Overview
Wiki Markup
To study and compare the algorithms we use the data sets collected by IEPM-BW spanning approximately 2 3 years (i.e. 2006 2005 - 2008). The Internet paths observed were the links between Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) and the following sites:
- University of Toronto, Canada.
- Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, Germany.
- Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Germany.
- San Diego Supercomputing Center (SDSC) USA,
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) USA,
- European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) , Geneva, Switzerland,
- Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe (FZK) Germany,
- Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) Germany,
- .
- San Diego Supercomputing Center, USA.
- Switch, Switzerland.
- University of Florida, USA.University of Toronto (UTORONTO) Canada and
- National Laboratory for Particle and Nuclear Physics (TRIUMF) , Canada.
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA.
- Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, Russia.
- Daresbury Laboratory, United Kingdom.
- California Institute of Technology - CACR, USA.
- Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Italy.
- Czech NREN Operator, Czech Republic.
- Brookhaven National Laboratory, USA.
- Argonne National Laboratory, USA.
- California Institute of Technology - Ultralight, USA.
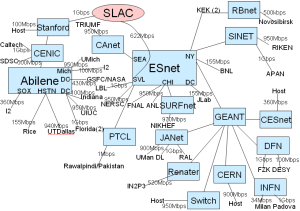
The topology of the monitoring framework is shown in figure 1.
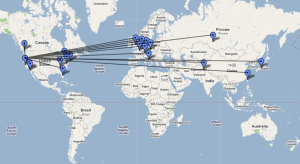
Fig. 1: Topology of IEPM as of 07/2008 | Fig. 2: Deployment of Selected Sites |
|---|---|
|
...
|
The data sets used in the study may be downloaded from the links listed below. These data sets were collected by the IEPM-BW project and the latest performance statistics may be accessed from here.
| Raw data | Labeled data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="a3f36546-b5a7-46f3-ae6e-f7bd455e1036"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | SDSC | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/SDSC-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/SDSC-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/UTORONTO-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="71c82f96-ce0c-43f4-bd99-35f7df34a669"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | CERN | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/CERN-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/CERN-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/CERN-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="abd2164d-3066-4ea5-b2d5-41e46e34317f"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | FZK | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/FZK-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/FZK-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/FZK-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="c1e03fb4-3154-4cec-bf6c-dc091c09ee37"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | DESY | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/DESY-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/DESY-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/DESY-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="1128dd79-aa06-48cc-9940-29ad8fef575f"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | UTORONTO | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/UTORONTO-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/UTORONTO-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/UTORONTO-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="0413ece2-194f-4022-8b0f-81d9f29bc2cb"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | TRIUMF | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/TRIUMF-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/TRIUMF-pathchirp.xls]] | [[txt | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/TRIUMF-pathchirp-labeled-events.txt]] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="f37f9d27-c146-4963-9539-81266b49e290"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | ORNL | [[csv | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/ORNL-pathchirp.csv]], [[xls | http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/ORNL-pathchirp.xls]] | [txt] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
Download the complete data archive \[[zip|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/published-data.zip] 10 MB\] or \[[7z|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-data/published-data.7z] 8 MB\] |
Labeling and Detection Algorithms
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
To perform a fair comparison between \[1\], \[2\], \[3\] and the proposed DTA we devised a labeling algorithm to identify true anomalies in the data sets. This labeled data was then used to determine the accuracy (true-positive rate), corresponding false-positive rate and the detection delay. The labeling algorithm and the decision theoretic approach for real-time anomaly detection are discussed at length in the research paper. (_The paper will be posted soon_.)
\\ |
Implementations and Parameter Tuning
The source code of the implementations and the tuning of parameters is discussed below. Please consider two important factors while we discuss the parameters tuning: a) We define an anomalous event as one which significantly varies from the normal behaviour of the Internet Path and the perturbation persists for at least three hours. b) The measurements made by IEPM-BW are at least 45 mins apart.
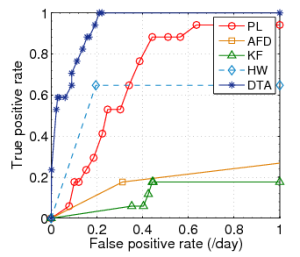
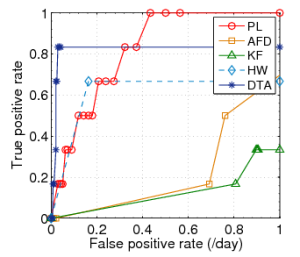
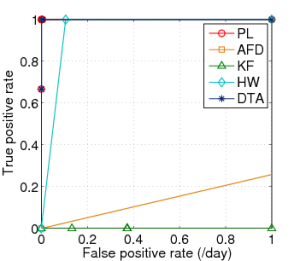
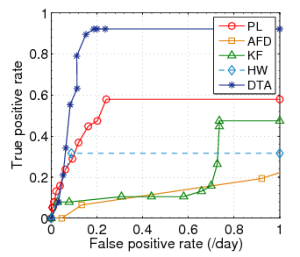
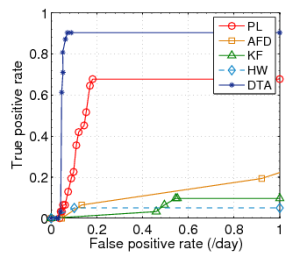
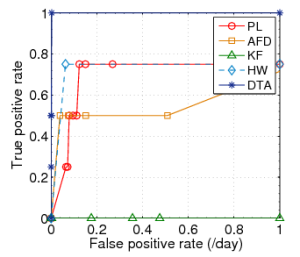
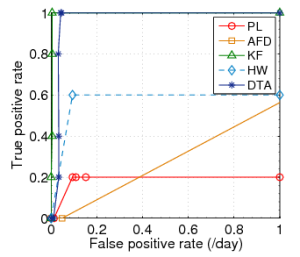
Fig. 2: ROC curves for Plateau (PL), |
|---|
|
a) Plateau Algorithm
The Plateau Algorithm takes four input parameters - history buffer length, trigger buffer length, sensitivity and threshold. We define the trigger buffer length to hold observations spanning at least 3 hours (since we define an anomalous event as one that persists for at least 3 hours). Since the measurements made by IEPM are 45 mins apart, we get about 6 observations. We then empirically determine the optimal length of the history buffer to span at least 5 days ~ 240 observations.
We initially define the sensitivity as one (1) and determine the optimal threshold value for each link (i.e. the value with the optimal ratio of true-positives to false positives). As suggested by the authors, this threshold falls between 30%-40%. Finally for the history buffer length, the trigger buffer length and the optimal threshold, we vary the sensitivity to determine the spectrum of the ratio of true-positive rate to false positive rate. Based on the observations we plot the ROC curves as shown in figure 2.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
The source code of the implementation is available in [C#|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/c-plateau-impl.html] \[[cs|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/plateau.cs]\] and [perl|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/plateau.pl.html] \[[pl|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/plateau.pl]\] |
b) Adaptive Fault Detection
Adaptive Fault Detection
c) Kalman Filters
Kalman Filters
d) Decision Theoretic Approach
Decision Theoretic Approach employs four parameters - the desired false positive rate (alpha), the desired detection rate (beta), the history buffer length and the low-pass median filter length.
This algorithm use three parameters one is threshold which is calculated in terms of Alpha and Beta, and other two are buffer lengths (History buffer and n-Tap Median filter). Same scheme is used for this algorithm, such that minimum value of n = 7 is used for n-Tap Median filter with some appropriate value of History buffer. By keeping these values same and changing different values of Alpha and Beta (Threshold) for each dataset ROCs are generated.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
([utilityFunctions|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/utilityFunctions.pm.html] \[[pm|http://www.slac.stanford.edu/~kalim/event-detection/published-src/utilityFunctions.pm]\]). |
References
...
number of measurements made to the following sites from SLAC:
Site | pathchirp | iperf | thrulay |
|---|---|---|---|
cern.ch | 48647 | 24586 | 39510 |
desy.de | 32247 | 4522 | 28689 |
fzk.de | 65536 | 4874 | 42708 |
nslabs.ufl.edu | 41206 | 1549 | 28613 |
switch.edu | 19668 | 4638 | 28744 |
sdsc.edu | 21176 | 4416 | 22456 |
triumf.ca | 26425 | 4669 | 27021 |
utoronto.ca | 40614 | 5003 | 21646 |
ornl.gov | 35339 | 5182 | 18375 |
anl.gov | 17968 | 1 | 27559 |
bnl.org | 23580 | 20708 | 16000 |
cacr.caltech.edu | 61871 | 25525 | 37293 |
dl.ac.uk | 27806 | 6096 | 28058 |
nsk.su | 20117 | 1 | 26845 |
cesnet.cz | 23618 | 3062 | 28426 |
infn.it | 30372 | 4343 | 28573 |
ultralight.caltech | 3739 | 88 | 1534 |
SubTotal | 539929 | 119263 | 452050 |
Data Sets
The data sets used in the study may be downloaded from the links listed below. These data sets were collected by the IEPM-BW project
Table 1: Performance measurement statistics compiled by IEPM, as seen from SLAC.
| Data Sets with Events | Data Sets with no Events |
|---|---|---|
IEPM |
All files with name "filename_raw_dataset.pathchirp" contain the raw data i.e the available bandwidth measurements along with the timestamps which are used in all algorithms.
All files with name "filename_event_file.txt" contain the list of events identified.
Technical Report - Labeling and Comparative Analysis
The technical report titled "A performance evaluation of anomaly detection algorithms for Internet Paths" will be available soon.
Input/Tuning parameters
Plateau Algorithm (PL)
History Buffer Length (H) | Trigger Buffer Length (T) | Threshold (th) | Sensitivity (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
240 | 6 - 45 | 0.10 - 0.70 | 1.0 - 2.8 |
Kalman Filters Method (KF)
Sensitivity (K) | Time Window (h) |
|---|---|
0.001 - 11.0 | 6 - 20 |
Holt Winter's Method (HW)
? - alpha | ? - beta | ? - gamma | ? - sigma |
|---|---|---|---|
0.1 | 0.1 - 0.3 | 0.1 - 0.5 | 2.0 |
Adaptive Fault Detector (AFD)
Window Size (N) | ? - alpha | ? - beta | No. of Training Data (Hn) |
|---|---|---|---|
20 | 0.95 | 0.0015 - 0.1 | 100 |
Decision Theoretic Approach (DTA)
History Buffer Length (N) | ? - alpha | ? - beta | Median filter length ( n) |
|---|---|---|---|
30 - 90 | 0.01 - 0.34 | 0.99 | 100 |
ROC Results
Datasets with Gaussian Distributions
CERN | FZK | SDSC |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
TRIMUF | UTORONTO |
|---|---|
|
|
Datasets with Weibull Distributions
DESY | NSLABS | SWITCH |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
...