...
This document is the basis of a paper (SLAC-PUB-16343) comparing PingER performance on a 1 U bare metal host to that on a Raspberry Pi. It has been running successfuly since July 2015.
This is a project suggested by Bebo White to build and validate a PingER Measurement Agent (MA) based on an inexpensive piece of hardware called a Raspberry Pi (see more about Raspberry Pi) using a linux distribution as the Operating System (see more about Raspbian). If successful one could consider using these in production: reducing the costs, power drain (they draw about 2W of 5V DC power compared to typically over 100W for a deskside computer or 20W for a laptop) and space (credit card size). This is the same type of power required for a smartphone so appropriate off the shelf products including a battery and solar cells are becoming readily available. Thus the Raspberry could be very valuable for sites in developing countries where cost, power utilization and to a lesser extent space may be crucial.
...
- The Raspberry Pi PingER MA must be robust and reliable. It needs to run for months to years with no need for intervention . This still needs to be verified, so far the Raspberry Pi has successfully run without intervention for over a month. This has included and needs automatic recovery after two test power outages.
- The important metrics derived from the measurements made by the Raspberry Pi should not be significantly different from those made by a bare metal PingER MA, or if they are then this needs to be understood.
- The For applications where there is no reliable power siource, the Raspberry Pi needs to be able to run 24 hours a day with only solar derived power. Let's say the power required is 3W at 5V or (3/5)A=0.6A. If we have a 10,000 mAh battery, then at 0.6A it should have power for 10Ah/0.6A ~ 16.6 hours. Then we need a solar cell to be able to refill the battery in a few hours of sunlight. Let's take a 20W 5 V solar panel (see http://www.amazon.com/SUNKINGDOM-trade-Foldable-Charger-Compatible/dp/B00MTEDTWG) = 20/5= 4 A solar panel. So initial guess is 10A-h/4A = 2.5hours. But inefficiences (see http://www.voltaicsystems.com/blog/estimating-battery-charge-time-from-solar/) of say 2.5 extends this to 6.25 hours.
...
Looking at the RTT frequency distributions it is apparent that:
- the pinger and raspberry host RTT frequency distributions hardly overlap at all (one sample (0.04%) of the raspberry pi distribution overlaps ~ 7% of the pinger distribution).
- the pinger host's Median RTT is 7 times smaller (0.03ms vs 0.2 ms) than that of the raspberry-pi
- the pinger host's maximum outlier (0.174ms) is ~ factor 60 smaller than the raspberry-pi.
- the pinger host exhibits a pronounced bimodaility not seen for the raspberry-pi.
- the IQRs are very similar (0.025 vs 0.020ms)
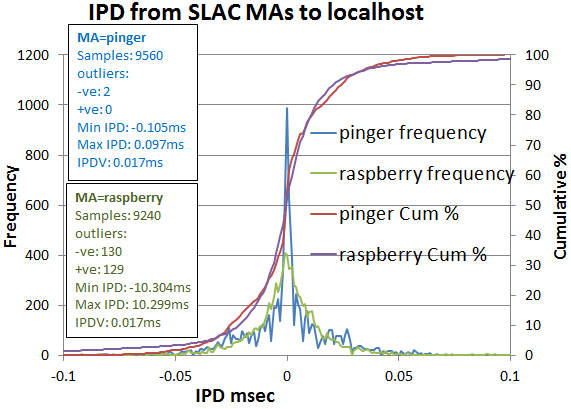
Looking at the IPD distributions it is apparent that:
- the pinger distribution is much sharper (max frequency 987 vs 408 for raspberry-pi)
- there is a slight hint of multi-modaility in the pinger distribution less visible in the raspberry-pi distribution
- the minimum and maximum outliers are about a factor 100 lower for pinger than the raspberry-pi (~ +-0.1 vs ~10ms)
- the IQRIPDV's are similar (0.017ms), whereas the standard deviations differ by almost a factor of 10 (0.021ms vs. 0.227ms. This further illustrates the impact of smaller outliers seen by pinger.
Comparing the IPD frequency distributions for the pinger.SLAC and pinger-raspberry MAs to their localhosts with those to TRIUMF it is seen that the differences are washed out as one goes to the longer RTTs.
Though there are large relative differences in the distributions, the absolute differences of the aggregated statistics (mediansThough there are large relative differences in the distributions, the absolute differences of the aggregated statistics (medians, IQRs) are sub millisecond and so should not noticeably affect PingER wide area network results.
...
If D-stat is greater than D-crit the samples are not considerated considered from the same distribution with a (1-Alpha) of accuracy. Remember that D-stat is the maximum difference between the two cumulative frequency curves.
...
In these links you can find the files containing the graphs, histograms and the complete analysis for Kolmogorov-Smirnov between Pinger and Pinger-Raspberry and for SITKA.
Futures
Extension to Android systems
Topher: Here is where we would like you to say something about the potential Android opportunity.
Installation process
The installation procedures for a PingER MA are relatively simple, but do require a Unix knowledgeable person to do the install and it typically takes a couple hours and may require a few corrections pointed out by the central PingER admin. It is possible to pre-configure the Raspberry Pi at the central site and ship it pre-configured to the MA site. However that requires funding the central site Raspberry Pi acquisitions, may raise issues of on-going commitment, and may not be acceptable for the Cyber security folks at the MA site. We are looking at simplifying the install process, possibly by creating an ISO Image
Robustness and Reliability
This still needs to be demonstrated in the field. We also need to more fully understand the solar power requirements.