Page History
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Introduction
This document explains how to jump-start the analysis environment on a laptop using a virtual machine (VM) image. The recipe would work as well for any other hardware (desktop, server). In this document we're exploring a technology based on Oracle VM VirtualBox. The main benefit of the software is that it's stable and it's free. Besides, it's easy to set up. The software is available for all popular platforms, including Linux (all distributions), Windows 7/8, MacOS, or Solaris. However a similar approach would work as well for other hypervisors, such as Parallels, VMware, etc. They all would recognize a format of the packaged VM images which we're exporting here.
...
It will take a few minutes for VirtualBox to "digest" the file. The software will read, unpack the input file and place the actual image (along with additional support files) some where on your file system. The actual location can be changes through one of the configuration option of the VirtualBox application. When the process is done then you should see the VM the GUI. Here is an example:
Note that the initial state of the machine will be "Powered Off".
...
| Code Block |
|---|
% sudo -i % su |
You should use the superuser account to manage your system (add/remove accounts, change passwords, configure the network, mount dists, etc.). The second account is used to install the LCLS releases. We do NOT recommend using that pcds account for your software development. The account has a special configuration for importing/updating releases. This document may later be extended to explain how one could upgrade to the latest analysis release using this account w/o re-installing the VM from scratch. We highly recommend that you created your own user accounts for your analysis activities. Just make sure you set up the analysis environment for that accounts as explained in the Analysis Environment Details document.
Which software is installed
Basically, we've tried to replicate the usual analysis environment, including the names of releases, a location of the release, the environment initialization commands (sit_setup), etc. And each VM image comes with at least one version of the full analysis release:
| Code Block |
|---|
% ls -al /reg/g/psdm/sw/releases/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x. 3 pcds pcds 4096 Aug 5 13:44 .
drwxrwxr-x. 5 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 18:04 ..
drwxr-xr-x. 101 pcds pcds 4096 Aug 5 13:38 ana-0.13.0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 pcds pcds 10 Aug 5 13:40 ana-current -> ana-0.13.0 |
We also put a few tutorials for using the interactive psana (explained at Tutorial) into the image:
| Code Block |
|---|
% ls -al /reg/g/psdm/tutorials/
total 28
drwxrwsr-x. 6 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:55 .
drwxr-xr-x. 7 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 18:04 ..
drwxrwsr-x. 3 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:55 common
drwxrwsr-x. 3 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:55 cxi
-rw-rw-r--. 1 pcds pcds 1554 Apr 4 17:55 README.1st
drwxrwsr-x. 3 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:55 sxr
drwxrwsr-x. 3 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:55 xcs |
There are some important notes regarding what's not available on the VM:
- you won't be able to see your NFS home directory even if you will add your own account to the system using your sudo privilege
- all accounts found on the machine have nothing to do with LCLS accounts
- you won't be able to see any data directories (you can mount the ones using sshfs as explained later in this document)
Testing and using the installed machine
Starting/stopping
The virtual machine can be in either of the following states:
- powered off (same as hibernated or temporarily suspended and saved to disk)
- shut down (similarly to shutting down your host system; all sessions will be closed)
- running (in memory and using CPU)
- paused (still in memory but not using CPU)
The VirtualBox GUI has the corresponding controls to move the machine between the states. It's important to know that the machine state will be properly preserved between running and powered off states only if the machine is brought down using the GUI operations. This will allow VirtualBox to save the machine's state to disk. If you just kill the application then all modifications made to the VM system may be lost.
Enabling/disabling network connection
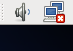
By default, after you start the machine, the network connection will not be enable on the VM. You shall locate the following sign on the title bar on the top right corner of the machine's GUI:
If you see what you see above then the network is disabled. You will still be able to log on that machine through the GUI, but you won't be able to ssh out of the machine. Click on that sign and then click on the name of the network interface System eth0 in order to enable the network.
Mounting host machine's directories
VirtualBox allows to make select file systems (of your choice) of your host system available within the VM. This can be configured by selecting a desired machine from the list and clicking on the Setting button on the VirtualBox top-level menu. Then proceed to the "Shared Folders" sections where you can specify which file systems of your host machine you would like to mount on the VM. You may also control what kind of access level you would allow for the directories. Note that you will need to do so when the machine is shut down (not just powered off). The directories will be mounted when the machine will start up.
Mounting data directories from PCDS
In principle, you can also mount all data directories which we have at PCDS on your virtual machine (one you start the one and logged into it as root or pcds), You will also need to enable the network as explained in the previous section. The simplest way to do so is to use sshfs. The tool is already installed on the VM. The data directories will be mounted at the usual location /reg/d/psdm/. And the mounting will require to use your real UNIX account and a password at SLAC. Here is a sample session illustrating the idea:
psana software has been installed using the conda system and can be used in the standard way.
There are some important notes regarding what's not available on the VM:
- you won't be able to see your NFS home directory even if you will add your own account to the system using your sudo privilege
- all accounts found on the machine have nothing to do with LCLS accounts
- you won't be able to see any data directories (you can mount the ones using sshfs as explained later in this document)
Testing and using the installed machine
Starting/stopping
The virtual machine can be in either of the following states:
- powered off (same as hibernated or temporarily suspended and saved to disk)
- shut down (similarly to shutting down your host system; all sessions will be closed)
- running (in memory and using CPU)
- paused (still in memory but not using CPU)
The VirtualBox GUI has the corresponding controls to move the machine between the states. It's important to know that the machine state will be properly preserved between running and powered off states only if the machine is brought down using the GUI operations. This will allow VirtualBox to save the machine's state to disk. If you just kill the application then all modifications made to the VM system may be lost.
Enabling/disabling network connection
By default, after you start the machine, the network connection will not be enable on the VM. You shall locate the following sign on the title bar on the top right corner of the machine's GUI:
If you see what you see above then the network is disabled. You will still be able to log on that machine through the GUI, but you won't be able to ssh out of the machine. Click on that sign and then click on the name of the network interface System eth0 in order to enable the network.
Mounting host machine's directories
VirtualBox allows to make select file systems (of your choice) of your host system available within the VM. This can be configured by selecting a desired machine from the list and clicking on the Setting button on the VirtualBox top-level menu. Then proceed to the "Shared Folders" sections where you can specify which file systems of your host machine you would like to mount on the VM. You may also control what kind of access level you would allow for the directories. Note that you will need to do so when the machine is shut down (not just powered off). The directories will be mounted when the machine will start up.
Mounting data directories from PCDS
In principle, you can also mount all data directories which we have at PCDS on your virtual machine (one you start the one and logged into it as root or pcds), You will also need to enable the network as explained in the previous section. The simplest way to do so is to use sshfs. The tool is already installed on the VM. The data directories will be mounted at the usual location /reg/d/psdm/. And the mounting will require to use your real UNIX account and a password at SLAC. Here is a sample session illustrating the idea:
| Code Block |
|---|
% whoami
pcds
% ls -al /reg/d/psdm/
total 8
drwxr-xr-x. 2 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:10 .
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Apr 4 17:10 ..
% sshfs gapon@psexport.slac.stanford.edu:/reg/d/psdm/ /reg/d/psdm/ -o transform_symlinks -o follow_symlinks
% ls -al /reg/d/psdm/
total 80
drwxr-xr |
| Code Block |
% whoami pcds % ls -al /reg/d/psdm/ total 8 drwxr-xr-x. 2 pcds pcds 4096 Apr 4 17:10 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Apr 4 17:10 .. % sshfs gapon@psexport.slac.stanford.edu:/reg/d/psdm/ /reg/d/psdm/ -o transform_symlinks -o follow_symlinks % ls -al /reg/d/psdm/ total 80 drwxr-xr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Sep 26 2013 . drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Apr 4 17:10 .. drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 7 10:54 amo drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 7 10:54 AMO drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 cxi drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 CXI drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Mar 4 15:08 dia drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Mar 4 15:08 DIA drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 mec drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 MEC drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 13 14:52 mob drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 13 14:52 MOB drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 MaySep 3026 16:412013 sxr. drwxr-srxr-x. 13 9997root 2279root 4096 MayApr 304 1617:4110 SXR.. drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 DecJul 197 201310:54 usramo drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 DecJul 197 201310:54 USRAMO drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 JunJul 2515 1112:1518 xcscxi drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 JunJul 2515 1112:1518 XCSCXI drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 JulMar 4 15 12:1808 xppdia drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 XPP |
At this point you may run of the tutorials by:
| Code Block |
|---|
% sit_setup
% python /reg/g/psdm/tutorials/xcs/princeton_movie/movie.py |
Working with SVN repositories from your test release
Quite often when you create your test release you may want to get some package (like psana_examples, etc.) from the SVN repository and modify it ti suit your needs, extend, etc. Normally you would do so by using the 'addpkg' command from your test release directory. The very same operation is also available from the VM. The only caveat is to obtain a Kerberos ticket in the SLAC.STANFORD.EDU realm. Your machine has already been configured to pretend it's a part of the SLAC network (even thought this is n't quite true). Hence, all you would need to do is to get the ticket first using your real UNIX account/password at SLAC. Here is sample session (replace user name gapon with your real UNIX name):
| Code Block |
|---|
% newrel ana-0.13.0 ana-0.13.0
% cd ana-0.13.0/
% sit_setup
% kinit gapon
Password for gapon@SLAC.STANFORD.EDU:
% addpkg psana_examples
Release ana-0.13.0 has tag V00-04-18 of package psana_examples, will use that
A psana_examples/include
A psana_examples/include/DumpPartition.h
A psana_examples/include/DumpLusi.h
A psana_examples/include/DumpPimax.h
.. |
If you have proper privileges for modifying the repository then you may even commit your modifications back to SVN.
Mar 4 15:08 DIA
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 mec
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 MEC
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 13 14:52 mob
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 13 14:52 MOB
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 May 30 16:41 sxr
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 May 30 16:41 SXR
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Dec 19 2013 usr
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Dec 19 2013 USR
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 25 11:15 xcs
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jun 25 11:15 XCS
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 xpp
drwxr-sr-x. 1 9997 2279 4096 Jul 15 12:18 XPP
|
At this point you may run of the tutorials by:
| Code Block |
|---|
% sit_setup
% python /reg/g/psdm/tutorials/xcs/princeton_movie/movie.py |
Problems
- On a macbook, I could not find a "File" menu item to import the .ova image file.
- By double clicking the .ova file image, virtual box will come up and digested it.
- When I started the virtual machine, I got an error about not having a USB 2.0 device?
- You did not install the Oracle Virtual Box Extension Pack.
- When first powering on the machine, I cannot see anything.
- There is sometimes a problem where the login screen is not using your computers video settings. After scrolling within the virtual machine so that you can see the login window, and then logging in, it should re-display within your computers video settings (after logging in).
...
- The default configuration of the virtual machine won't allow external login into the machine (one can'e t do 'ssh' into the system). However, it's possible to give you machine a unique IP address to allow the logins. Instructions can be found in the VirtualBox documentation. And make sure you change the default passwords of both root and pcds accounts in your virtual image.Please, read the documentation on VirtualBox