...
- Futures:
- Mobile Payments: Mobile network operators, often in partnership with banks, card issuers and mobile payment service providers, are fast developing platforms and applications to offer mobile payment services, and with such initiatives in place, the mobile payments segment has established itself in several advanced mobile markets worldwide and is now also expanding its reach in emerging markets. The worldwide mobile payments volume – denoting the face value of purchases and transactions through mobile handsets – stood at USD 68.7 billion in 2009, up from USD 45.6 billion in 2008, and is set to surge nine-fold to reach USD 633.4 billion by end-2014.
In 2009, there were 81.3 million mobile payment users worldwide and this number is forecast to grow over six-fold to reach nearly 490 million by the end of 2014, seeing the worldwide penetration of mobile payment users increasing over four-fold to reach almost 8 percent by end-2014. From simple SMS-based services to advanced bar-coded tickets and beyond, mobile payment services have come a long way and yet still remain in a relatively nascent stage compared to other mobile services.
According to GSMA there will be 1.7M phone users by end 2012 who do not possess a formal bank account.
The worldwide mobile payments market, including purchases of digital and physical goods, money transfers and NFC transactions, will grow from $170bn in 2010 to almost $630bn in 2014 according to Juniper Research. - Location Based Services (LBS) is on the rise, and with iSuppli's recent forecast that 79.9% of Smartphones shipped by Q4 2011 will be GPS enabled it seems mass adoption is not far away.
- In US AT&T, Verizon and T-Mobile teaming up with Discover Card and Barclays Bank to test system at stores in Atlanta & 3 other cities to let consumer pay with the contactless wave of a smartphone, thus replacing credit cards (1B in US consumer wallets). SJ Mercury Aug 3, 2010. Security (see later)
- Medical
- Mobile health, or what the industry is calling mHealth or m-health, is a term used for the practice of medical and public health, supported by mobile devices. The term is most commonly used in reference to using mobile communication devices, such as mobile phones and PDAs, for health services and information.* The Mobilizing for Healthsm grant program will fund U.S. based pilot research projects and ongoing studies in need of additional funding focused on mobile phone-based interventions for low-income patients with chronic diseases, with an immediate interest in diabetes management over the next two years. * *Source: mHealth definition from Wikipedia.org, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MHealth
- New apps to determine drug doses based on weight, the size of endotracheal tube inserted down throat to help breathing (PediStat); learn about rare conditions (Eponyms) also use Wikipedia; to determine drug interactions (Epocrates); learn about drug trials (Drug Trials); breaking medical news; teaching tools You have a whole medical library in the palm of your hand, 70% doctors use mobile phone 80% say it is essentials (the new stethoscope?)
- Mobile Payments: Mobile network operators, often in partnership with banks, card issuers and mobile payment service providers, are fast developing platforms and applications to offer mobile payment services, and with such initiatives in place, the mobile payments segment has established itself in several advanced mobile markets worldwide and is now also expanding its reach in emerging markets. The worldwide mobile payments volume – denoting the face value of purchases and transactions through mobile handsets – stood at USD 68.7 billion in 2009, up from USD 45.6 billion in 2008, and is set to surge nine-fold to reach USD 633.4 billion by end-2014.
- Concerns
- cell phones & cancer link inconclusive (see http://www.iarc.fr/, San Francisco requires emission disclosure on mobile handsets, main source of RF is produced by antenna, closer to head higher the exposure, no scientific concensus on link to cancer, lots of studies (e.g. WHO) measured metric is Specific absorption rate (SAR), < 1.6 watts/kg of body weight considered safe by FCC. Manufactured phones vary from 0.1 to 1.59 w/kg (see http://reviews.cnet.com/cell-phone-radiation-levels/)
- Tower emission
- Emergency services (911, 999, 112 etc.) mobility adds another level of complexity
- Use while driving etc.,
- Security:
- today’s high end smartphones are 1GHz or higher, have up to 32GB store, and with 4G will have 3Gbps connection speeds. Expect to see a growth in malware and spyware. Handheld technology is being driven by the consumer world, not the enterprise. Further IT departments not ready to support the new OS’, yet smart phones may have access to sensitive corporate data and can get lost (need remote wipe (Blackberry and iPhone but not Android), need encryption for private data being sent on web (e.g. SSL, VPN), SMS being used for money transfer in Indonesia in small amounts $0.45-$0.90, infect phones with Trojan-SMS.Python.Flocker (exercise caution when browsing Internet to avoid contamination by mistakenly downloading Trojan), need ant-virus, anit-malware apps, firewalls etc.
- Mimic a cell phone tower/radio transmitter, it is illegal but can be done (see http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/073110-hacker-snoops-on-gsm-cell.html?source=NWWNLE_nlt_daily_am_2010-08-02 )
- Use as credit, security only as long as do not lose smartphone, need remote wipe (followed by a need for remote backup/restore), login password with complex password policies etc.
- Use multilateration based on RTT to towers to discover location of cell phone whether turned on or not
- Remotely turn on microphone of some cell phones and listen to conversations (see http://news.cnet.com/FBI-taps-cell-phone-mic-as-eavesdropping-tool/2100-1029_3-6140191.html)
- Smartphones are not for everyone yet
- Developing regions such as India have poor power, and little WiFi, or 3G
- More important than smartphone capabilities are: large batteries with 5 day (30 day on standby)
- Tailor to local tastes, multiple SIM cards and accounts, water resistent, FM radio, memory card pre-loaded with songs
- Much cheaper
- Integration of mobile phones with other communications Unified Communications)
- email, unified messaging, instant messaging, voice mail, presence, Web 2.0
- Needs integrating with corporate tool set (not point solutions), traditionally UC has been deskbound
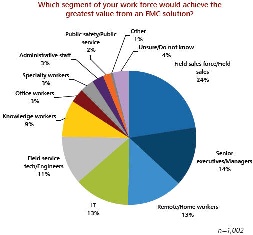
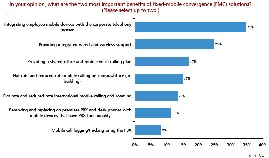
- The Yankee Group Anywhere Enterprises have studied which segment of the work force benefits from the Fixed-Mobile-Convergence (FMC) and the most important benefits of FMC:
- Mobile UC addresses the problem of latency in communications between workers.
- Enablers are: 3G->4G to remove the distinction between broadband and mobile broadband; rebuilding processes with mobility in mind; evolution in smartphones; evolution in UC (adding presence, conferencong, chat and mobile support).
- US providers
- OS’: Symbian (open source, Feb 2010) , Windows, Android (Google built on Linux, open source and Open handset alliance – Intel, HTC, ARM, Motorola, eBay etc., version 2.2 supports Flash, Microsoft Exchange friendly), Palm WebOS (Linux), iPhone OS (BSD/NextStep)
- Mobile phone, SMS, WiFi, Apps stores, touch screens, color displays, sync with computer
- Internet apps (web, weather, YouTube, email, calendar, maps), camera, video, clock, calculator, phone, GPS, MP3 player, gyroscope in new iPhone (great for Wii type games), Mobile payment:
- Apps stores: Apple (by April 2010 hosted > 185K apps, 3Billion downloads early Jan 2010), RIM, Nokia (Ovi launched May 2009), Palm (June 2009), Microsoft (October 2009 launch), Google
- Delay Tolerant networking & Smartphones (ByteWalla),
- Space Communicatons Protocol Specifications set of extensions to existing protocols (e.g. TCP, security (IPsec), FT == TCP)) developed by the Consultative Committee for Data Space Systems (CCSCS) to improve performance of Internet protocols in space environment
...