...
- Emergencies, reporting fires, accidents
- keeping in touch
- Given to victims of domestic violence
- market prices, weather, crop information
Mobile computing (in future any micro-processor will have a wireless access):
- Rent a car check in at the curb
- Real time Bus schedules for students
- Push button access to nurse practitioners
Wireless
- WiFi 802.11a, b, g, n (reliability, performance, security, ubiquity (starting to appear on airlines)
- 802.11n throughput increase 8 times per radio, WiFi connect rates increase nearly 6 times
- Reliability vs wired
- RF obstacles like walls, heavy channel utilization, poor RF network design, bad client drivers, difficulty of management
- WiFi relies on shared access RF medium in unlicensed spactra prone to interference (cordless phones, video controllers ...).
- Requires multiprong approach resilient architecture with no single point of failure, mesh support, power adjustments and automatic channel changing to cover gaps if AP goes offline, automatic backup cellphone link
- Mesh networks of clients discover each other, connect securely (WiFi Direct standard) in ad hoc networks. As long as carriers allow it, they will also be able to serve as hubs for small local networks, linking several devices via Wi-Fi and letting them share the phone's 3G or 4G Internet connection.
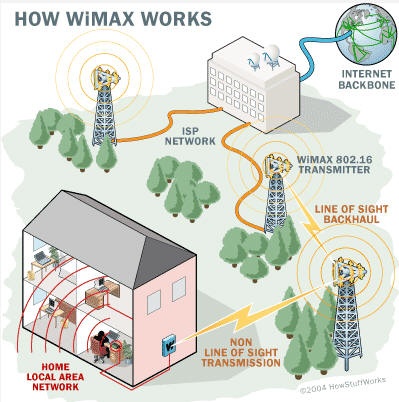
- 802.16m will be significantly faster than its predecessor. WiMAX Forum Vice President Mohammad Shakouri has said the goal is for the new WiMAX standard to deliver average downlink speeds of more than 100Mbps to users. In contrast, Sprint's initial Xohm WiMAX offering, which debuted commercially in 2008, delivered downlink speeds ranging between 3.7M to 5Mbps. But while 802.16m will give WiMAX a major speed boost, don't expect it to propagate any further than the current WiMAX technology that covers around 31 square miles per access point.
Integration with phones
The number of phones shipped with Wi-Fi jumped to 139.3 million in 2009, up from 92.5 million in 2008, ABI's research indicates that annual shipping number will surpass 500 million units by 2014, when 90 percent of all smartphones will have the technology. At least one phone with 11n – Samsung's Wave – has been announced. An 11n network is also more efficient, so the phone will expend less energy communicating http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/032310-wi-fi-spreading-fast-among.html
Other Mobile devices
- Not considering cordless phones, CB radios, pagers, car phones etc.
- Iridium: catastrophes (Haiti), hard to reach places: expeditions, Arctic …
- ATT Terrestar hybrid cell & satellite switches to satellite when out of range, covers US, looks like Blackberry, not cheap $799 + $5/month on top of regular voice & data. Calls are $0.65/min. See http://www.pcworld.com/article/172944/terrestar_satellite_phone_coming_to_atandt.html
- Laptops, netbooks (OLPC), smartbooks (kindle,iPADs), Cell phone and smartphones
Cell phones
- See presentation** How they work
- History
- Cell phone components
- Power
- Carriers
- Coverage
- Bars
- Growth
- Concerns
Smartphones
(see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smartphone)
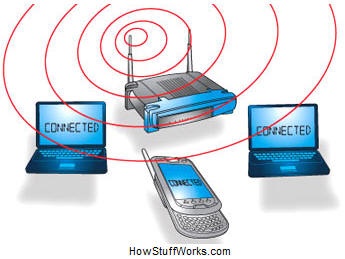
- Need a wireless router This is a single unit that contains:
- A port to connect to your cable or DSL modem
- A router
- An Ethernet hub to connect wired computers to
- A firewall for security
- A wireless access point for wireless computers
- How it works:
- Basically a 2 way radio
- A computer's wireless adapter translates data into a radio signal and transmits it using an antenna.
- A wireless router receives the signal and decodes it. The router sends the information to the Internet using a physical, wired Ethernet connection.
- May provide power to the access point via Ethernet cable
- In the home typically sends the data to the Internet via a DSL or cable connection
- Frequencies
- 2.4Hz & 5GHz unlicensed RF spectrum ( so may interfere with uwave, cordless phones, video controllers etc).
- Protocols
- WiFi 802.11a (55MHz, 5GHz, OFDM), b (11Mbps, 2.4Ghz, CCK), g (55Mbps (typical 24Mbps, 2.4GHz, , OFDM), n reliability, performance, security, ubiquity (starting to appear on airlines, Virgin trains in UK)
- Each frequency has 3 bands to reduce interference
- 802.11n (published Oct 29, 2009) throughput increase by using 4 antennas increase max data rate 54Mbps to 600Mbps.8 times per radio, WiFi connect rates increase nearly 6 times
- WiFi 802.11a (55MHz, 5GHz, OFDM), b (11Mbps, 2.4Ghz, CCK), g (55Mbps (typical 24Mbps, 2.4GHz, , OFDM), n reliability, performance, security, ubiquity (starting to appear on airlines, Virgin trains in UK)
- Reliability vs wired
- RF obstacles like walls, heavy channel utilization, poor RF network design, bad client drivers, difficulty of management
- Requires multiprong approach resilient architecture with no single point of failure, mesh support, power adjustments and automatic channel changing to cover gaps if AP goes offline, automatic backup cellphone link
- Mesh networks of clients discover each other, connect securely (WiFi Direct standard) in ad hoc networks. As long as carriers allow it, they will also be able to serve as hubs for small local networks, linking several devices via Wi-Fi and letting them share the phone's 3G or 4G Internet connection.
- 802.16m will be significantly faster than its predecessor. WiMAX Forum Vice President Mohammad Shakouri has said the goal is for the new WiMAX standard to deliver average downlink speeds of more than 100Mbps to users. In contrast, Sprint's initial Xohm WiMAX offering, which debuted commercially in 2008, delivered downlink speeds ranging between 3.7M to 5Mbps. But while 802.16m will give WiMAX a major speed boost, don't expect it to propagate any further than the current WiMAX technology that covers around 31 square miles per access point.
Integration with phones
The number of phones shipped with Wi-Fi jumped to 139.3 million in 2009, up from 92.5 million in 2008, ABI's research indicates that annual shipping number will surpass 500 million units by 2014, when 90 percent of all smartphones will have the technology. At least one phone with 11n – Samsung's Wave – has been announced. An 11n network is also more efficient, so the phone will expend less energy communicating http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/032310-wi-fi-spreading-fast-among.html
Other Mobile devices
- Not considering cordless phones, CB radios, pagers, car phones etc.
- Iridium: catastrophes (Haiti), hard to reach places: expeditions, Arctic …
- ATT Terrestar hybrid cell & satellite switches to satellite when out of range, covers US, looks like Blackberry, not cheap $799 + $5/month on top of regular voice & data. Calls are $0.65/min. See http://www.pcworld.com/article/172944/terrestar_satellite_phone_coming_to_atandt.html
- Laptops, netbooks (OLPC), smartbooks (kindle,iPADs), Cell phone and smartphones
Cell phones
- See presentation** How they work
- History
- Cell phone components
- Power
- Carriers
- Coverage
- Bars
- Growth
- Concerns
Smartphones
(see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smartphone)
- First production cell phone with Internet access introduced in late 1990's by Nokia (see http://xml.coverpages.org/nokiaWAP9902.html)
- Major players: Blackberry (RIM ran into state security issues in Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, UAE), Nokia, Ericsson, Palm, Android (Google), iPhone (Apple), Microsoft
- Android was in fourth place during the first three months of 2010, trailing the Research In Motion (RIM) and Apple smartphone OSes by a margin of about 5 million and 3 million, according to market research company Gartner, which tracks the number of smartphones sold to end users. However, since then sales have picked up significantly. In February, Google said 60,000 Android phones were sold per day and in June that number had gone up to 160,000, according to Google. Today, 200,000 Android-based smartphones are sold every day, Google CEO Eric Schmidt said on 8/4/2010 (see http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9180197/Android_growing
- First production cell phone with Internet access introduced in late 1990's by Nokia (see http://xml.coverpages.org/nokiaWAP9902.html)
- Major players: Blackberry (RIM ran into state security issues in Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, UAE), Nokia, Ericsson, Palm, Android (Google), iPhone (Apple), Microsoft
- Android was in fourth place during the first three months of 2010, trailing the Research In Motion (RIM) and Apple smartphone OSes by a margin of about 5 million and 3 million, according to market research company Gartner, which tracks the number of smartphones sold to end users. However, since then sales have picked up significantly. In February, Google said 60,000 Android phones were sold per day and in June that number had gone up to 160,000, according to Google. Today, 200,000 Android-based smartphones are sold every day, Google CEO Eric Schmidt said on 8/4/2010 (see http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9180197/Android_growing_much_faster_than_expected_say_analysts?source=CTWNLE_nlt_pm_2010-08-05).
- According to Nielsen's most recent tally (as reported in SJ Mercury 8/8/2010) US subscribers: Blackberry 35%, iPhone 28%, Android 13%.
- Smartphones not only lucrative in themselves they are also gateways to apps and services markets
- Handsets evolving, adding email, larger screens, touch screens, qwerty keyboards, integrating cameras, voice recognitions (see http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/080410-windows-phone-7-to-excel.html?source=NWWNLE_nlt_daily_pm_2010-08-05), line between smartphone and mobile phone is merging
- 247B emails/day, 1.4 unique email users worldwide, enormous market for mobile email
...
- Futures:
- Mobile Payments: Mobile network operators, often in partnership with banks, card issuers and mobile payment service providers, are fast developing platforms and applications to offer mobile payment services, and with such initiatives in place, the mobile payments segment has established itself in several advanced mobile markets worldwide and is now also expanding its reach in emerging markets. The worldwide mobile payments volume – denoting the face value of purchases and transactions through mobile handsets – stood at USD 68.7 billion in 2009, up from USD 45.6 billion in 2008, and is set to surge nine-fold to reach USD 633.4 billion by end-2014.
In 2009, there were 81.3 million mobile payment users worldwide and this number is forecast to grow over six-fold to reach nearly 490 million by the end of 2014, seeing the worldwide penetration of mobile payment users increasing over four-fold to reach almost 8 percent by end-2014. From simple SMS-based services to advanced bar-coded tickets and beyond, mobile payment services have come a long way and yet still remain in a relatively nascent stage compared to other mobile services.
According to GSMA there will be 1.7M phone users by end 2012 who do not possess a formal bank account.
The worldwide mobile payments market, including purchases of digital and physical goods, money transfers and NFC transactions, will grow from $170bn in 2010 to almost $630bn in 2014 according to Juniper Research. - Location Based Services (LBS) is on the rise, and with iSuppli's recent forecast that 79.9% of Smartphones shipped by Q4 2011 will be GPS enabled it seems mass adoption is not far away.
- In US AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile teaming up with Discover Card and Barclays Bank to test system at stores in Atlanta & 3 other cities to let consumer pay with the contactless wave of a smartphone, thus replacing credit cards (1B in US consumer wallets). SJ Mercury Aug 3, 2010. Security (see later)
- Medical
- Mobile health, or what the industry is calling mHealth or m-health, is a term used for the practice of medical and public health, supported by mobile devices. The term is most commonly used in reference to using mobile communication devices, such as mobile phones and PDAs, for health services and information.* The Mobilizing for Healthsm grant program will fund U.S. based pilot research projects and ongoing studies in need of additional funding focused on mobile phone-based interventions for low-income patients with chronic diseases, with an immediate interest in diabetes management over the next two years. * *Source: mHealth definition from Wikipedia.org, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MHealth
- New apps to determine drug doses based on weight, the size of endotracheal tube inserted down throat to help breathing (PediStat); learn about rare conditions (Eponyms) also use Wikipedia; to determine drug interactions (Epocrates); learn about drug trials (Drug Trials); breaking medical news; teaching tools You have a whole medical library in the palm of your hand, 70% doctors use mobile phone 80% say it is essentials (the new stethoscope?)
- New sensory interfaces: accelerometers, biometric sensors (fingerprints), magnetometers (digital compasses), GPS, gyroscopes, haptics, pico projectors, pressure sensors
- Some key applications: augmented reality, gaming and navigation
- ARCchart estimates combined shipments of these components will grow from 653 million units in 2009 to 4 billion by 2014. In terms of market value, we estimate that the revenue generated from the sale of these hardware sensors and sensory interfaces will more than triple by 2014, reaching $3.6 billion.
- Medical
- Mobile health, or what the industry is calling mHealth or m-health, is a term used for the practice of medical and public health, supported by mobile devices. The term is most commonly used in reference to using mobile communication devices, such as mobile phones and PDAs, for health services and information.* The Mobilizing for Healthsm grant program will fund U.S. based pilot research projects and ongoing studies in need of additional funding focused on mobile phone-based interventions for low-income patients with chronic diseases, with an immediate interest in diabetes management over the next two years. * *Source: mHealth definition from Wikipedia.org, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MHealth
- New apps to determine drug doses based on weight, the size of endotracheal tube inserted down throat to help breathing (PediStat); learn about rare conditions (Eponyms) also use Wikipedia; to determine drug interactions (Epocrates); learn about drug trials (Drug Trials); breaking medical news; teaching tools You have a whole medical library in the palm of your hand, 70% doctors use mobile phone 80% say it is essentials (the new stethoscope?)
- Mobile Payments: Mobile network operators, often in partnership with banks, card issuers and mobile payment service providers, are fast developing platforms and applications to offer mobile payment services, and with such initiatives in place, the mobile payments segment has established itself in several advanced mobile markets worldwide and is now also expanding its reach in emerging markets. The worldwide mobile payments volume – denoting the face value of purchases and transactions through mobile handsets – stood at USD 68.7 billion in 2009, up from USD 45.6 billion in 2008, and is set to surge nine-fold to reach USD 633.4 billion by end-2014.
- Concerns
- cell phones & cancer link inconclusive (see http://www.iarc.fr/, San Francisco requires emission disclosure on mobile handsets, main source of RF is produced by antenna, closer to head higher the exposure, no scientific concensus on link to cancer, lots of studies (e.g. WHO) measured metric is Specific absorption rate (SAR), < 1.6 watts/kg of body weight considered safe by FCC. Manufactured phones vary from 0.1 to 1.59 w/kg (see http://reviews.cnet.com/cell-phone-radiation-levels/)
- Tower emission
- Emergency services (911, 999, 112 etc.) mobility adds another level of complexity
- Use while driving etc.,
- Security:
- today’s high end smartphones are 1GHz or higher, have up to 32GB store, and with 4G will have 3Gbps connection speeds. Expect to see a growth in malware and spyware. Handheld technology is being driven by the consumer world, not the enterprise. Further IT departments not ready to support the new OS’, yet smart phones may have access to sensitive corporate data and can get lost (need remote wipe (Blackberry and iPhone but not Android), need encryption for private data being sent on web (e.g. SSL, VPN), SMS being used for money transfer in Indonesia in small amounts $0.45-$0.90, infect phones with Trojan-SMS.Python.Flocker (exercise caution when browsing Internet to avoid contamination by mistakenly downloading Trojan), need ant-virus, anit-malware apps, firewalls etc.
- Mimic a cell phone tower/radio transmitter, it is illegal but can be done (see http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/073110-hacker-snoops-on-gsm-cell.html?source
- cell phones & cancer link inconclusive (see http://www.iarc.fr/, San Francisco requires emission disclosure on mobile handsets, main source of RF is produced by antenna, closer to head higher the exposure, no scientific concensus on link to cancer, lots of studies (e.g. WHO) measured metric is Specific absorption rate (SAR), < 1.6 watts/kg of body weight considered safe by FCC. Manufactured phones vary from 0.1 to 1.59 w/kg (see http://reviews.cnet.com/cell-phone-radiation-levels/)
- Tower emission
- Emergency services (911, 999, 112 etc.) mobility adds another level of complexity
- Use while driving etc.,
- Security:
- today’s high end smartphones are 1GHz or higher, have up to 32GB store, and with 4G will have 3Gbps connection speeds. Expect to see a growth in malware and spyware. IT departments not ready to support the new OS’, yet smart phones may have access to sensitive corporate data and can get lost (need remote wipe (Blackberry and iPhone but not Android), need encryption for private data being sent on web (e.g. SSL, VPN), SMS being used for money transfer in Indonesia in small amounts $0.45-$0.90, infect phones with Trojan-SMS.Python.Flocker (exercise caution when browsing Internet to avoid contamination by mistakenly downloading Trojan), need ant-virus, anit-malware apps, firewalls etc.
- Mimic a cell phone tower/radio transmitter, it is illegal but can be done (see http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/073110-hacker-snoops-on-gsm-cell.html?source=NWWNLE_nlt_daily_am_2010-08-02 )
- Use as credit, security only as long as do not lose smartphone, need remote wipe (followed by a need for remote backup/restore), login password with complex password policies etc.
- Use multilateration based on RTT to towers to discover location of cell phone whether turned on or not
- Remotely turn on microphone of some cell phones and listen to conversations (see http://news.cnet.com/FBI-taps-cell-phone-mic-as-eavesdropping-tool/2100-1029_3-6140191.html)
- Smartphones are not for everyone yet
- Developing regions such as India have poor power, and little WiFi, or 3G
- More important than smartphone capabilities are: large batteries with 5 day (30 day on standby)
- Tailor to local tastes, multiple SIM cards and accounts, water resistent, FM radio, memory card pre-loaded with songs
- Much cheaper
- Integration of mobile phones with other communications Unified Communications)
- email, unified messaging, instant messaging, voice mail, presence, Web 2.0
- Needs integrating with corporate tool set (not point solutions), traditionally UC has been deskbound
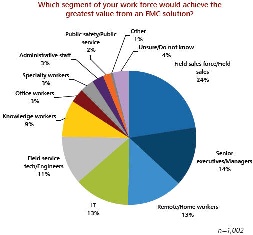
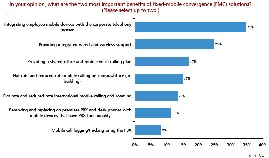
- The Yankee Group Anywhere Enterprises have studied which segment of the work force benefits from the Fixed-Mobile-Convergence (FMC) and the most important benefits of FMC:
- Mobile UC addresses the problem of latency in communications between workers.
- Enablers are: 3G->4G to remove the distinction between broadband and mobile broadband; rebuilding processes with mobility in mind; evolution in smartphones; evolution in UC (adding presence, conferencong, chat and mobile support).
- US providers
- OS’: Symbian (open source, Feb 2010) , Windows, Android (Google built on Linux, open source and Open handset alliance – Intel, HTC, ARM, Motorola, eBay etc., version 2.2 supports Flash, Microsoft Exchange friendly), Palm WebOS (Linux), iPhone OS (BSD/NextStep)
- Mobile phone, SMS, WiFi, Apps stores, touch screens, color displays, sync with computer
- Internet apps (web, weather, YouTube, email, calendar, maps), camera, video, clock, calculator, phone, GPS, MP3 player, gyroscope in new iPhone (great for Wii type games), Mobile payment:
- Apps stores: Apple (by April 2010 hosted > 185K apps, 3Billion downloads early Jan 2010), RIM, Nokia (Ovi launched May 2009), Palm (June 2009), Microsoft (October 2009 launch), Google
- Delay Tolerant networking & Smartphones (ByteWalla),
- Space Communicatons Protocol Specifications set of extensions to existing protocols (e.g. TCP, security (IPsec), FT == TCP)) developed by the Consultative Committee for Data Space Systems (CCSCS) to improve performance of Internet protocols in space environment
...