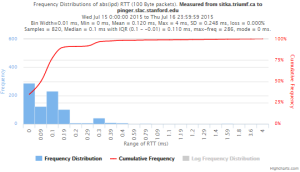
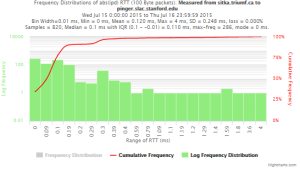
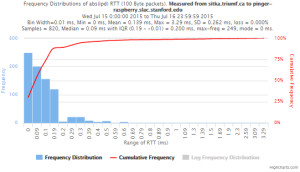
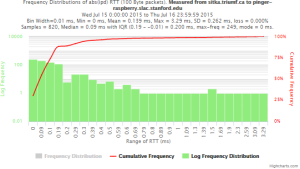
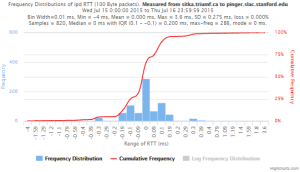
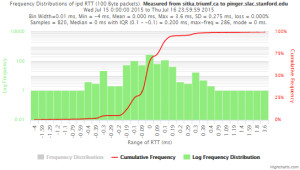
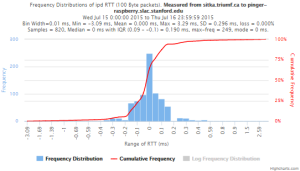
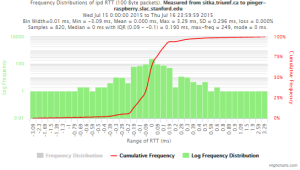
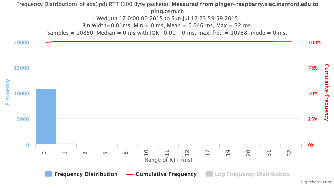
Example target sitka.triumf.ca (~22msec.)
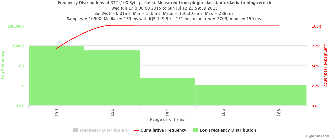
For 100Byte the round trip time series for RTTs did not have similar behaviour. We noticed a great change mainly in the maximum round trip time. The average minimum RTT did not change that much. Another point about pinger-raspberry is that it increases significantly the RTT for near nodes (about ~1ms). The difference is greater than if we compare a node which is in a long distance.
| Time series | Frequency distributions |
|---|---|
...
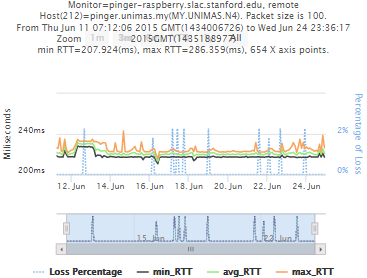
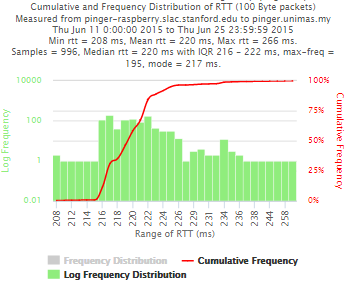
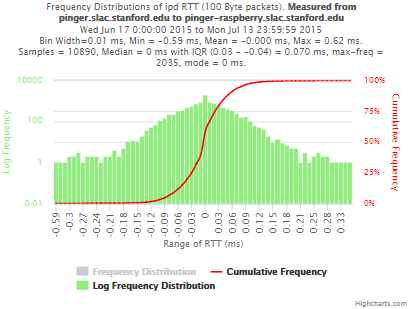
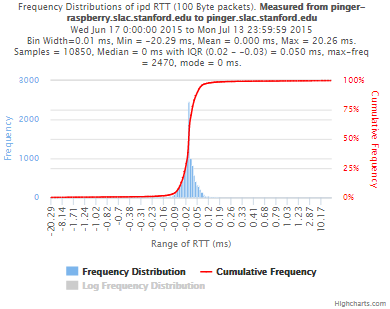
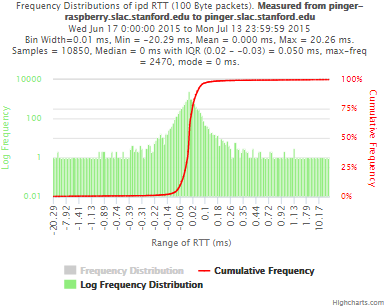
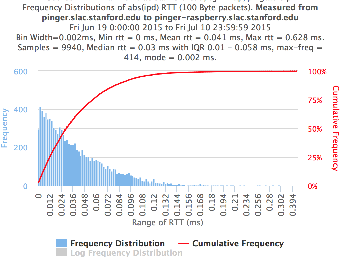
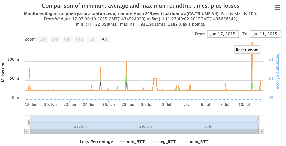
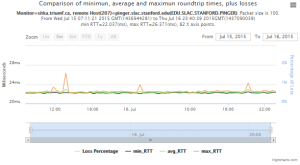
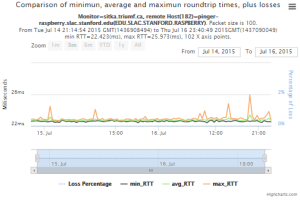
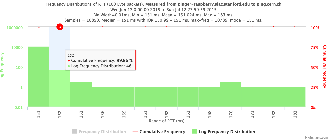
pinger.slac.stanford.edu and pinger-raspberry.slac.stanford.edu
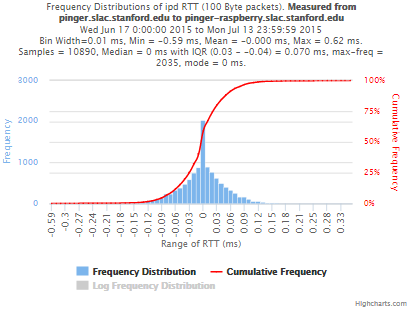
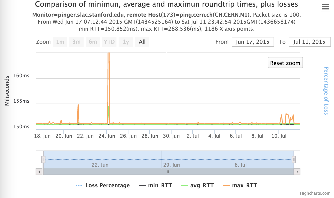
Now, we compared the RTT between pinger and pinger-raspberry. They are located in the same network and the RTT should be very small. However, as noticed before pinger-raspberry has a greater maximum RTT than pinger. The average RTT also has some difference, but now as much as the maximum time has. Note that the second graph represents the third graph using the same scale as the first (pinger graph).
...
| pinger to pinger-raspberry | pinger-raspberry to pinger | |
|---|---|---|
| IPD | ||
| Abs(IPD) |
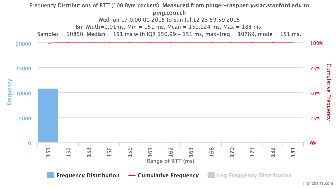
To sitka.triumf.ca from SLAC
| pinger.slac.stanford.edu to sitka.triumf.ca | pinger-raspberry.slac.stanford.edu to sitka.triumf.ca | |
|---|---|---|
| Time Series | ||
| Frequency distribution RTT | ||
| Frequency distribution Abs(IPD) | ||
| Frequency distribution IPD |
From sitka.triumf.ca to SLAC
| sitka.triumf.ca to pinger.slac.stanford.edu | sitka.triumf.ca to pinger-raspberry.slac.stanford.edu | |
|---|---|---|
| Time series | ||
| Frequency Distribution of RTT | ||
| Frequency distribution of Abs(IPD) | ||
| Frequency distribution of IPD |
To
...
sitka.triumf.ca from SLAC
| To ping.cern.ch from pinger | To ping.cern.ch from pinger-raspberry | |
|---|---|---|
| Time series | ||
| Frequency Distribution RTT |
| |
Frequency Distribution Abs(IPD) | ||
| Frequency Distribution IPD |
...
Source: http://www.real-statistics.com/non-parametric-tests/two-sample-kolmogorov-smirnov-test/
Futures
Extension to Android systems
Topher: Here is where we would like you to say something about the potential Android opportunity.
Installation process
The installation procedures for a PingER MA are relatively simple, but do require a Unix knowledgeable person to do the install and it typically takes a couple hours and may require a few corrections pointed out by the central PingER admin. It is possible to pre-configure the Raspberry Pi at the central site and ship it pre-configured to the MA site. However that requires funding the central site Raspberry Pi acquisitions, may raise issues of on-going commitment, and may not be acceptable for the Cyber security folks at the MA site. We are looking at simplifying the install process, possibly by creating an ISO Image
Robustness and Reliability
This still needs to be demonstrated in the field. We also need to more fully understand the solar power requirements.