Page History
...
- Flexibility; HDF5 file has indexed structure, that means direct access to any data of any file from your code.
Pythonis a high-level scripting language allows to write transparent and compact code based on well-elaborated standard libraries.- In general, code in
Pythonworks slow comparing to C++, but there are libraries likeNumPywritten on C++, which solve this problem for manipulation with large arrays.
...
Here is a list of Python libraries which we use in examples below:
These libraries can be imported in the top of the Python-code file, for example
| Code Block |
|---|
#!/usr/bin/env python
import h5py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
HDF5 file structure
Detailed description of the HDF5 file structure can be found in HDF5 or h5py web sites. Briefly speaking, its structure resembles the file system directory tree. The top level of the HDF5 tree is a file; file may contain groups and datasets; each group may contain other groups and datasets; each dataset contains the data objects, which in most cases can be associated with NumPy types. Group and file may also have additional parameters, which are called as attributes. So, there are three basic type of items in HDF5 file: File, Group, and Dataset. Their names are used as access keys.
...
Example 1: Basic operations
| Code Block |
|---|
#!/usr/bin/env python import h5py import numpy as np!/usr/bin/env python import h5py import numpy as np eventNumber = 5 file = h5py.File('/reg/d/psdm/XPP/xppcom10/hdf5/xppcom10-r0546.h5', 'r') dataset = file['/Configure:0000/Run:0000/CalibCycle:0000/Camera::FrameV1/XppSb4Pim.1:Tm6740.1/image'] arr1ev = dataset[eventNumber] file.close() print 'arr1ev.shape =', arr1ev.shape print 'arr1ev =\n', arr1ev |
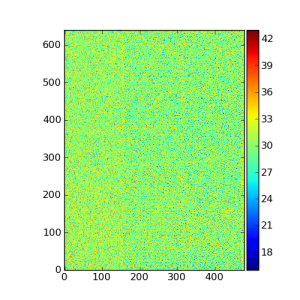
Similar code plots the dataset as an image using the matplotlib library
| Code Block |
|---|
#!/usr/bin/env python import h5py import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def plotImage(arr) : fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8), dpi=80, facecolor='w',edgecolor='w',frameon=True) imAx = plt.imshow(arr, origin='lower', interpolation='nearest') fig.colorbar(imAx, pad=0.01, fraction=0.1, shrink=1.00, aspect=20) plt.show() eventNumber = 5 file = h5py.File('/reg/d/psdm/XPP/xppcom10/hdf5/xppcom10-r0546.h5', 'r') dataset = file['/Configure:0000/Run:0000/CalibCycle:0000/Camera::FrameV1/XppSb4Pim.1:Tm6740.1/image'] arr1ev = dataset[eventNumber] plotImage(arr1ev) file.close() print 'arr1ev.shape =', arr1ev.shape print 'arr1ev =\n', arr1ev |
Example 2: Extract and print the time variables
...
| Code Block |
|---|
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os
import sys
import h5py
import numpy as np
class TwoDatasetSynchronization ( object ) :
"""Matching elements of two datasets using their time stamps"""
def __init__ ( self, file, Xdsname, Ydsname ) :
"""Initialization"""
self.dsX = file[Xdsname]
self.dsY = file[Ydsname]
XTimedsname = get_item_path_to_last_name(Xdsname) + '/time'
YTimedsname = get_item_path_to_last_name(Ydsname) + '/time'
self.dsXT = file[XTimedsname]
self.dsYT = file[YTimedsname]
self.XTarr = 0.000000001 * self.dsXT['nanoseconds'] + self.dsXT['seconds']
self.YTarr = 0.000000001 * self.dsYT['nanoseconds'] + self.dsYT['seconds']
self._nXpoints = self.dsX.shape[0]
self._nYpoints = self.dsY.shape[0]
self._indX = 0
self._indY = 0
self._tmapXlist = []
self._tmapYlist = []
print 'Xdsname =',Xdsname
print 'Ydsname =',Ydsname
print 'XTimedsname =',XTimedsname
print 'YTimedsname =',YTimedsname
print 'Initialization: datasets X and Y have length =', self._nXpoints, self._nYpoints
def twoDatasetSynchronizationIterations( self ) :
"""Iteration over time indexes and appending of syncronized arrays."""
while self._indX < self._nXpoints and self._indY < self._nYpoints :
if self.XTarr[self._indX] == self.YTarr[self._indY] : # Time is the same
self._tmapXlist.append(self.dsX[self._indX])
self._tmapYlist.append(self.dsY[self._indY])
self._indX += 1
self._indY += 1
elif self.XTarr[self._indX] > self.YTarr[self._indY] : # Time X > Time Y
self._indY += 1
self.printMissingSynchronization()
else : # Time X < Time Y
self._indX += 1
self.printMissingSynchronization()
def printMissingSynchronization( self ) :
print 'Missing of syncronization for X,Y indexes ',self._indX,self._indY
def runSynchronization( self ) :
"""Executes synchronization and makes the references for synchronized arrays."""
self.twoDatasetSynchronizationIterations()
self.Xarr = np.array(self._tmapXlist)
self.Yarr = np.array(self._tmapYlist)
print 'Number of synchronized in time X and Y array elements =', self.Xarr.shape, self.Yarr.shape
def get_item_path_to_last_name(dsname):
"""Returns the path to the last part of the item name"""
path,name = os.path.split(str(dsname))
return path
def main() :
"""EXAMPLE: Time synchronization of two datasets.
In this example we open the file, which contains normal dataset (Y) and the dataset with lost records (X).
We access these arrays and associated time arrays through the class TwoDatasetSynchronization.
Then we iterate over indexes of these arrays and appends the lists of syncronized arrays.
Program prints the message in case of missing synchronization.
"""
file = h5py.File('/reg/d/psdm/CXI/cxi80410/hdf5/cxi80410-r0730.h5', 'r')
Xdsname = '/Configure:0000/Run:0000/CalibCycle:0000/Bld::BldDataFEEGasDetEnergy/NoDetector.0:NoDevice.2/data'
Ydsname = '/Configure:0000/Run:0000/CalibCycle:0000/Ipimb::DataV1/CxiDg1.0:Ipimb.0/data'
synchro = TwoDatasetSynchronization (file, Xdsname, Ydsname)
synchro.runSynchronization()
#--------------------------------
if __name__ == "__main__" :
main()
sys.exit ( "That's it!" )
#--------------------------------
|