1. Overview
This page describes the circle selection algorithm while calculating results from the Apollonius (AP) method. Details of the AP method can be found here.
2. Objective
The AP method provides multiple results (in the form of a solution set) when calculating the target location using RTT measurements from landmarks. At the moment we manually select the most appropriate result (by comparing the results with geo-ip lat and log records).
...
Explanation of the tests:
Two methods were used to optimize the Apollonius AP results:
1) In the first method (the "manual method") , we used all the circles and then one circle with giving closer results relative to Geo IP was considered to be Apollonius the AP circle.
2) In second method (the "cluster method"), we tried to find out which cluster of circles and for this following approach was used:
1) three circles out of the n (<= 8) circles is closest together. This cluster was determined as follows:
- Let's suppose, we obtained n circles using
...
- AP. Now, we took each of these n circles (where j = 1 .. n) and for each
...
- circle we calculated the distance
...
- s i (where i = 1.. n-1) between it's center and the center of all other n-1 circles and summed it.
...
- We refer to this sum as: Sum
...
- (s i ) (where i = 1.. n-1). Then we took average of this value, i.e. avg j = Sum(s i ) / n j .
In this way we calculated the average distance value for each of circle and finally one circle with the smallest average value was considered as Apollonius the AP circle.
For results please see the attachments.
Conclusion:
The cluster based approach takes one circle as the AP circle and the final coordinates are calculated on the basis of this circle. The manual approach of using all the circles for calculating latitude and longitude, uses all the circles, so the cluster approach can theoretically (if the Geo IP result is correct) perform equal to the manual approach only in the best case scenario.
However, the main advantage of the cluster based approach is that it does not rely on an a-priori knowledge of the location of the target from Geo IP and instead uses a proper mathematical scheme to select the apollonius circles.
In some cases, however, the cluster approach is performing better than the manual approach. This appears to negate the fact that the manual approach chooses the circle with the minimum error distance. So how can this be? then can the how this could be minimum then 'minimum error distance circle' its because landmarks keep on changing due to which clusters keep on changing so minimum error distance circles keep on changing.
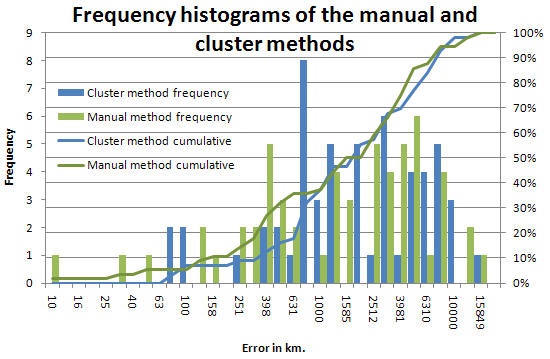
A comparison of the accuracies yielded by the two methods as applied to 74 targets in 46 countries is seen below (also see the spreadsheet ):
It is seen that there is little difference with the manual method in general being slightly better.
Reference
Apollonius and its PerformanceTODO:
Add description page of Apollonius
Add page describing landmark selection method.