...
CBG algorithm is currently implemented in Matlab code. Whereas [TULIP and Apollonius deployment|http://www-wanmon.slac.stanford.edu/cgi-wrap/tulip-viz.cgi?target=slac.stanford.edu] at SLAC is [Java|http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/index.html] based. at SLAC is Java based. We will integrate the two such that TULIP and Apollonius will keep running at SLAC and there'll be a Matlab server at SEECS running CBG code. There are two things which we need to take care of:
- Integration should be transparent i.e. the end user will execute the [TULIP GUI|http://www-wanmon.slac.stanford.edu/cgi-wrap/tulip-viz.cgi?target=slac.stanford.edu] as the TULIP GUI as before without any changes.
- Integration should introduce minimum possible changes into the current TULIP architecture.
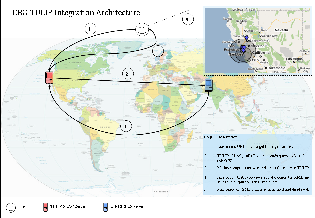
Proposed Architecture
Execution steps:
- User enters the URL with target to be geolocated.
- The TULIP visualization GUI calls the Java code to compute the answer and meanwhile sends a query string via a web service/remote routine to the Matlab server.
- The Java code computes the answer and waits for a reply from the Matlab server. The Matlab code computes an answer from data provided in the query string.
- Matlab server sends back a reply in the form of a dataset.
- The Java code receives the reply and merges this to other results to create a standardized XML file.
- This XML file is then read by TULIP visualization GUI to display the result on Google map. Each algorithm's result is represented in a distinct fashion.
This above is illustrated below in a diagram:
Matlab implementation
Package for Matlab implementation contains the code. To run the code:
...