Examples of effectiveness of mobile phone and computing
...
- Rent a car check in at the curb
- Real time Bus schedules for students
- Push button access to nurse practitioners
Wireless
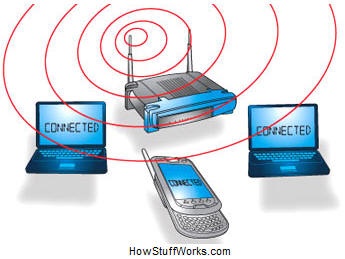
- Need a wireless router This is a single unit that contains:
- A port to connect to your cable or DSL modem
- A router
- An Ethernet hub to connect wired computers to
- A firewall for security
- A wireless access point for wireless computers
- How it works:
- Basically a 2 way radio
- A computer's wireless adapter translates data into a radio signal and transmits it using an antenna.
- A wireless router receives the signal and decodes it. The router sends the information to the Internet using a physical, wired Ethernet connection.
- May provide power to the access point via Ethernet cable
- In the home typically sends the data to the Internet via a DSL or cable connection
- Frequencies
- 2.4Hz & 5GHz unlicensed RF spectrum ( so may interfere with uwave, cordless phones, video controllers etc).
- Protocols
- WiFi 802.11a (55MHz, 5GHz, OFDM), b (11Mbps, 2.4Ghz, CCK), g (55Mbps (typical 24Mbps, 2.4GHz, , OFDM), n reliability, performance, security, ubiquity (starting to
- appear on airlines, Virgin trains in UK)
- Each frequency has 3 bands to reduce interference
- 2.4Hz & 5GHz unlicensed RF spectrum ( so may interfere with uwave, cordless phones, video controllers etc).
- 802.11n (published Oct 29, 2009) throughput increase by using 4 antennas increase max data rate 54Mbps to 600Mbps.8 times per radio, WiFi connect rates increase nearly 6 times
- A port to connect to your cable or DSL modem
- A router
- An Ethernet hub to connect wired computers to
- A firewall for security
- A wireless access point for wireless computers
- Reliability vs wired
- RF obstacles like walls, heavy channel utilization, poor RF network design, bad client drivers, difficulty of management
- Requires multiprong approach resilient architecture with no single point of failure, mesh support, power adjustments and automatic channel changing to cover gaps if AP goes offline, automatic backup cellphone link
- Mesh networks of clients discover each other, connect securely (WiFi Direct standard) in ad hoc networks. As long as carriers allow it, they will also be able to serve as hubs for small local networks, linking several devices via Wi-Fi and letting them share the phone's 3G or 4G Internet connection.
- 802.16m will be significantly faster than its predecessor. WiMAX Forum Vice President Mohammad Shakouri has said the goal is for the new WiMAX standard to deliver average downlink speeds of more than 100Mbps to users. In contrast, Sprint's initial Xohm WiMAX offering, which debuted commercially in 2008, delivered downlink speeds ranging between 3.7M to 5Mbps. But while 802.16m will give WiMAX a major speed boost, don't expect it to propagate any further than the current WiMAX technology that covers around 31 square miles per access point.
...
- Not considering cordless phones, CB radios, pagers, car phones etc.
- Iridium: catastrophes (Haiti), hard to reach places: expeditions, Arctic …
- ATT Terrestar hybrid cell & satellite switches to satellite when out of range, covers US, looks like Blackberry, not cheap $799 + $5/month on top of regular voice & data. Calls are $0.65/min. See http://www.pcworld.com/article/172944/terrestar_satellite_phone_coming_to_atandt.html
- Laptops, netbooks (OLPC), smartbooks (kindle,iPADs), Cell phone and smartphones
Cell phones
- See presentation** How they work
- History
- Cell phone components
- Power
- Carriers
- Coverage
- Bars
- Growth
- Concerns
...