Work in progress!!
b+Jet+MET topology-based physics signatures
One Supersymmetry is one of the most attractive extensions of the Standard Model:. It solves the hierarchy problem
...
, the unification of the gauge forces
...
, and provides a natural candidate for the dark matter in the
...
Universe
...
Large cross sections for SUSY particles with
masses bellow 1TeV.
Squarks and gluinos, if they exist, will be copiously produced at the LHC via the strong interaction.
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
|  |
| Column |
|---|
|
Using the precise track reconstruction of the ATLAS inner detector, it is possible to identify jets arising from b quark hadronization by reconstructing the decay vertex of long-lived B hadrons within the jet.
The decay of a long-lived hadron produces several charged particles emanating from a secondary vertex, displaced from the primary interaction point. b-tagging plays a major role on top quark identi?cation and searches for the Higgs boson and Super-symmetry.
Our group is investigating the use of track-based (instead of calorimeter based) jets to feed the b-tagging algorithms, event tagging, and high pT b-jet tagging.
|
|
...
| Section |
|---|
| Column |
|---|
|  |
| Column |
|---|
|
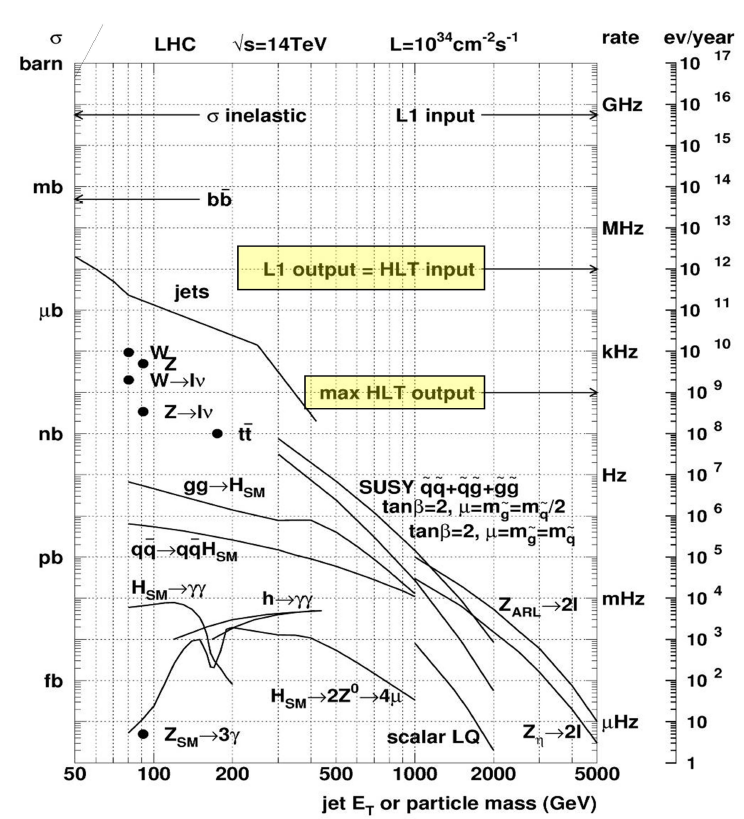
The LHC will produce collisions at a rate of 40MHz. The purpose of the trigger system is to reduce the output event storage rate to about 300MB/s or approximately 200Hz.
Since most of the collisions at the LHC center of mass energy will result in non-interesting physics events, such QCD multi-jet production, the main task of the trigger system is to reject QCD events while maintaining high efficiency for low cross section processes like Super-symmetry, Higgs, etc.
The ATLAS trigger consists of three levels: Level 1, which is hardware based, and the high level trigger (HLT) which consists of Level 2, and the Event Filter. The HLT is based on software algorithms that analyze region of interests (RoI) identified by the level 1 trigger. The output rates of the three trigger levels are 75KHZ, 2KHz, 200Hz.
Tagging b-jets at the trigger level can expand the physics reach of ATLAS in many ways: it allows to lower the jet ET threshold to increase the acceptance of interesting physics events containing multiple b-jets (like bbH and ttH ), and can be used to reduce non-b backgrounds and improve the purity of Super-symmetry searches involving b-jets in the ?nal state. The SLAC group has implemented one of the two ATLAS b-tagging algorithms at level 2 trigger: the Impact Parameter ?2 Probability tagger (IPChi2) |
|
Current and future work involves the optimization of the operational parameters of the algorithm, determination of performance in real data events, on-line and off-line validation, and the investigation of new trigger menus involving b-quarks and missing transverse energy for Super-symmetry searches.
...

